An indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder
Clinical features
•2M:1F
•Crops of rapidly growing, self-healing, pink papules up to 1.0 cm diameter
•Heal with atrophic scars
•Occasionally large nodules
•Trunk & limbs are sites of predilection
•Regional variant
•Exceptional mucosal involvement
•Follicular variant
•Pustular variant
•Self-limiting or protracted course
•Up to 20% associated with mycosis fungoides, primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma or Hodgkin lymphoma


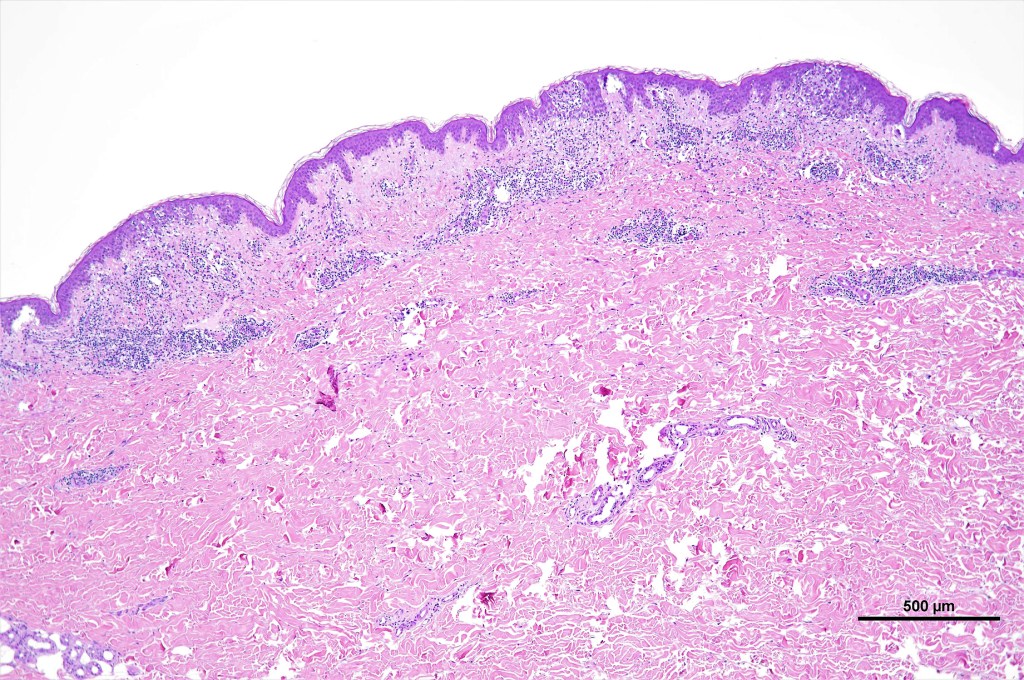
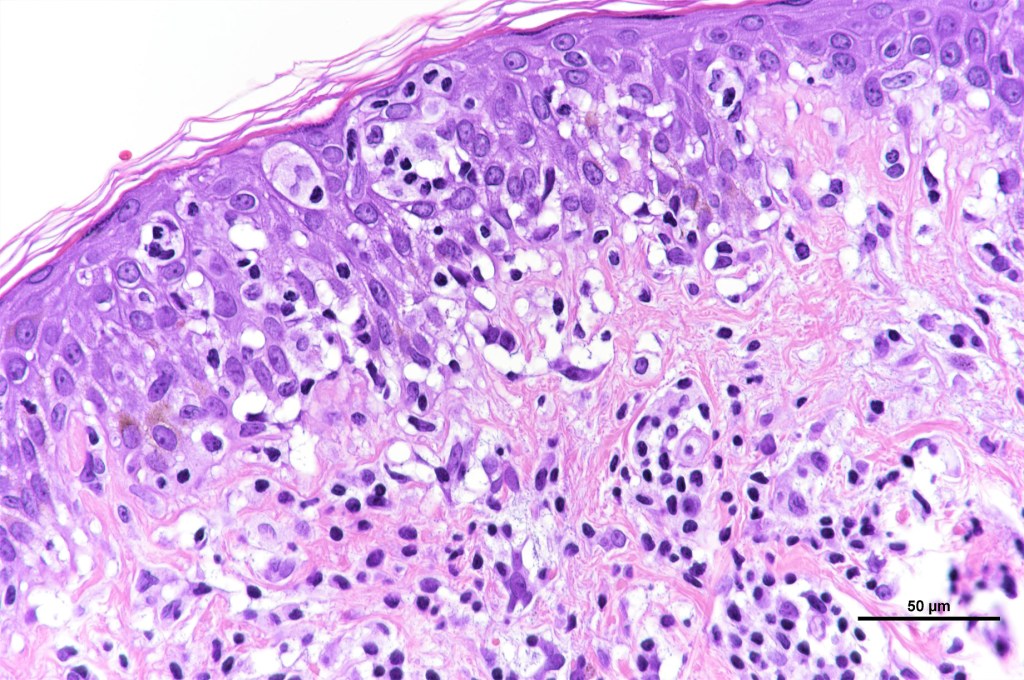
Histological features
•Subdivided into 5 major & several rarer variants
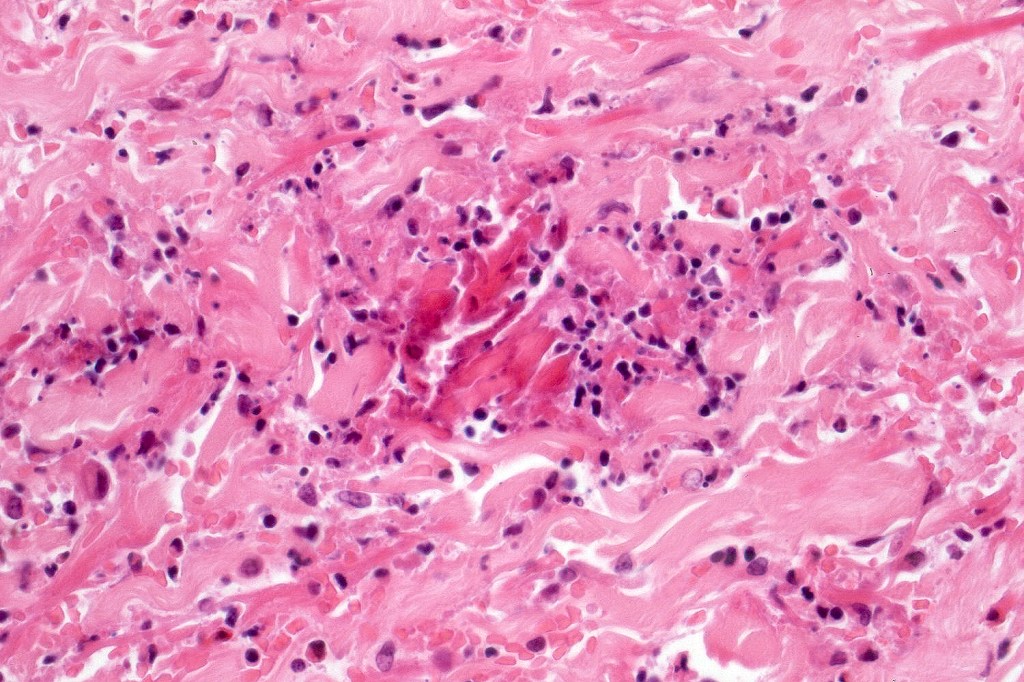
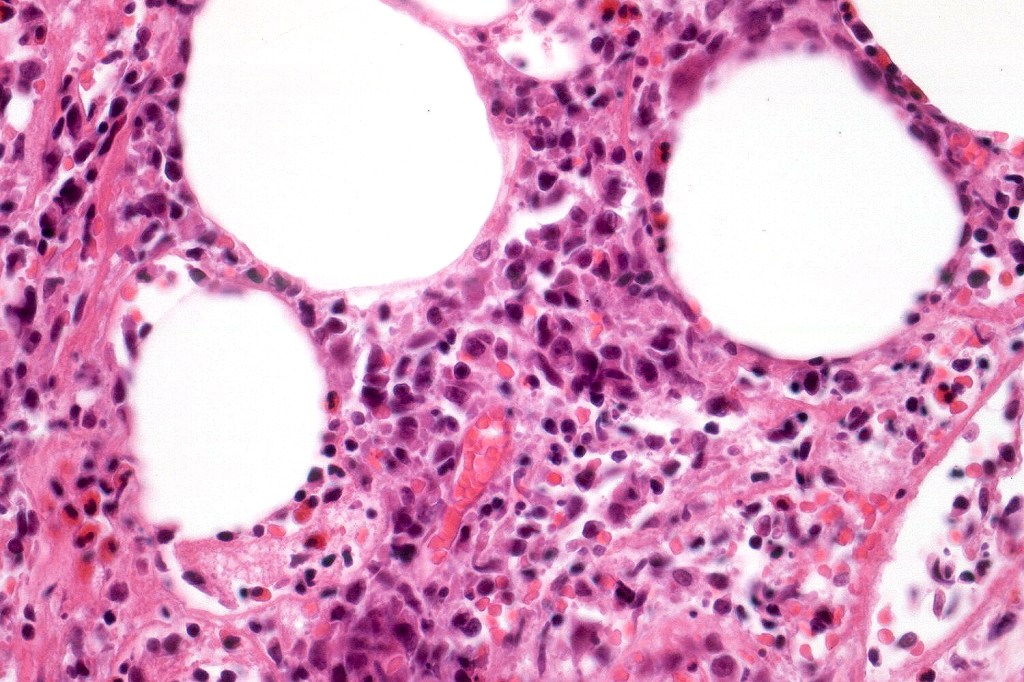
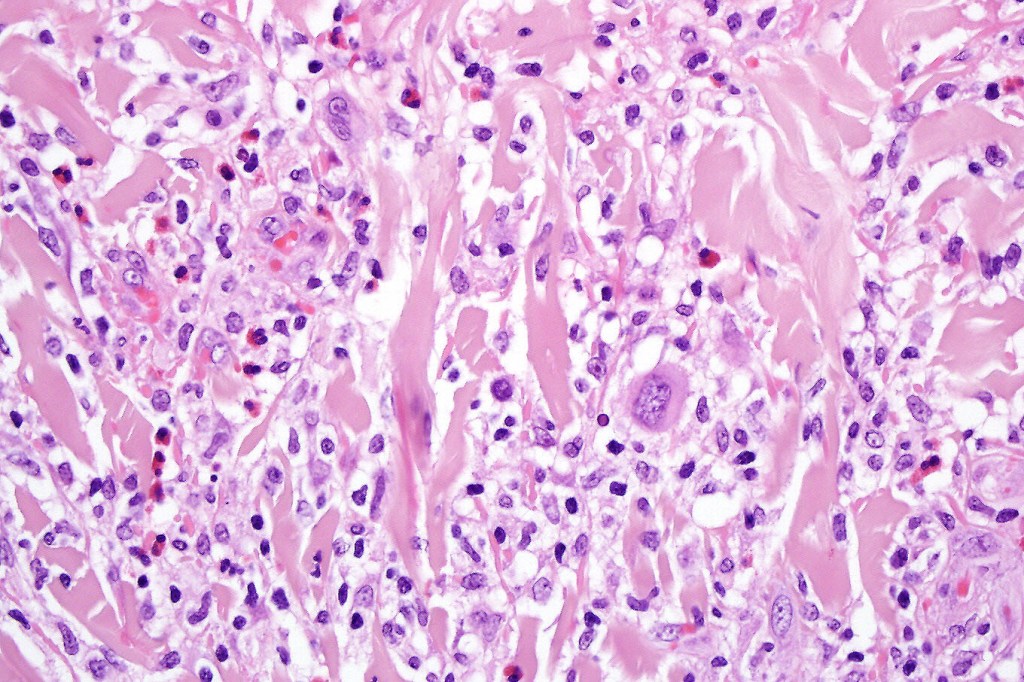
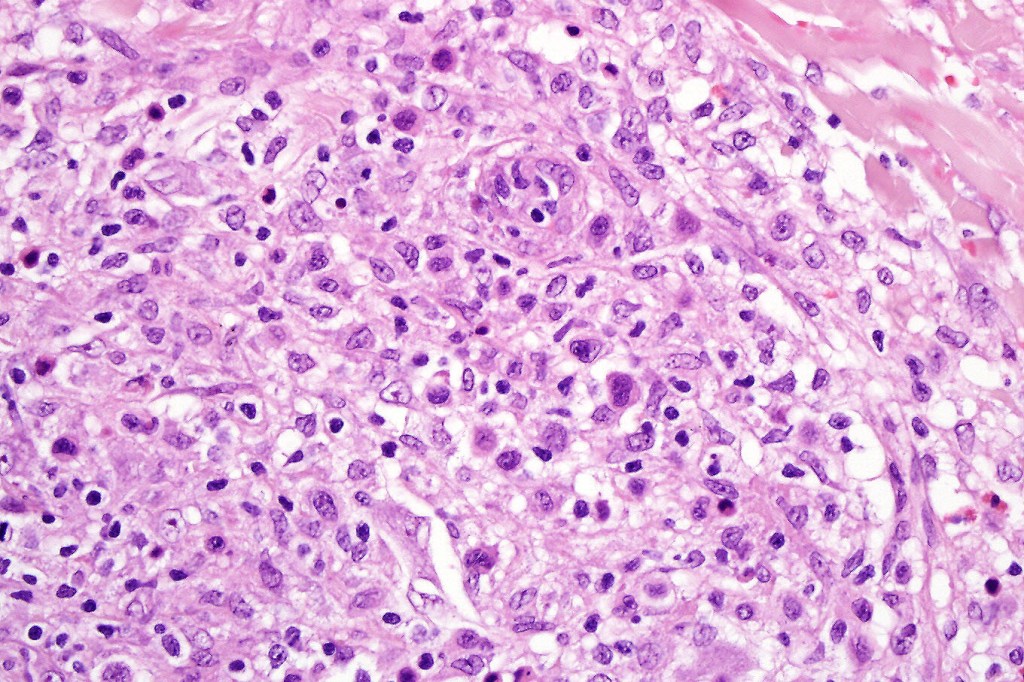
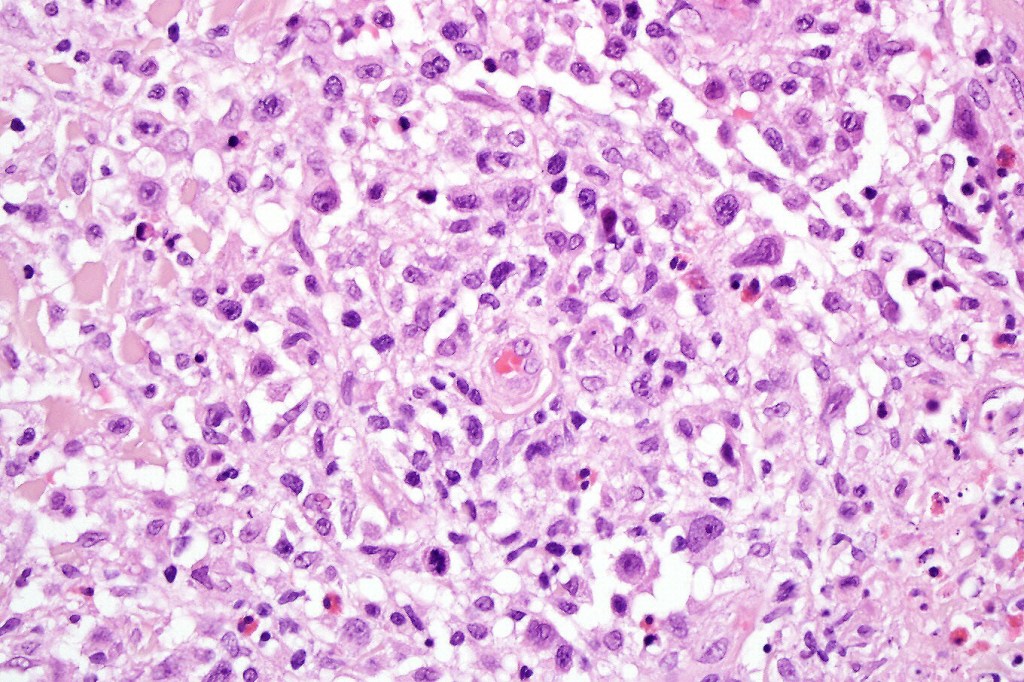
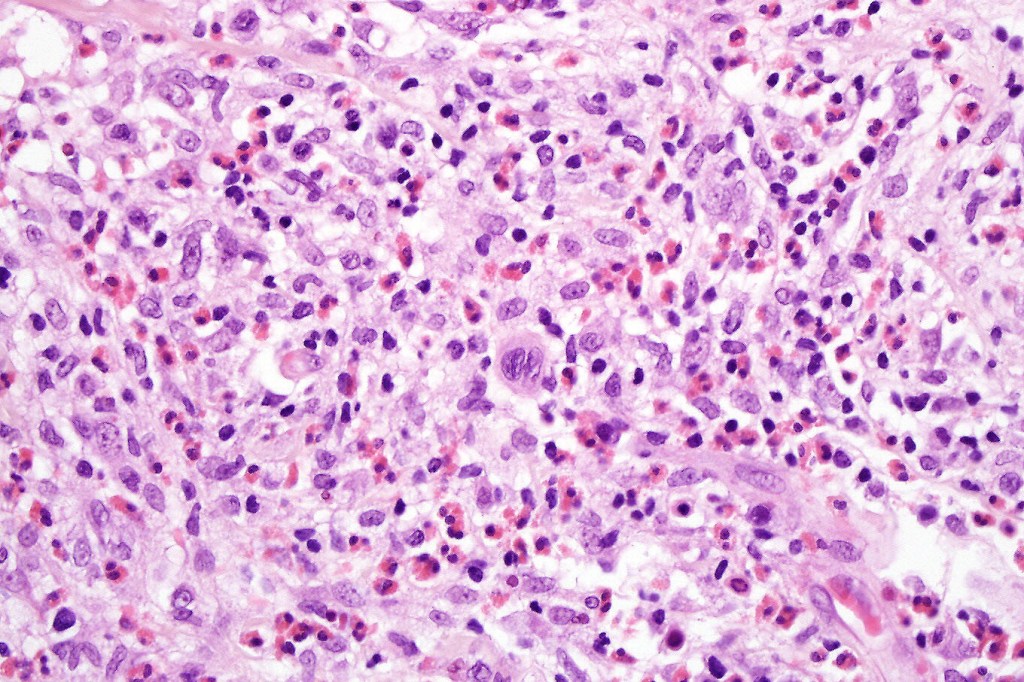
