Clinical features
•Should be distinguished from trichoepithelioma since the latter may be multiple and associated with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome & multiple familial trichoepitheliomas
•Exceptional association with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome
•M=F
•5th-7th decades
•Presents as a solitary, slowly growing nodule particularly affecting the scalp, head & neck, trunk, extremities & genitalia in decreasing order of frequency
Plaque-like variant (F>>M)
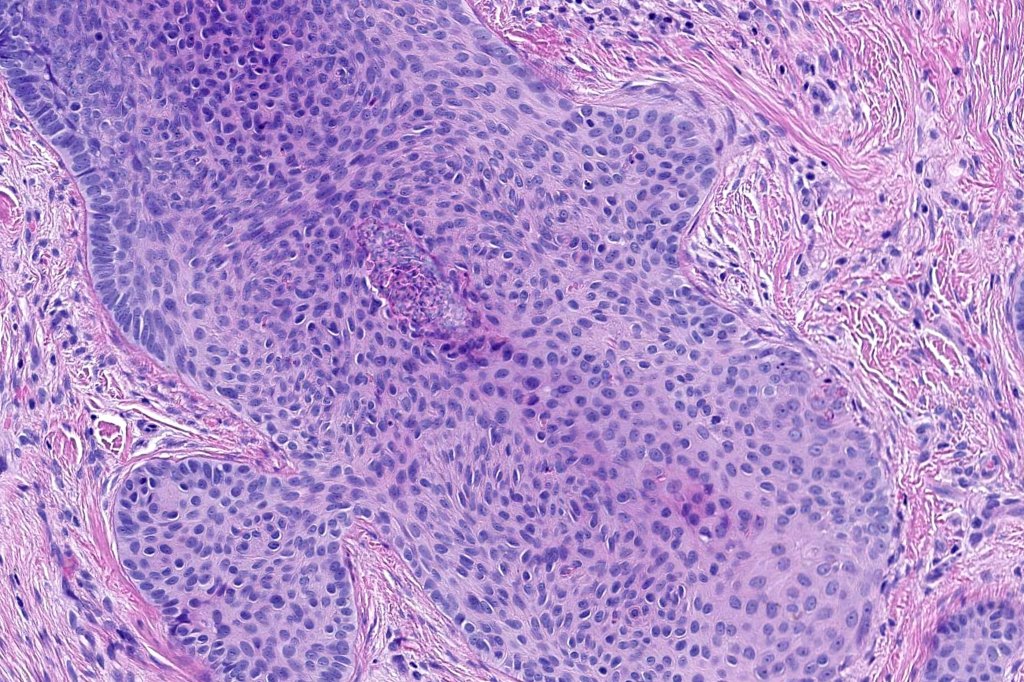
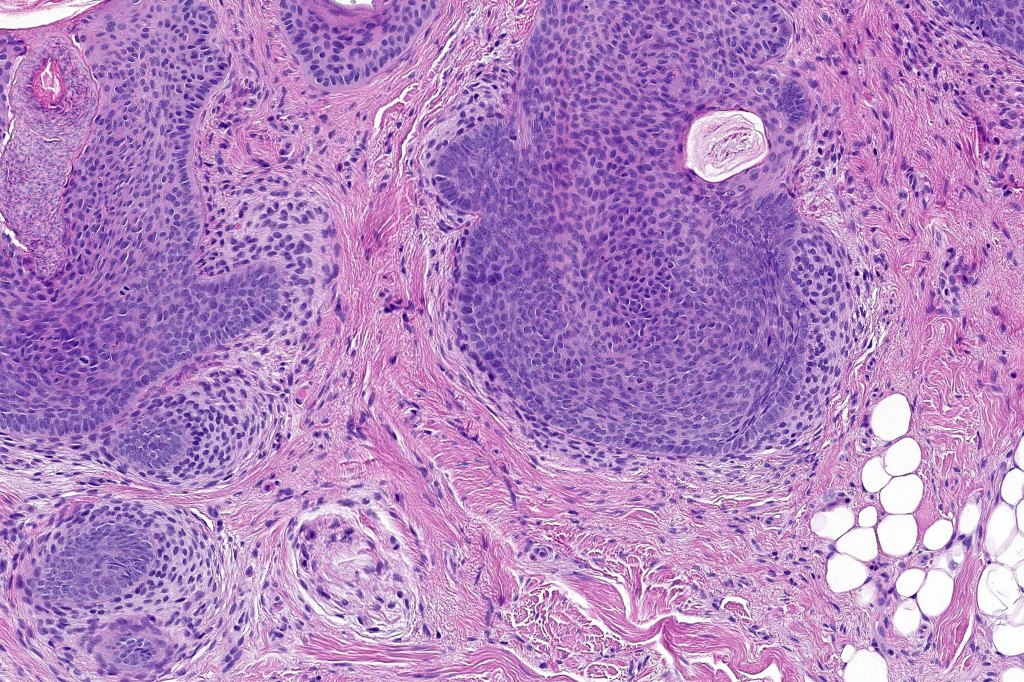
Histological features
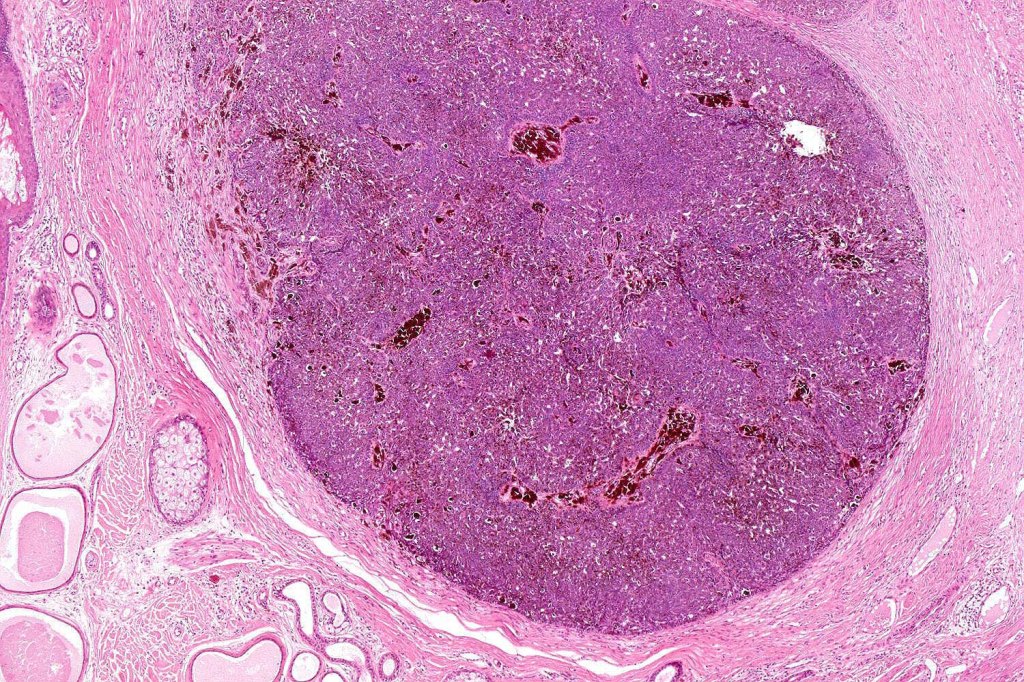
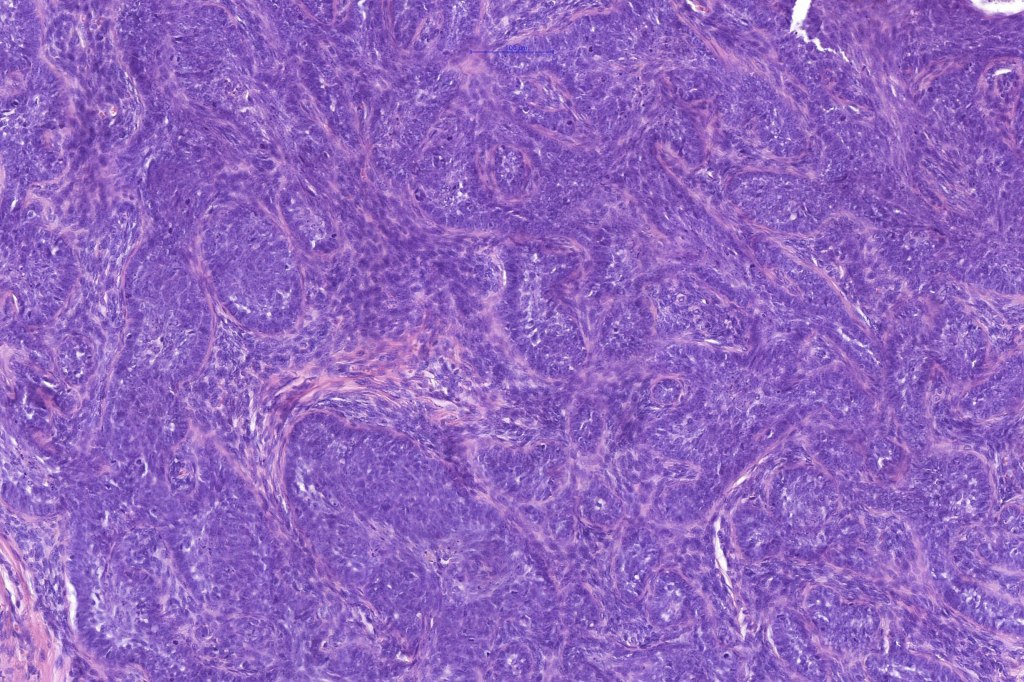
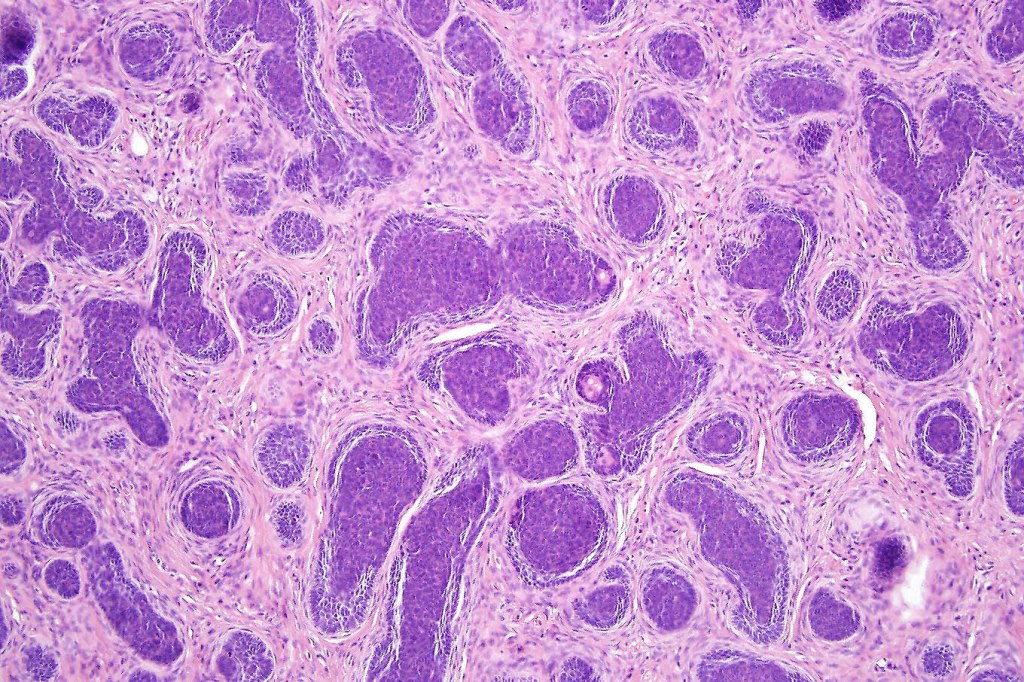
