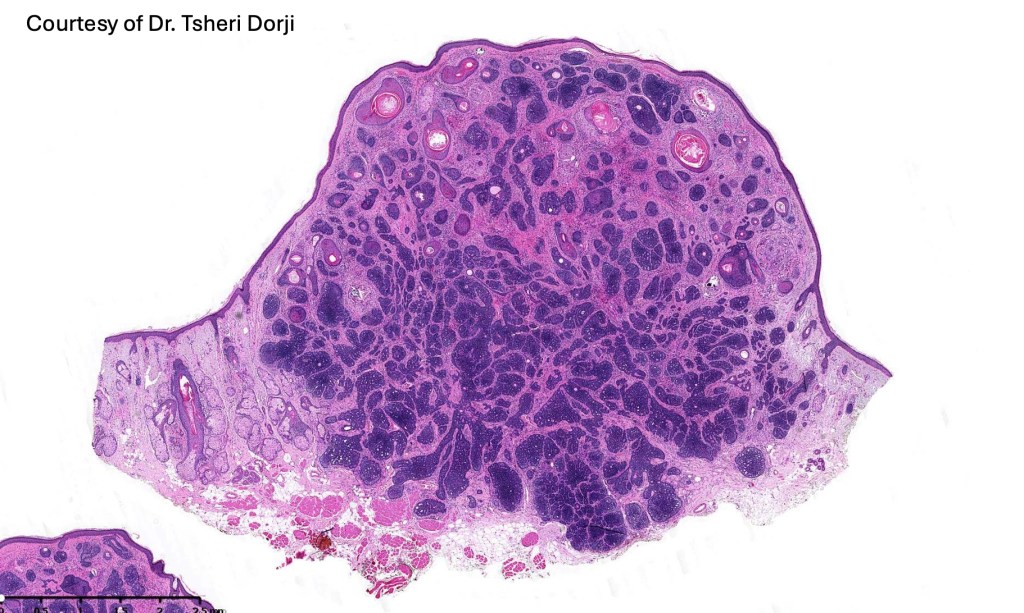
The entities trichoblastic fibroma, trichogenic trichoblastoma, giant solitary trichoepithelioma, subcutaneous trichoepithelioma, immature trichoepithelioma are all included under the rubric trichoblastoma. Trichoblastoma shared many histological similarites with trichoepithelioma but differs by its much larger size, extension into the deep dermis/subcutaneous fat or deeper and large circumscribed nodules Papillary mesenchymal bodies are often absent or more difficult to identify. The distinction is important as trichoblastoma is not syndromic.
Clinical features
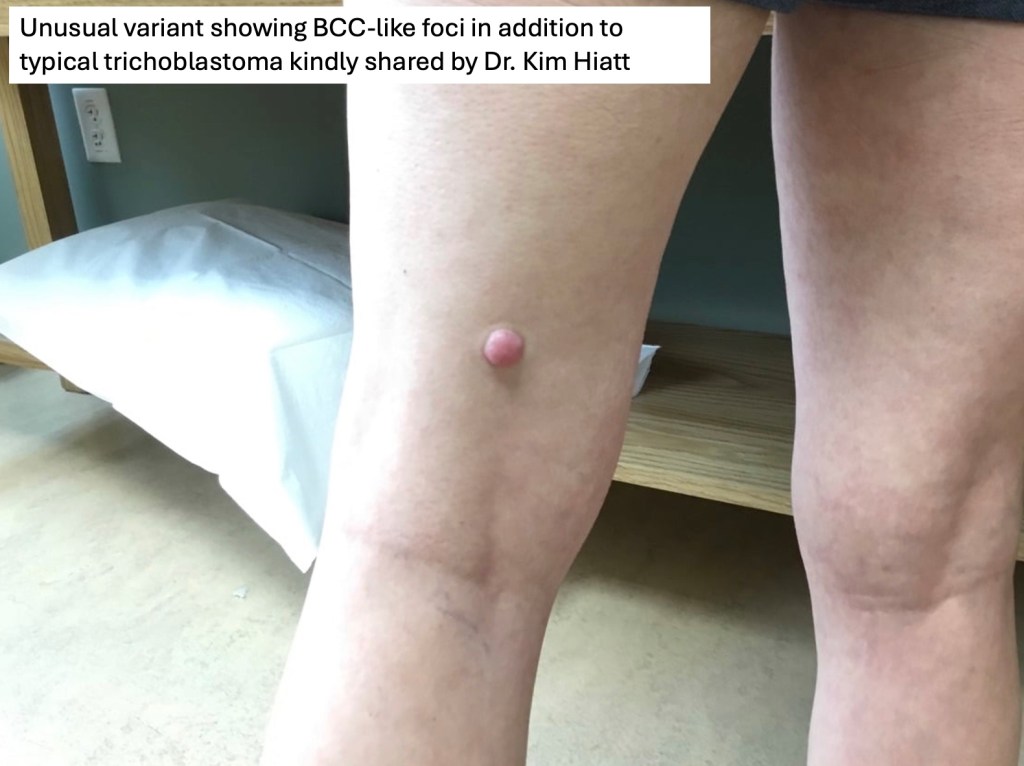