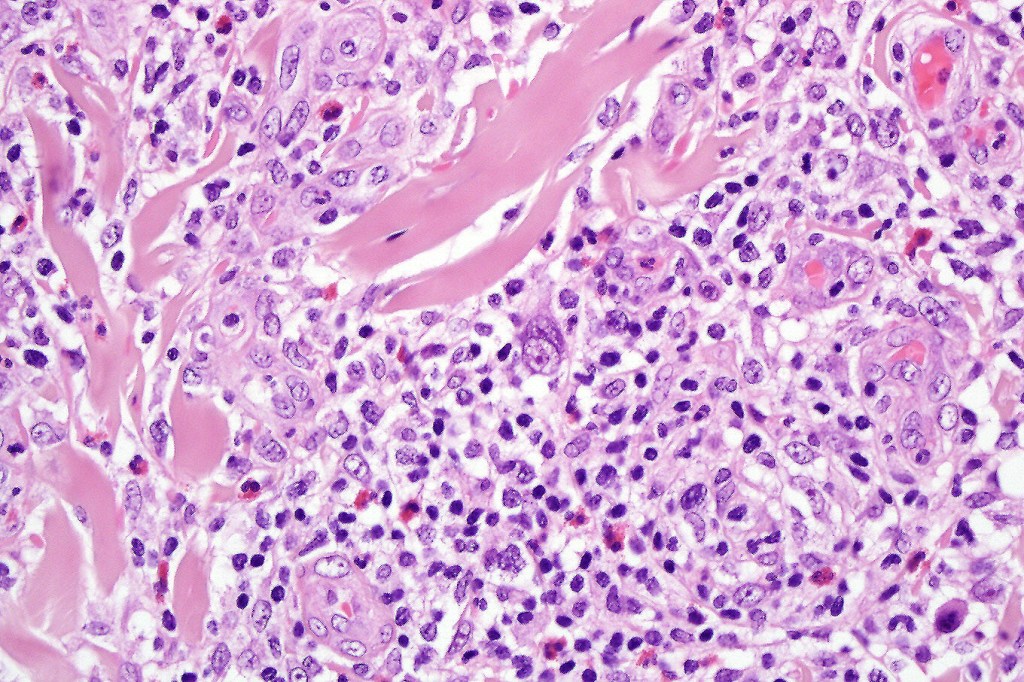
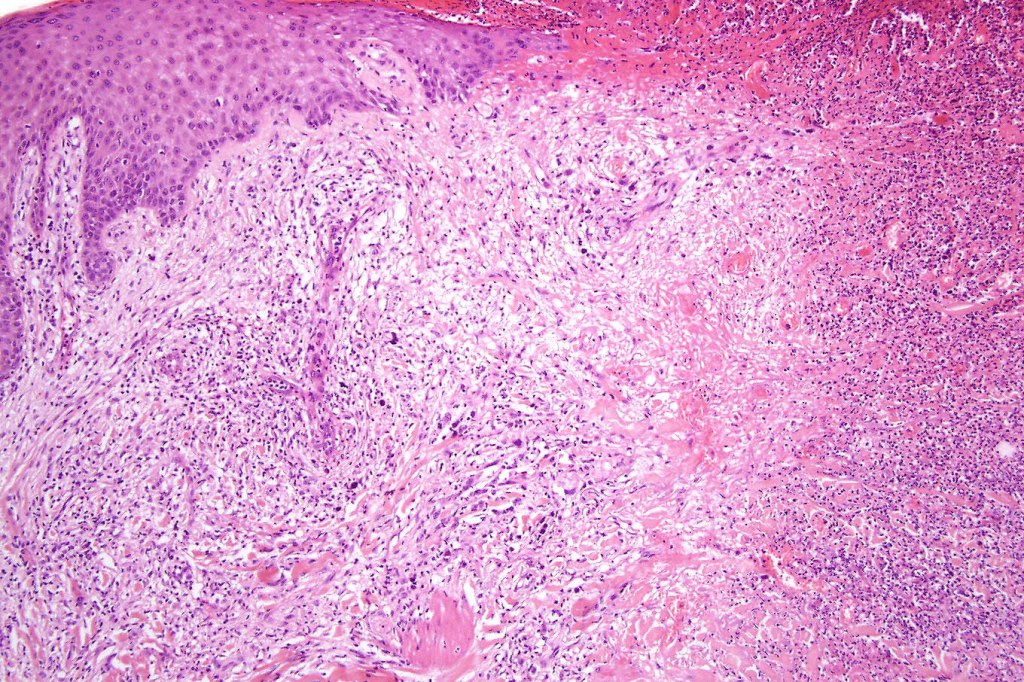
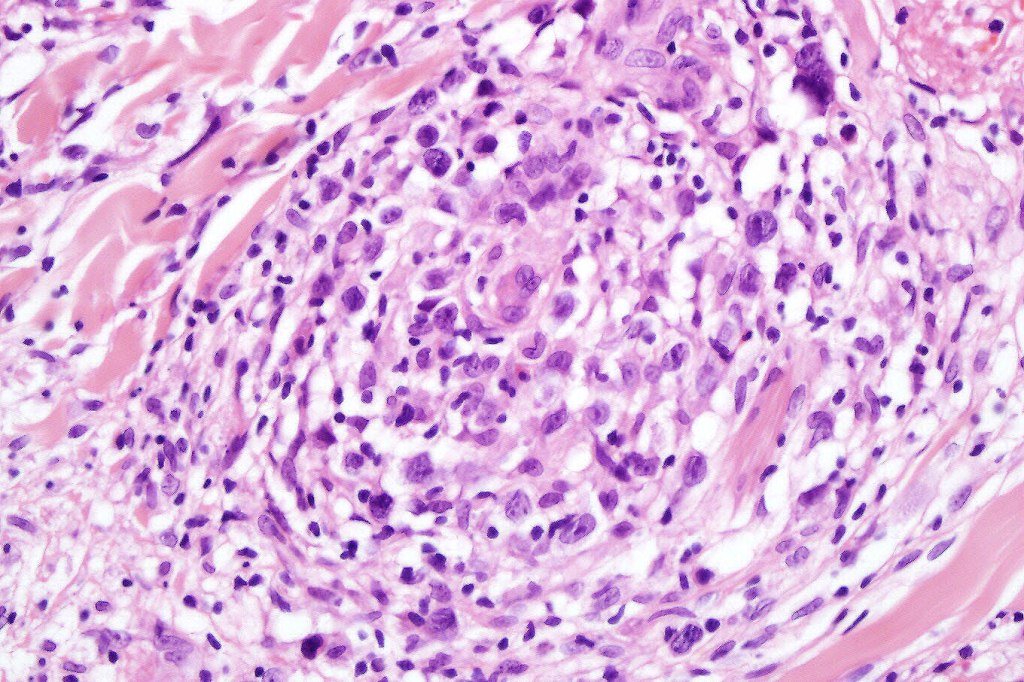
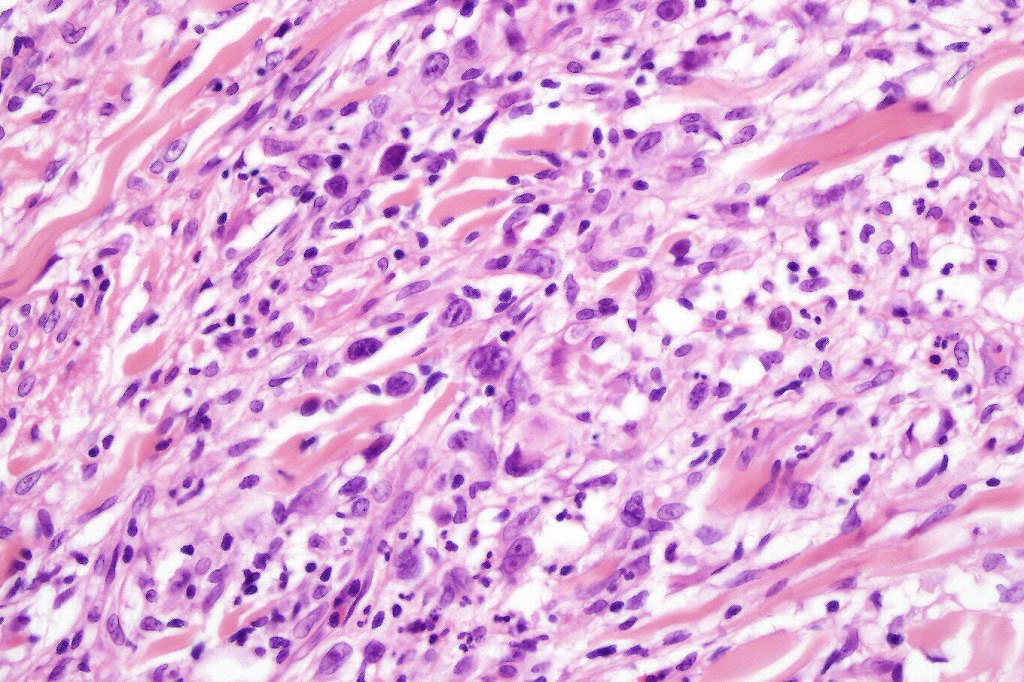
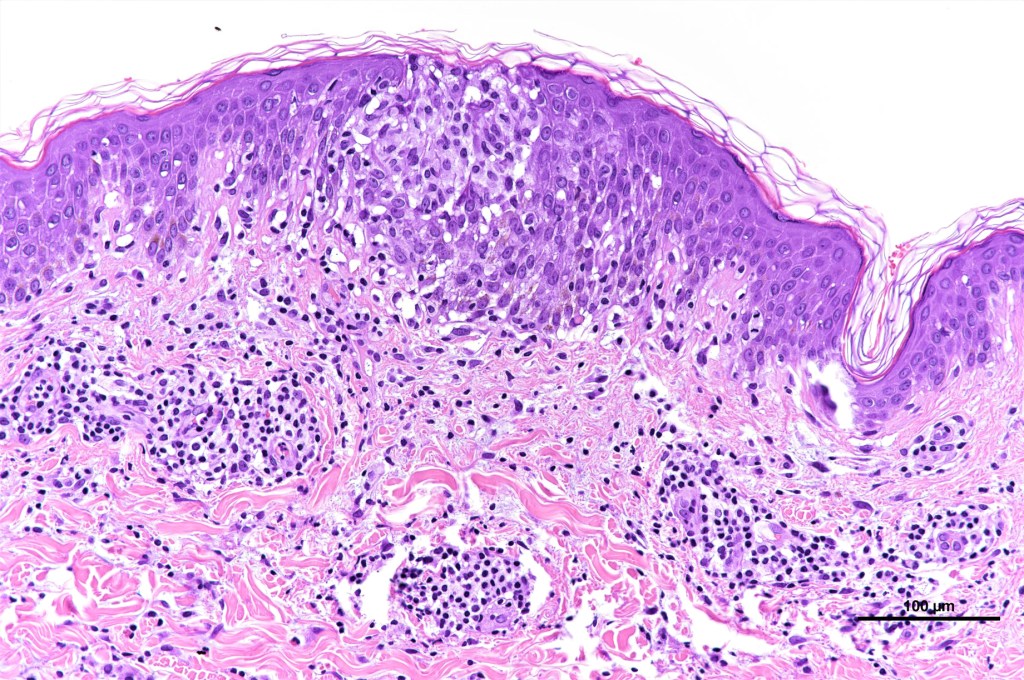
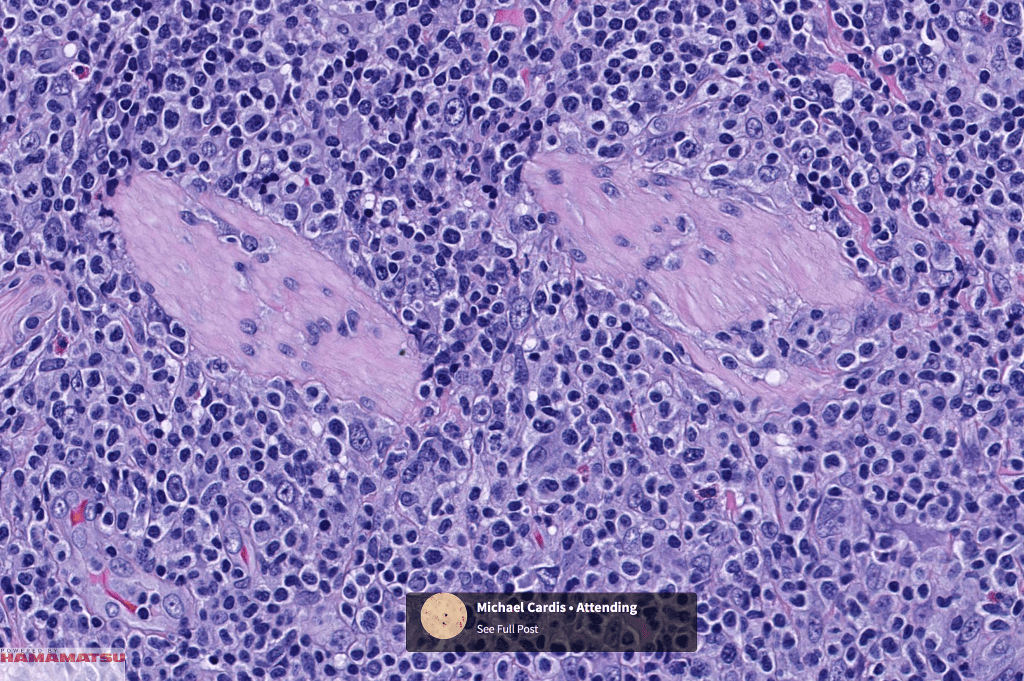
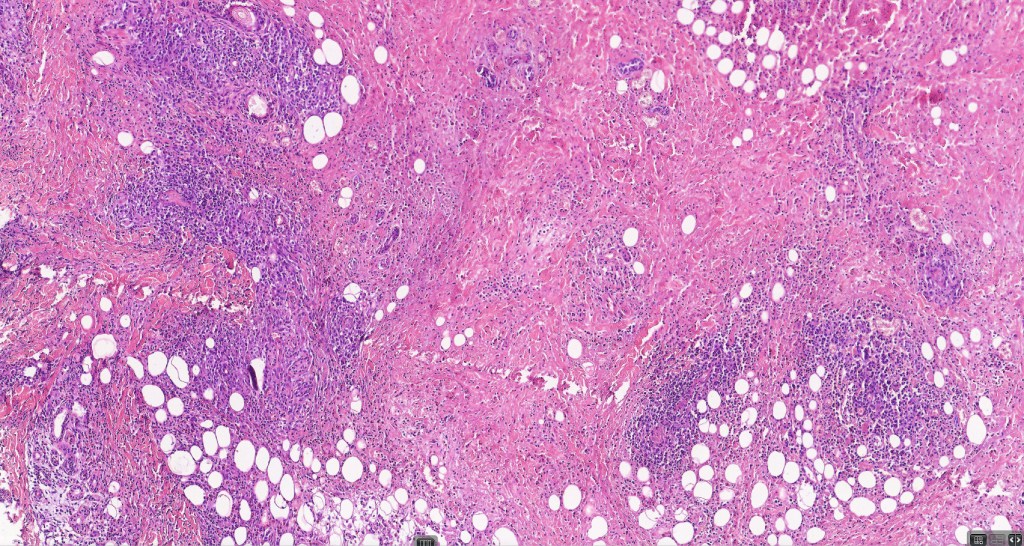
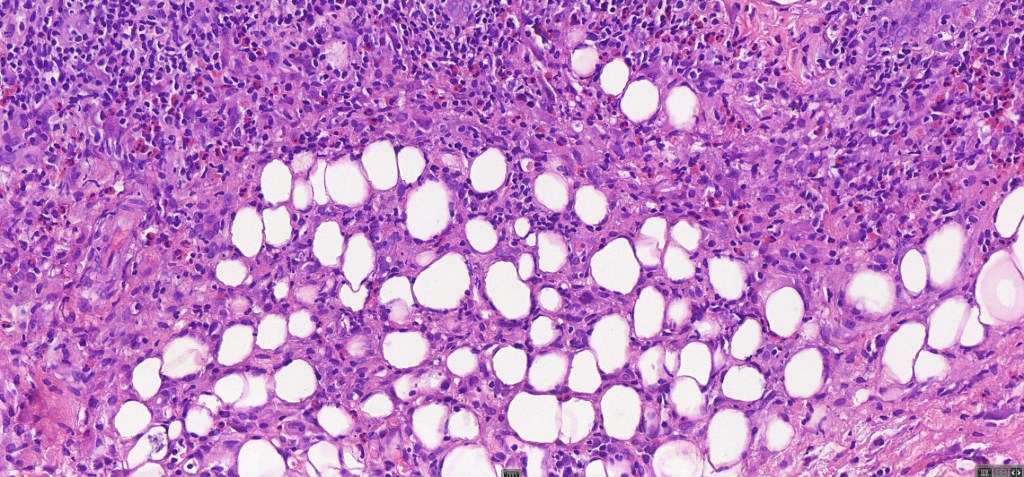
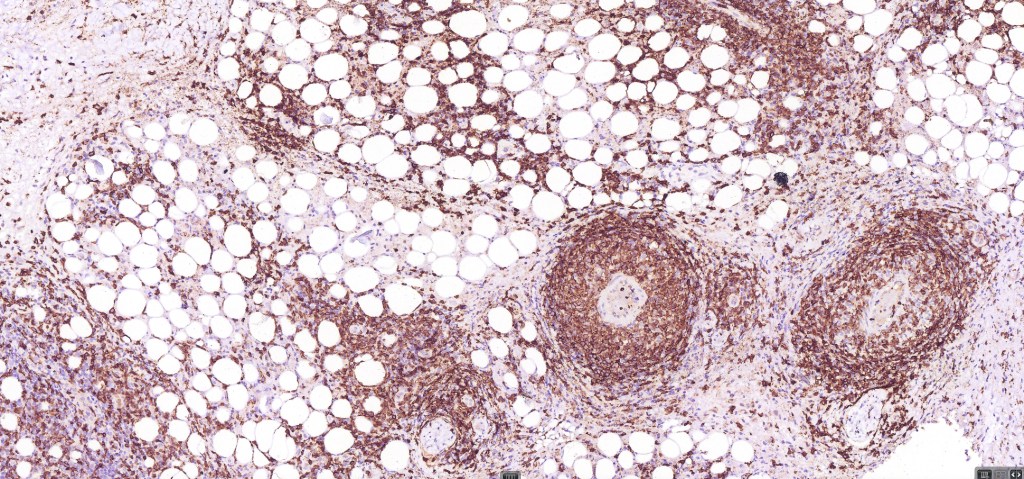
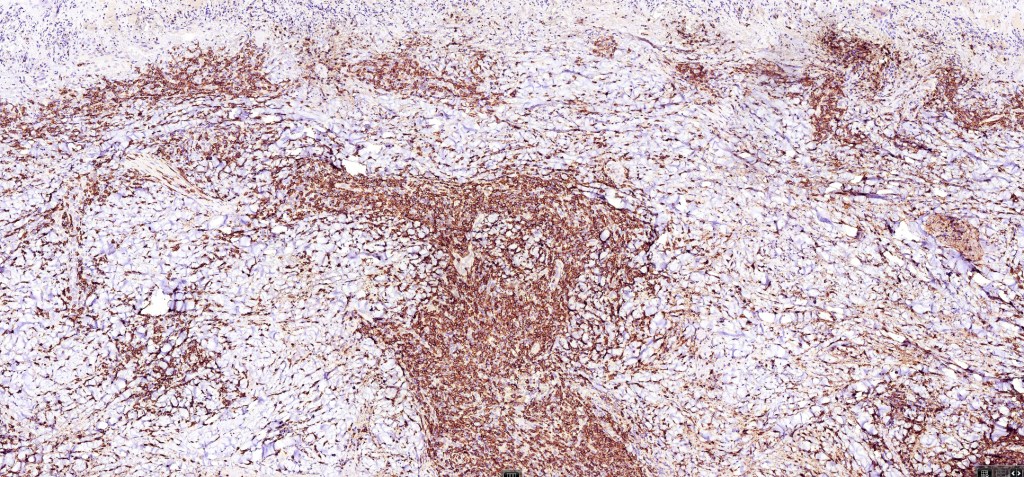