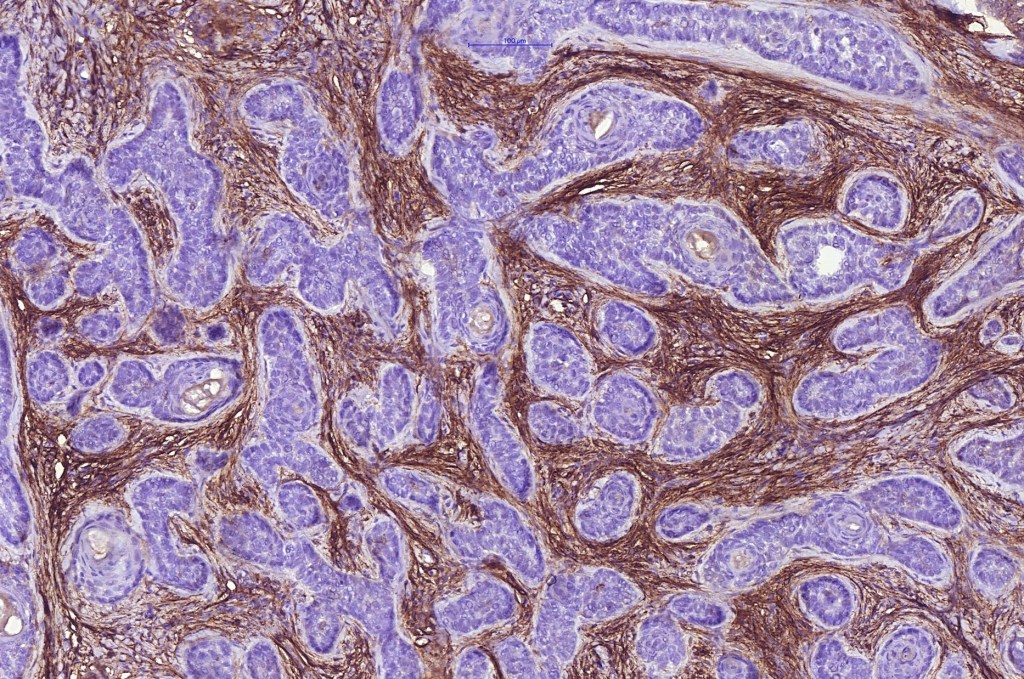
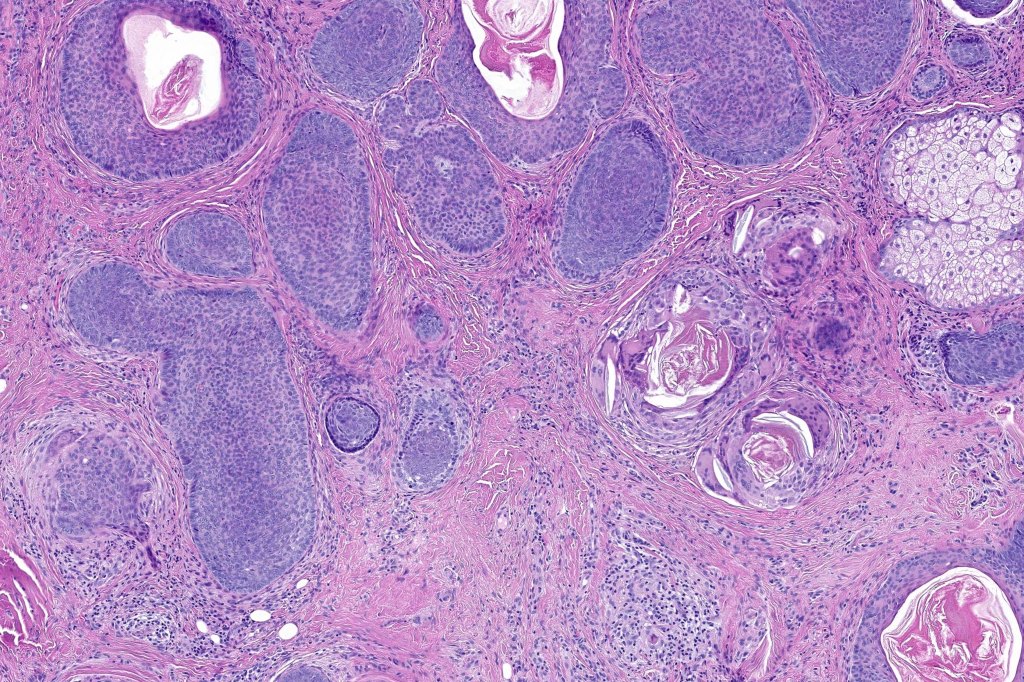
•Biphasic tumors comprising germinative epithelial and mesenchymal components
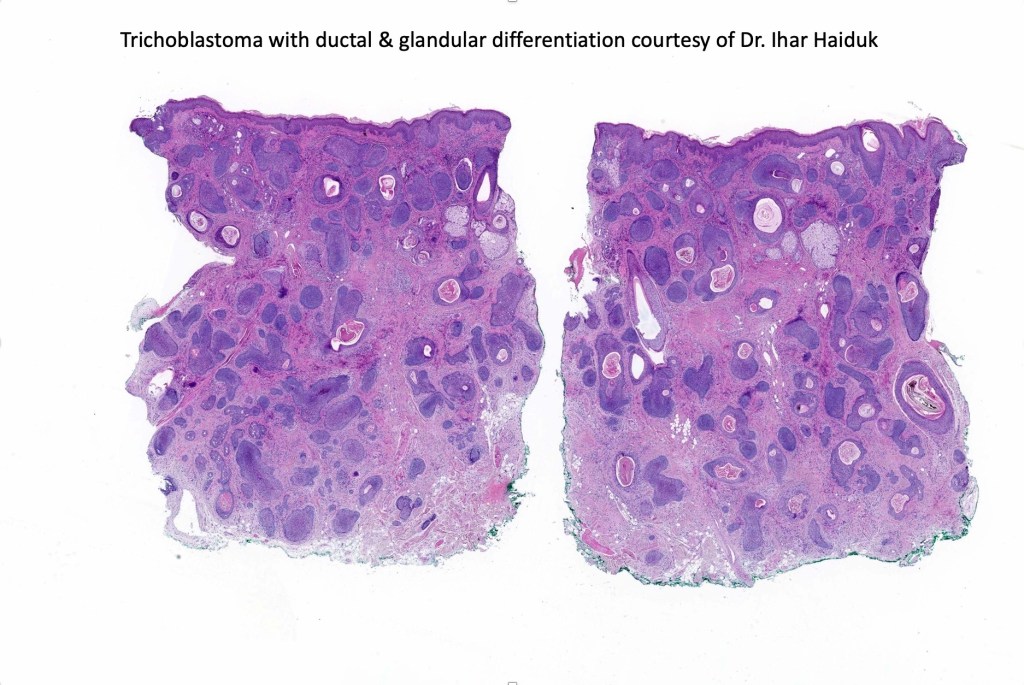
•Sharply circumscribed nodule, sometimes with a pseudocapsule
