Definition
A destinctive melanocytic tumor which may arise sporadically or less often represent a germline mutation in the tumor-suppressor gene BRCA1-associated protein-1 (BAP1). The latter is associated with an increased risk of devloping mesothelioma, uveal melanoma, cutaneous melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, meningioma & renal cell carcinoma
Alternative nomenclature
•BAP1-inactivated melanocytic tumors (BINT)
•Wiesner’s nevus
•Melanocytic BAP1-mutated atypical intradermal tumor (MBAIT)
•Epithelioid atypical Spitz tumor
•Spitz nevus with halo-like reaction
•BAP1-negative atypical Spitz tumor
•BAP1-inactivated Spitzoid nevus
•Spitzoid tumor of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP)
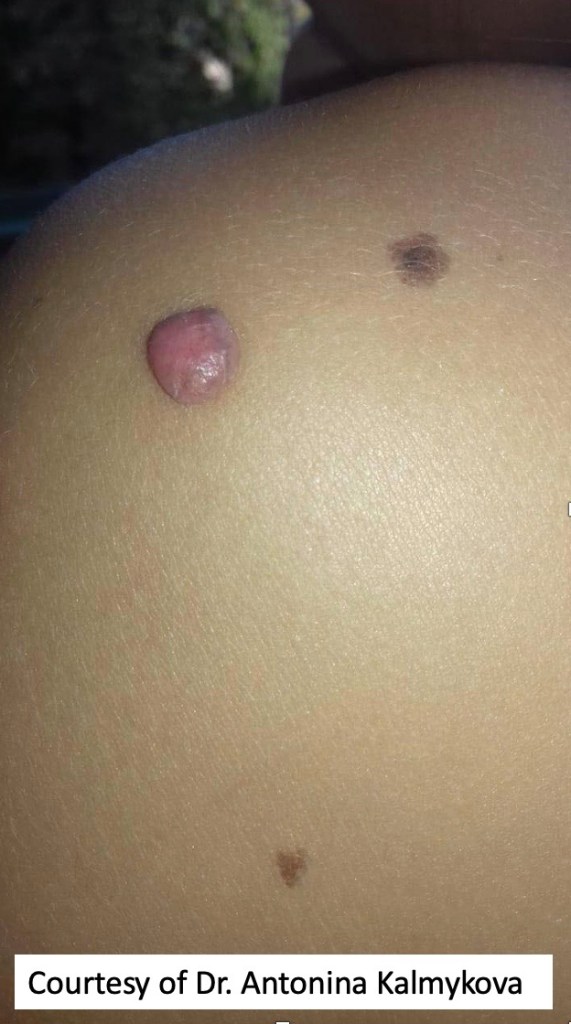
Clinical features
•Pedunculated orange-brown or erythematous dome-shaped nodules
•0.5-1.0 cm diameter
•Head, neck, trunk & limbs
•Mostly 2-3rd decade
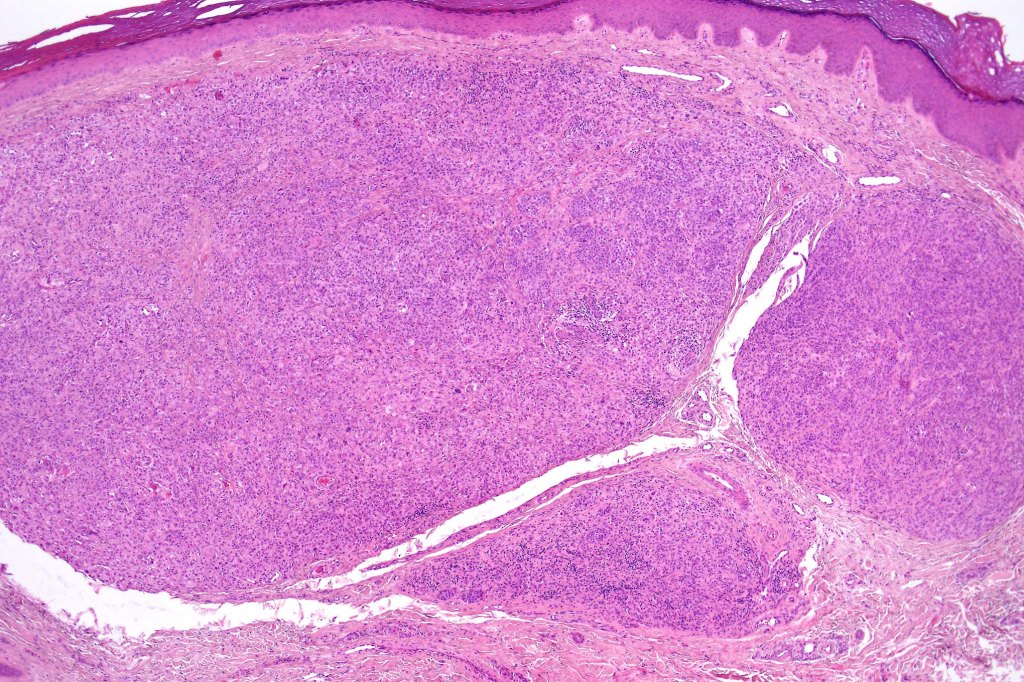
Histological features, immunohistochemistry and molecular studies
•Spitzoid
•Rhabdoid
•Nevoid (don’t misdiagnose as nevoid melanoma)
•BAP1 loss in blue nevus-like melanoma (GNAQ & GNA11 mutations)
•Lacks acanthosis, clefting, Kamino bodies and spindle cells as seen in Spitz nevus
•May be a pure population (rare) or biphasic in association with banal or congenital nevus-like component
•Lymphocytic infiltrate
•Large epithelioid (sometimes Spitzoid or rhabdoid) cells with ground-glass cytoplasm
•Nuclear pseudoinclusions
•Few mitoses & variable pleomorphism
•Perinuclear clumps (Gammon)
•SOX10, S100, Melan-A, PRAME (often positive)
•BAP1 almost invariably negative (nuclear) however see abstract below
•BRAF p.V600E (67-89%) mutation in all tumor cells, loss of BAP1 in epithelioid cells
•BAP1 gene product is a nuclear located deubiquitinase and affects transcription, differentiation and DNA damage response through the Ataxia Telangiectasia (ATM) pathway
•Possible role in apoptosis through Ca2+flux
•(Zhang A. et al J Cut Pathol, 2019;46:965-972)


Leave a comment