•Type A: 75-80%, wedge shaped infiltrate with base uppermost, large, anaplastic cells with abundant cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei containing prominent nucleoli, can resemble Reed-Sternberg cells, conspicuous mitoses & background infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes, neutrophils & eosinophils
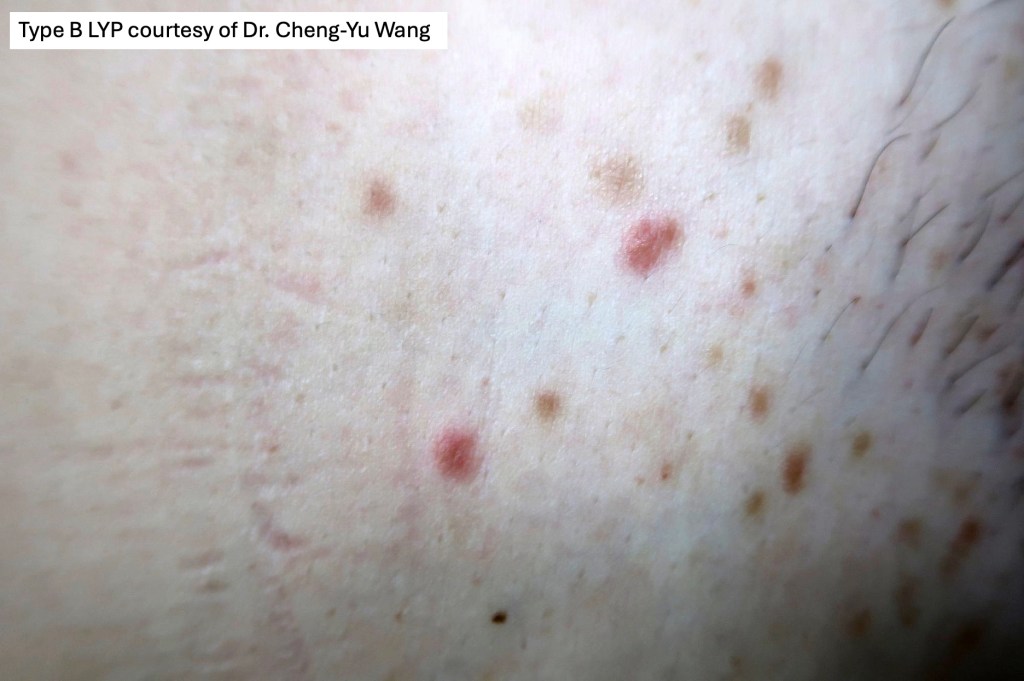
•Type B: 5-10% resembles plaque stage mycosis fungoides
•Type C: 7-10% nodular infiltrate similar to primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma