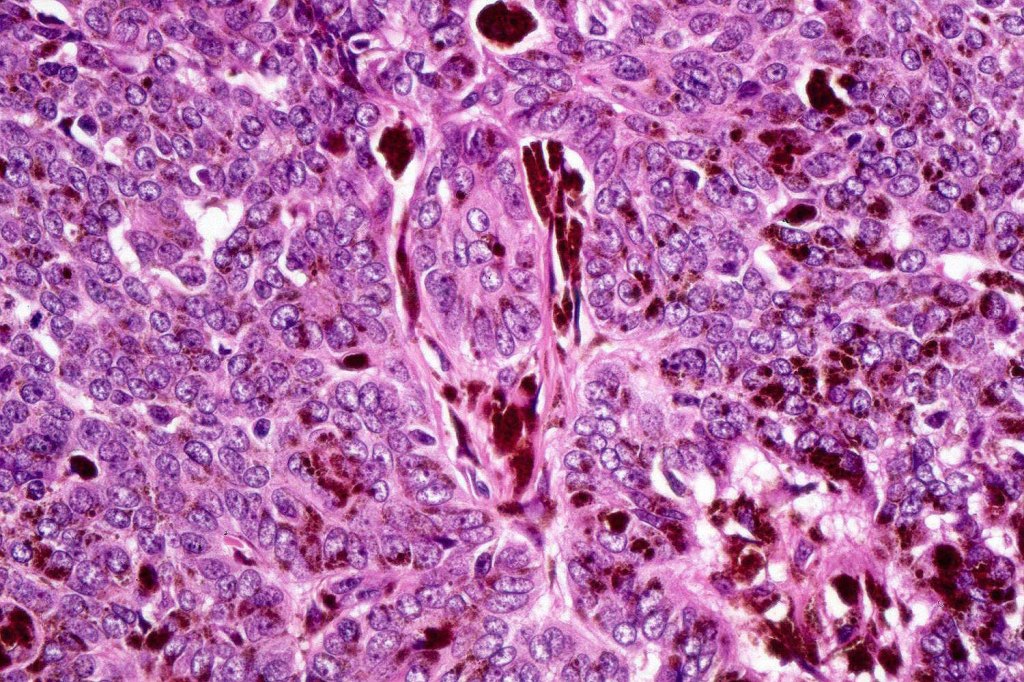
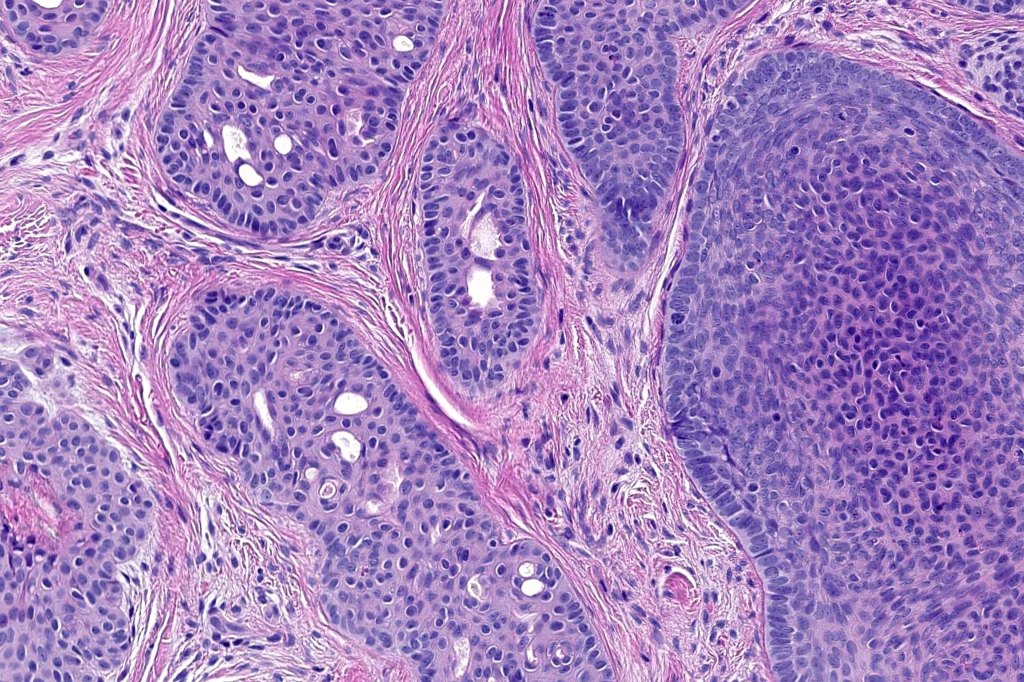
•Uniform basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and often marked mitotic activity
•No pleomorphism
•Absence of retraction artifact and mucin deposition