•Type D: epidermotropic form composed of CD8 T cells
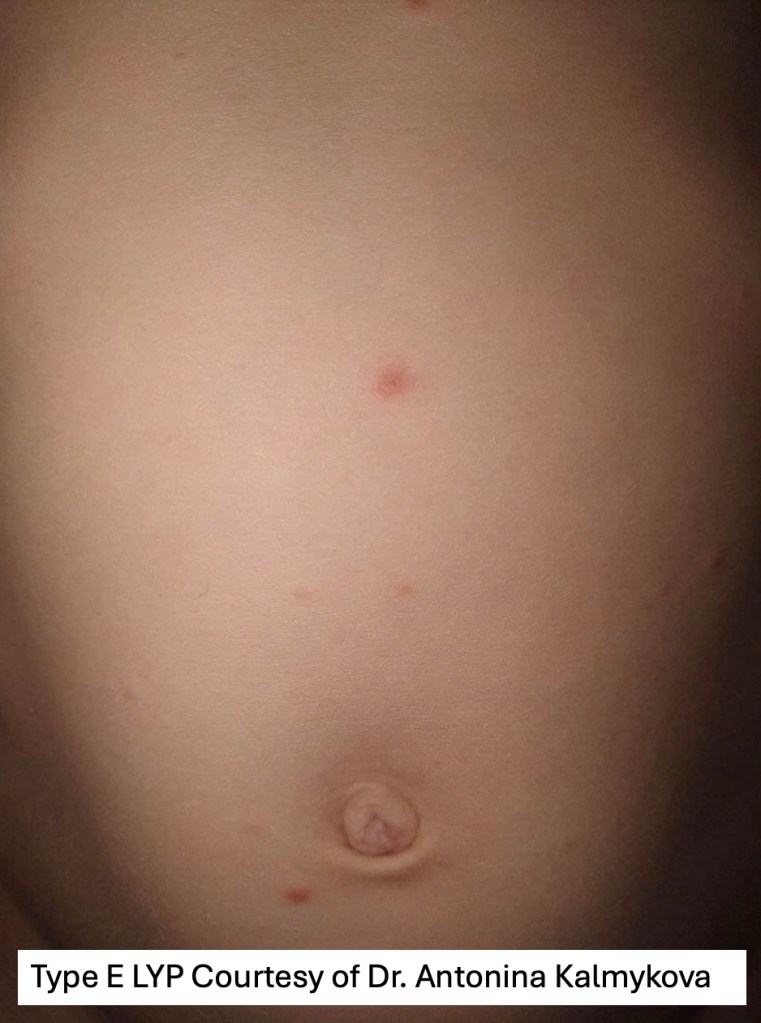
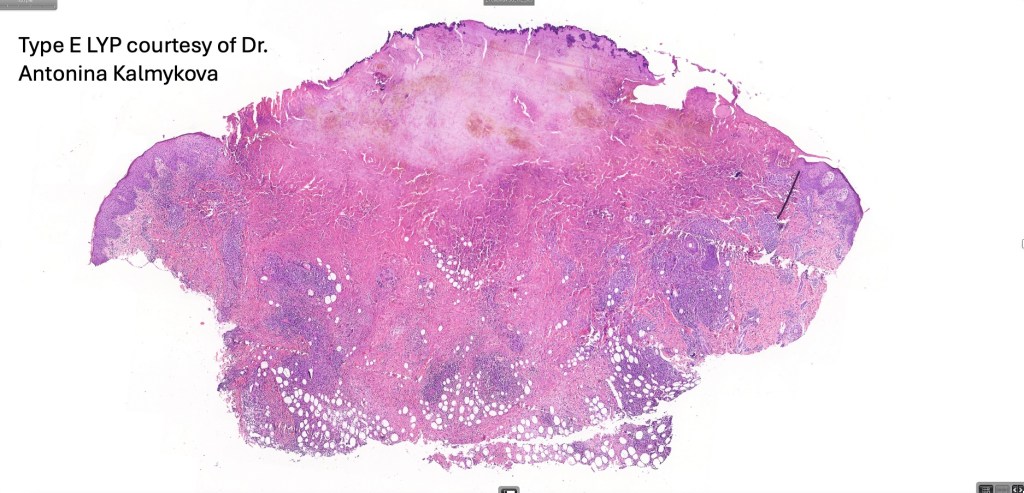
•Type E: angioinvasive & angiodestructive
•Type F folliculotropic variant often with follicular mucinosis
•Mixed variants are not uncommon
•Myxoid, sarcomatous variant
•Syringotropic variant
•Variable epidermal necrosis, epidermotropism, edema, hemorrhage & vasculitis/thrombosis
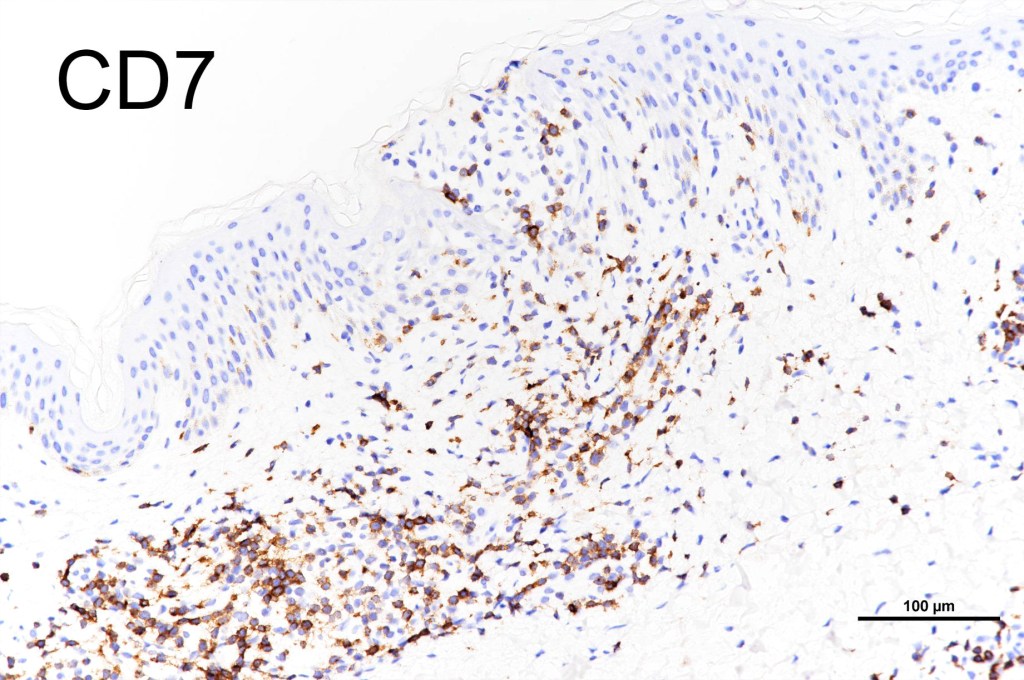
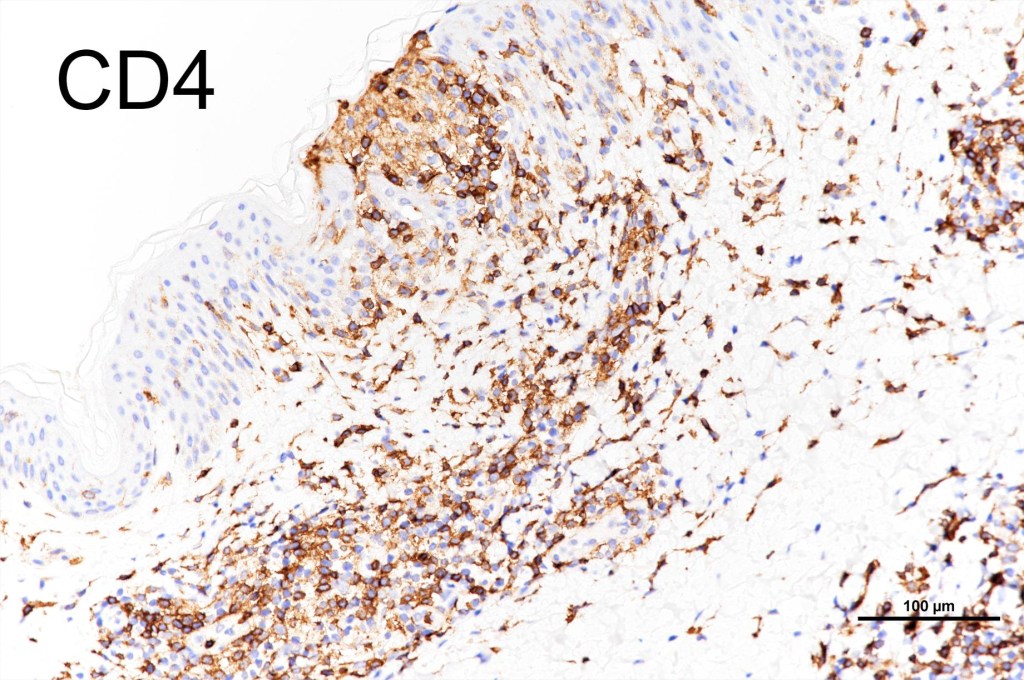
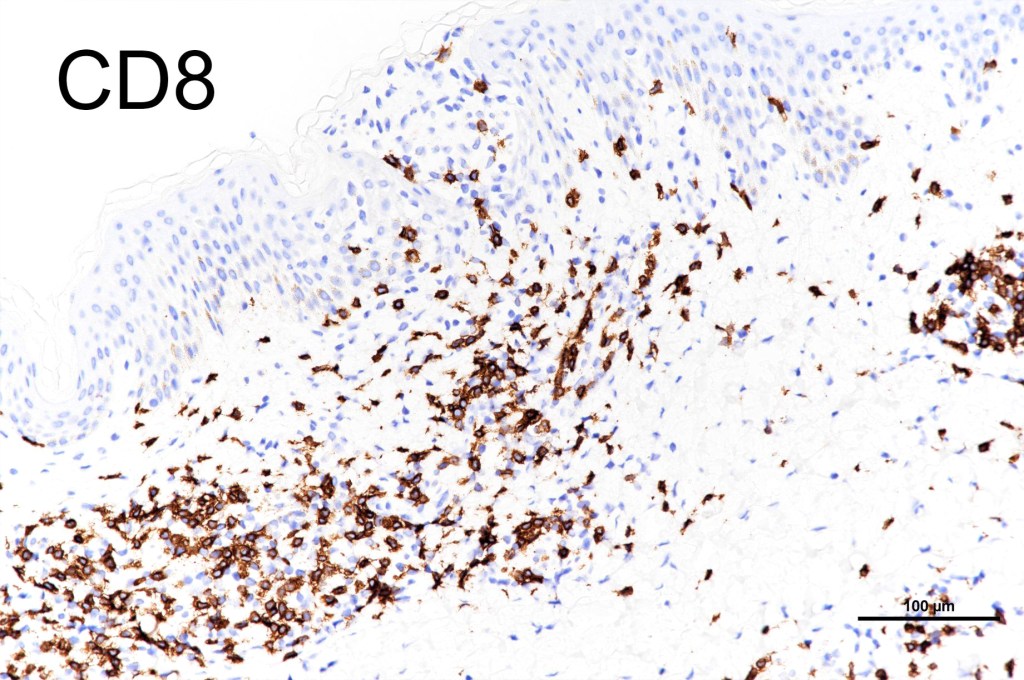
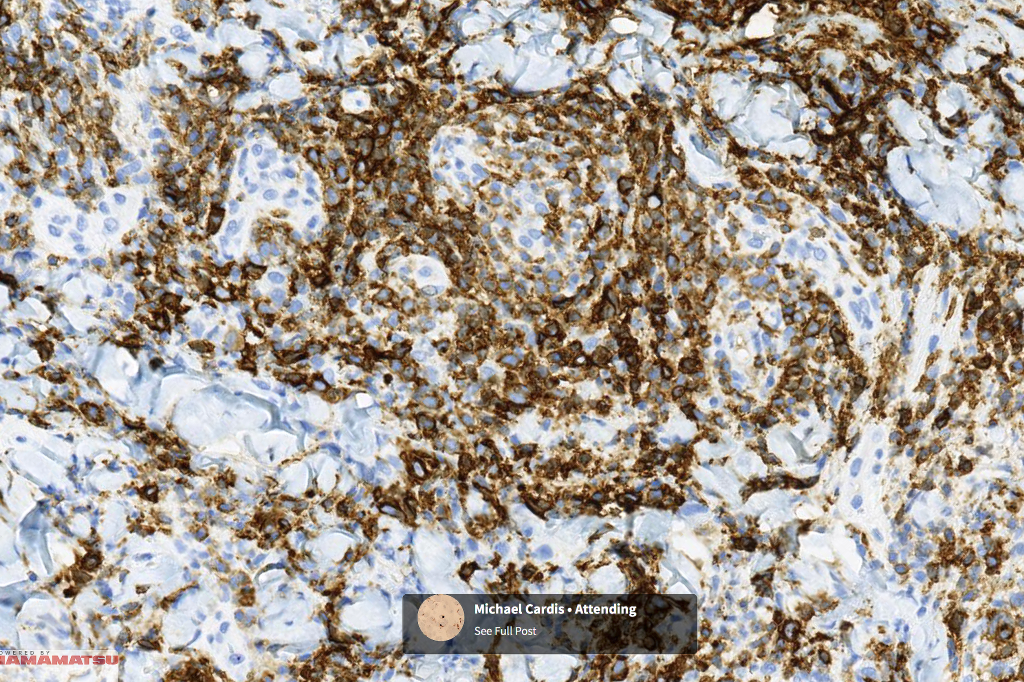
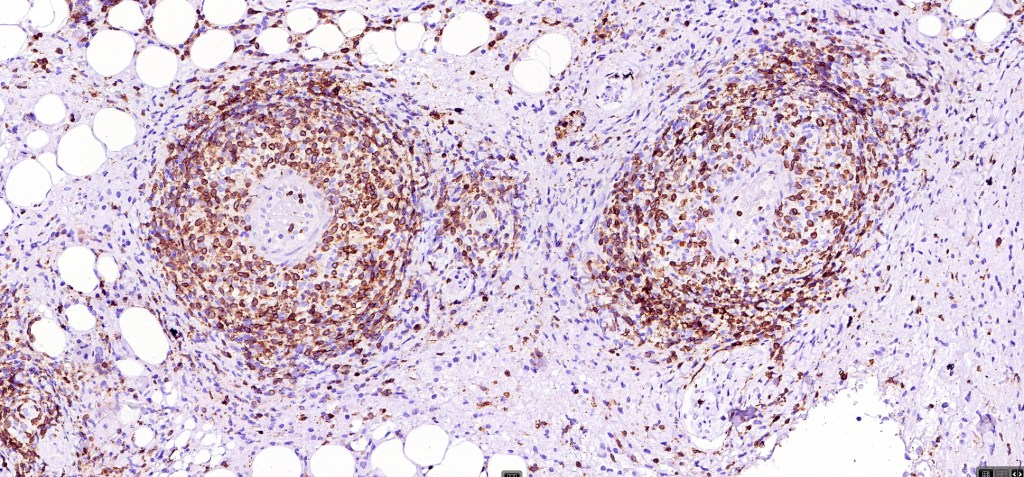
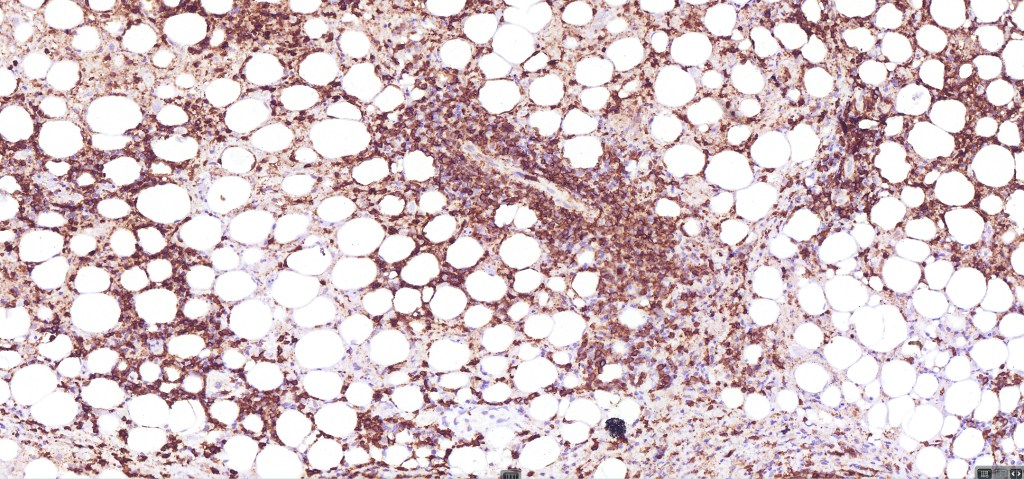
•CD4, CLA, MUM1 +ve
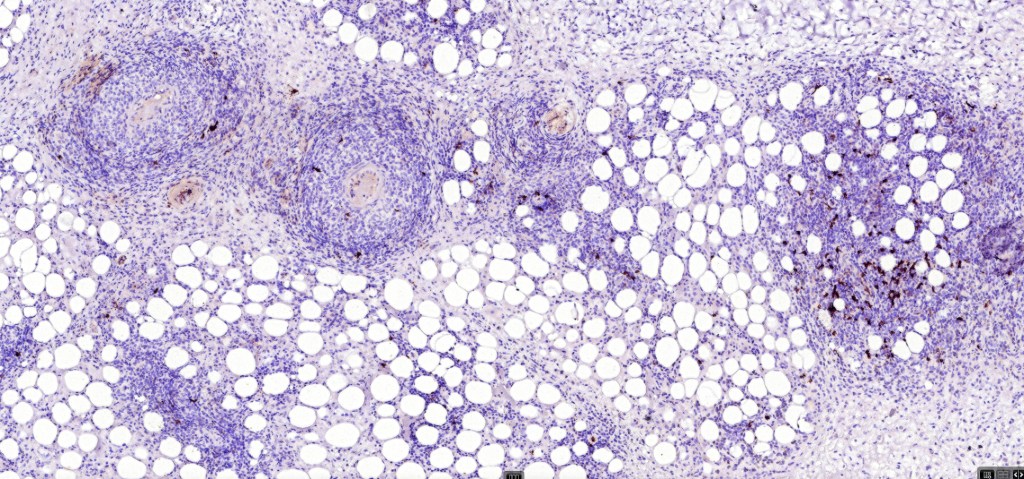
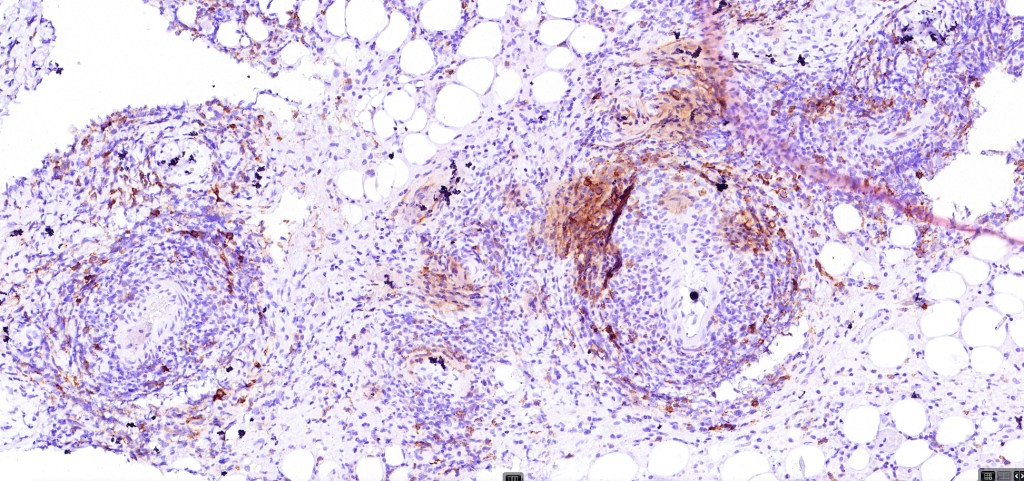
•CD8-ve (except for types D & E variants)
•Exceptional. CD4+/CD8+ & CD4-/CD8- variants
•Granzyme-B, TIA-1 & perforin +ve)