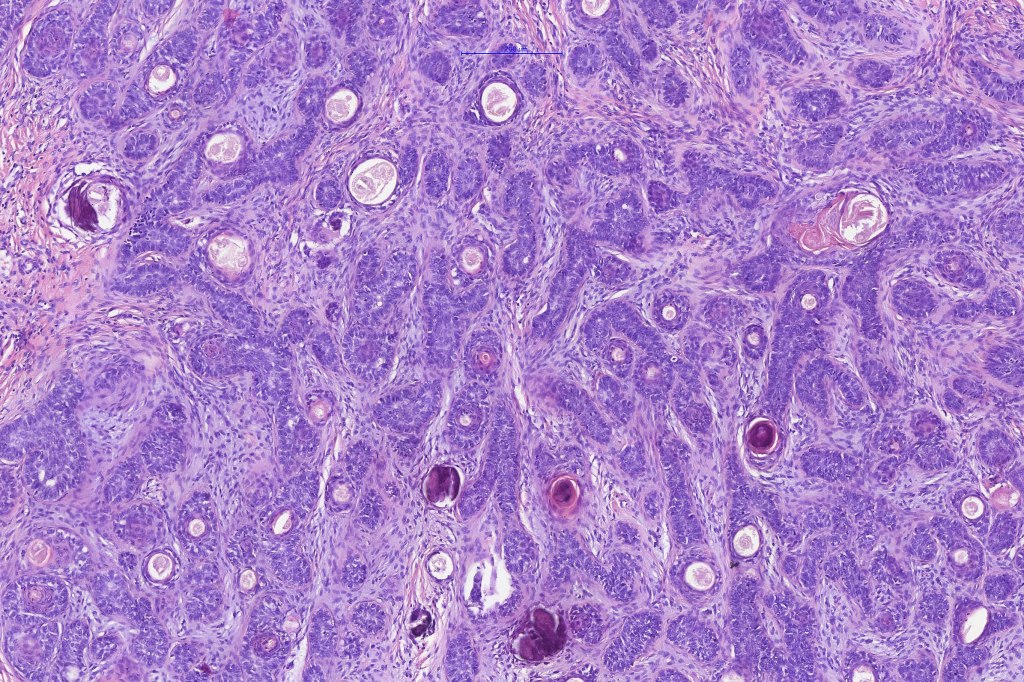
•Variable keratin cysts
•Clear cell change
•Sebaceous & glandular differentiation
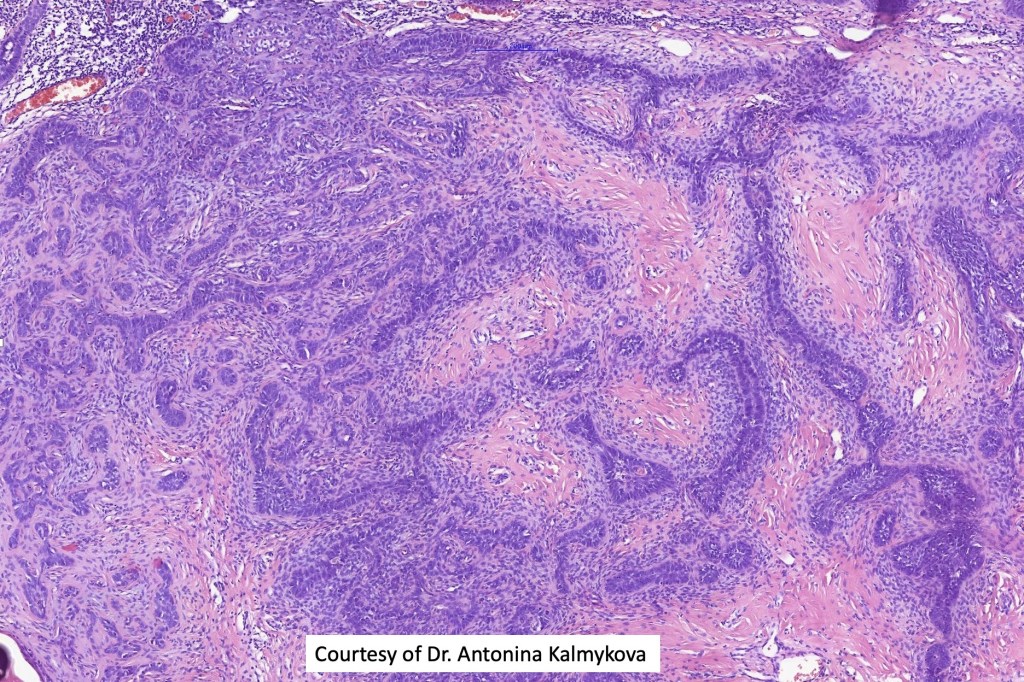
•Cribriform and palisaded (rippled) pattern
•Pigmented variant