•CD45, CD30 +ve/CD15 –ve (types A & C)
•Type B often CD30-ve
•Generally, ALK & EMA -ve
•Variable CD56+ve
























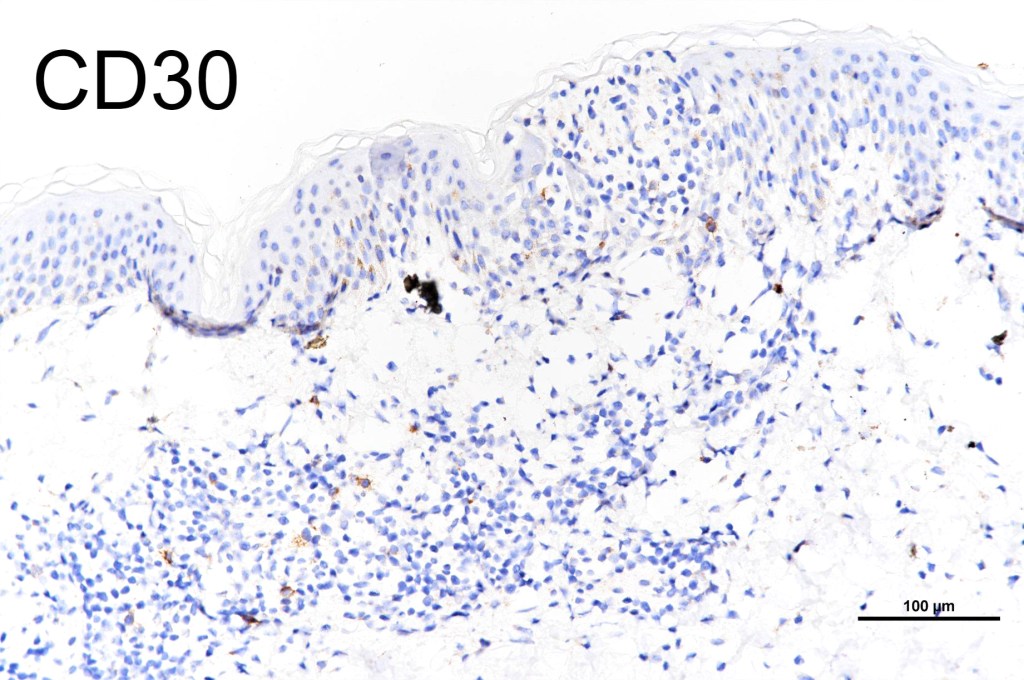



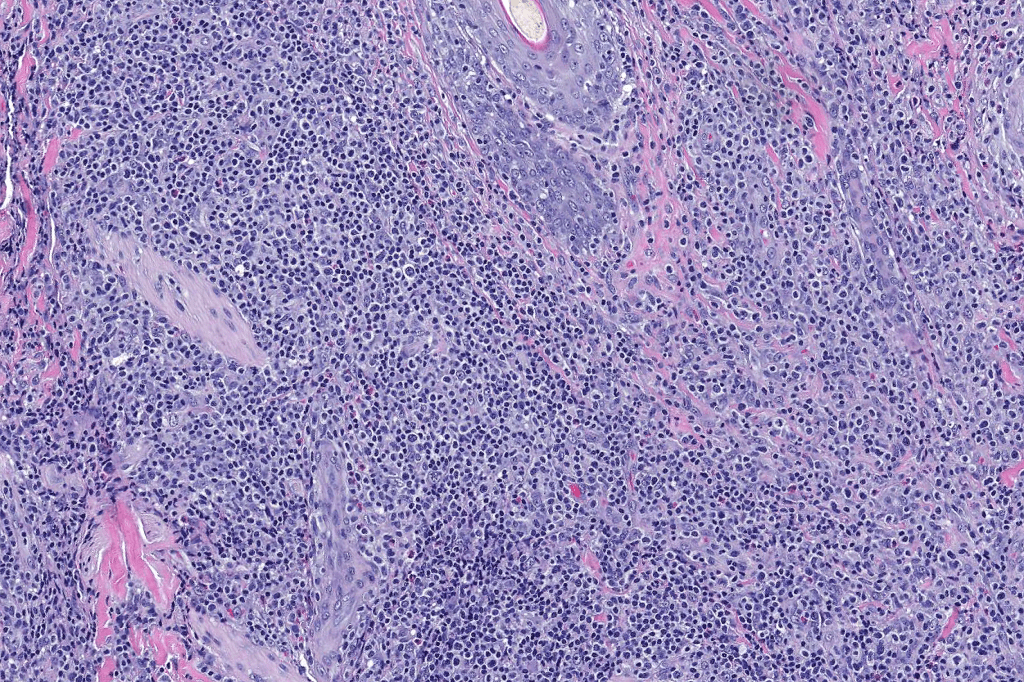

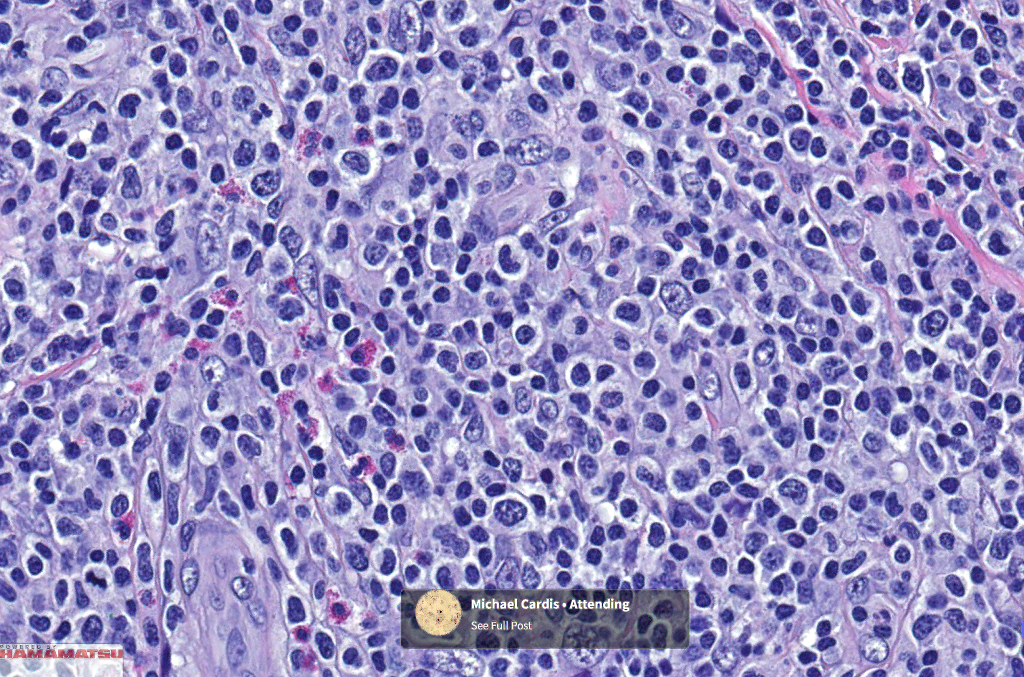

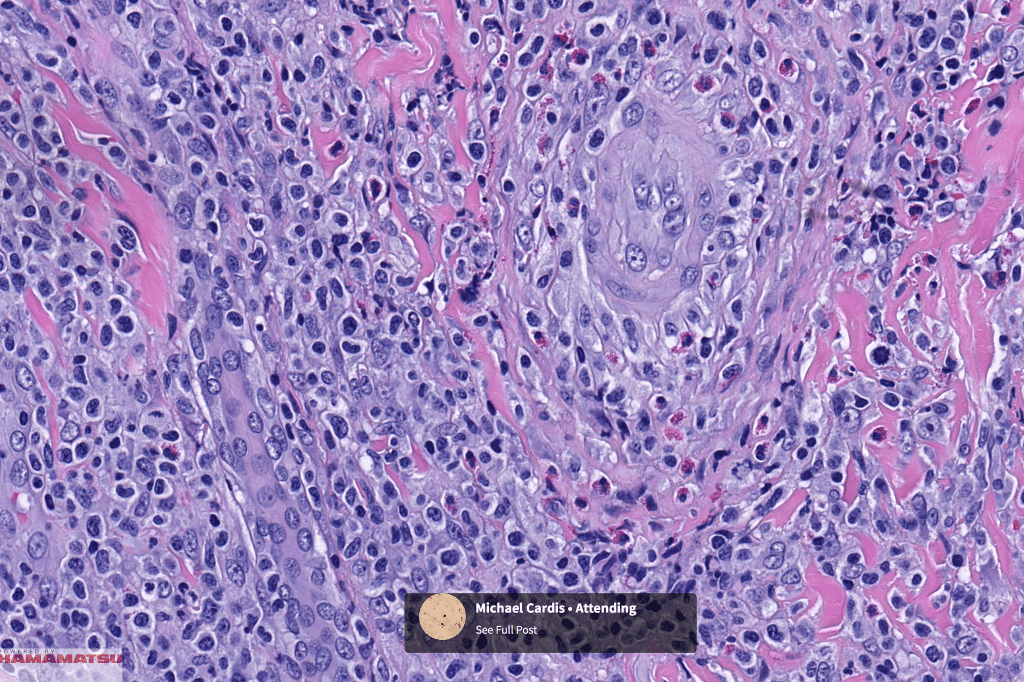








Differential diagnosis
There is considerable overlap with primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma & transformed mycosis fungoides. Distinction can be readily made in the majority of cases with clinicopathological correlation.
CD30+ve cells may be seen in a wide range of infections including molluscum contagiosum, herpes simplex, Milker’s nodule, EBV, HTLV-1, HIV, scabies & syphilis. CD30+ve cells may also be seen in PLEVA & drug reactions
Type B variant is histologically indistinguishable from mycosis fungoides. Type D variant is indistinguishable from other epidermotropic lymphomas.
Leave a comment