•Stromal component associated with indentation of epithelial component- follicular mesenchymal bodies (uncommon, more often seen in trichoepithelioma)
•Stromal amyloid often present
•Merkel cells are commonly present
•Trichogerminoma (see images)
•Most common tumor arising in nevus





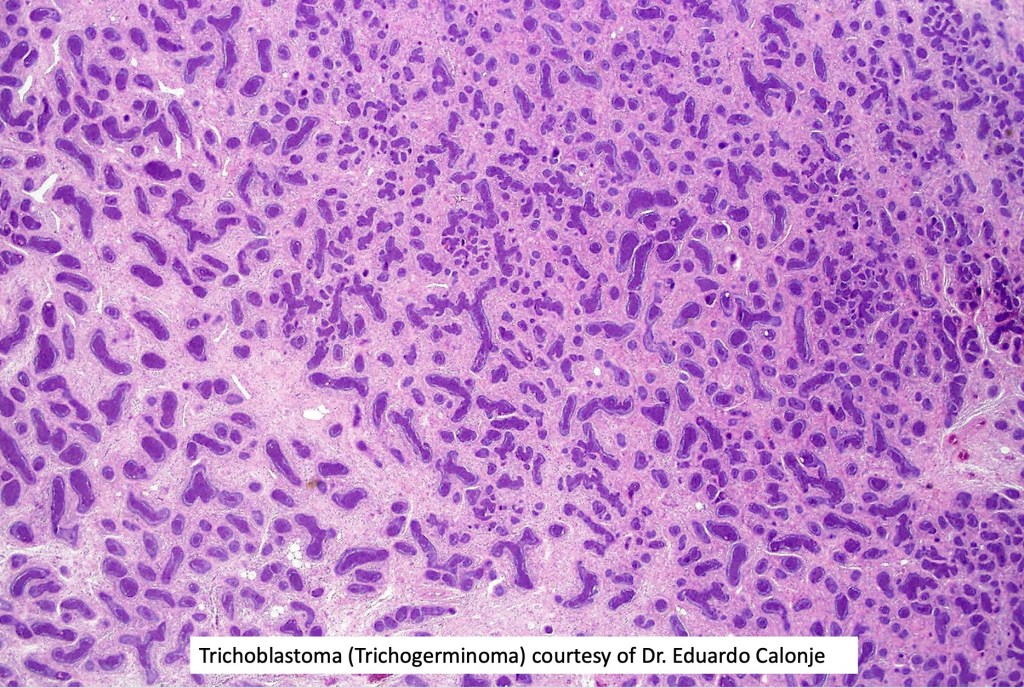


•CK20, PHLDA1 +ve Merkel cells+
•Androgen receptor –ve
•CD10+ (stromal)
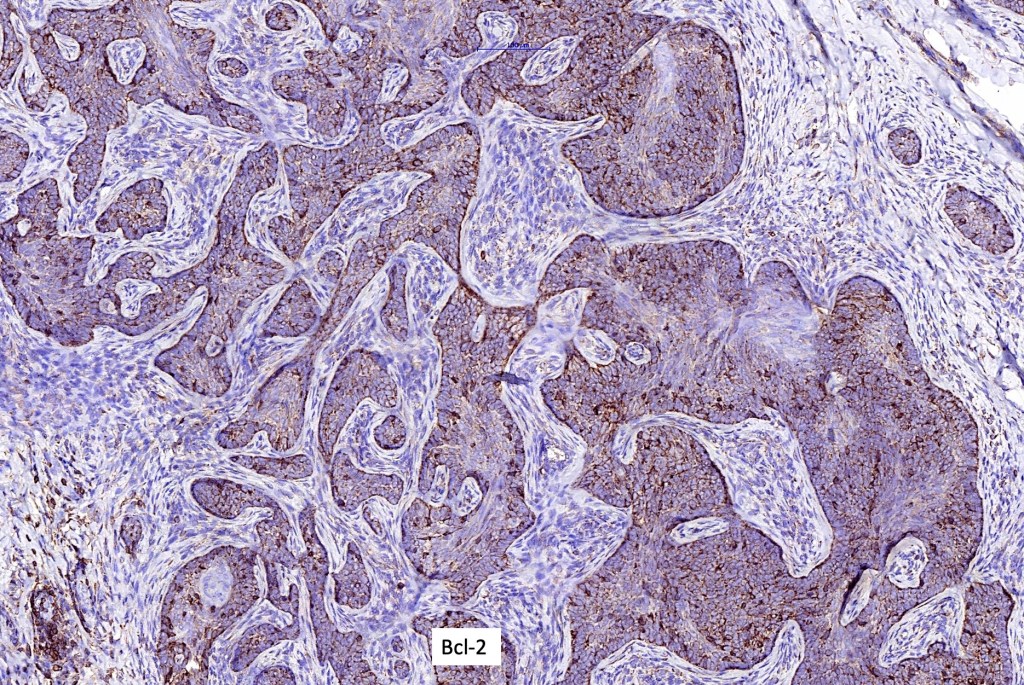
•CD34 + (stromal)Bcl2+ve (peripheral)









Leave a comment