•A solitary, slowly growing sharply delineated nodule, often of very long duration (sometimes years), generally large (> 1.0 cm up to 10 cm diameter)
•Skin colored or pigmented
•Predilection for head & neck (especially the scalp) although other sites including the trunk, proximal arms & legs, external genitalia & perianal region
•Plaque variant particularly on the cheek of females
•M=F, 5—80 years
•No association with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome or familial multiple trichoepithelioma
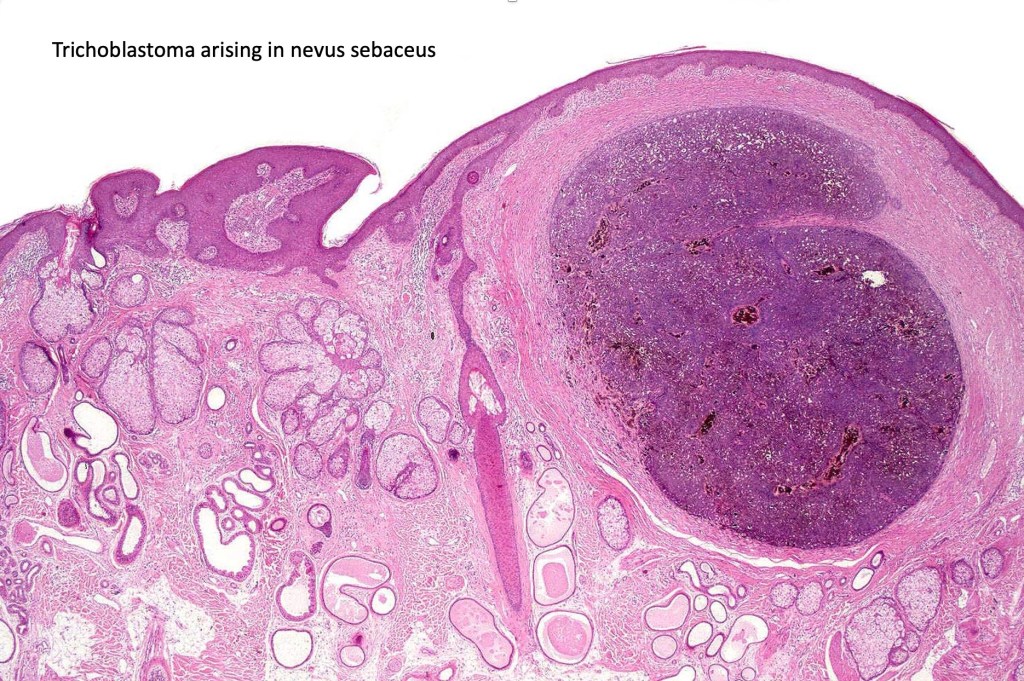
•One of the more common tumors to complicate nevus sebaceus
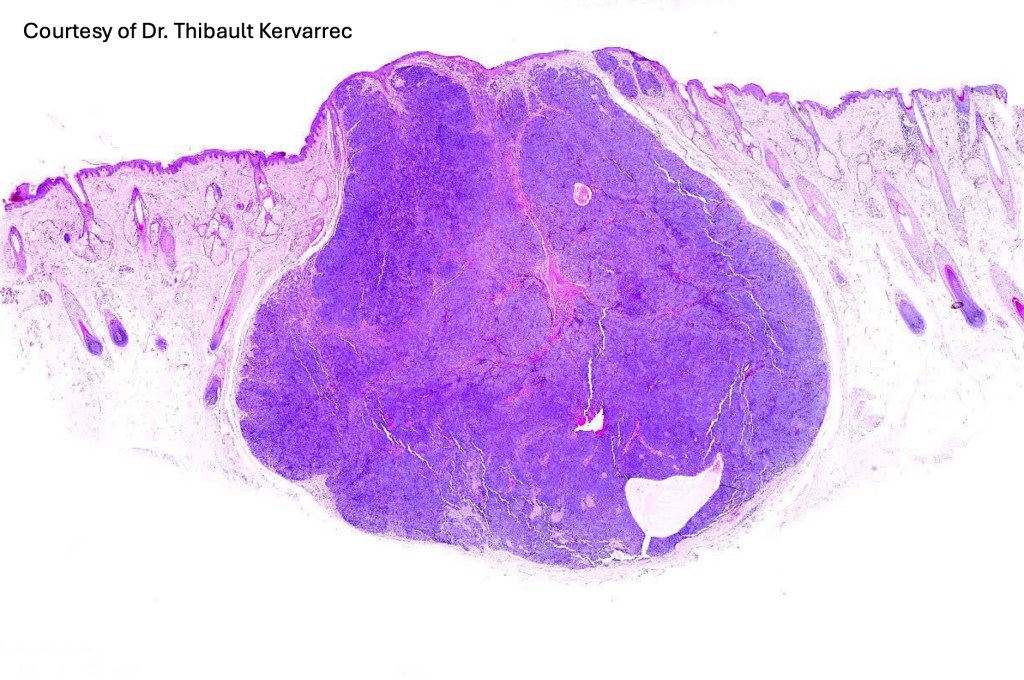
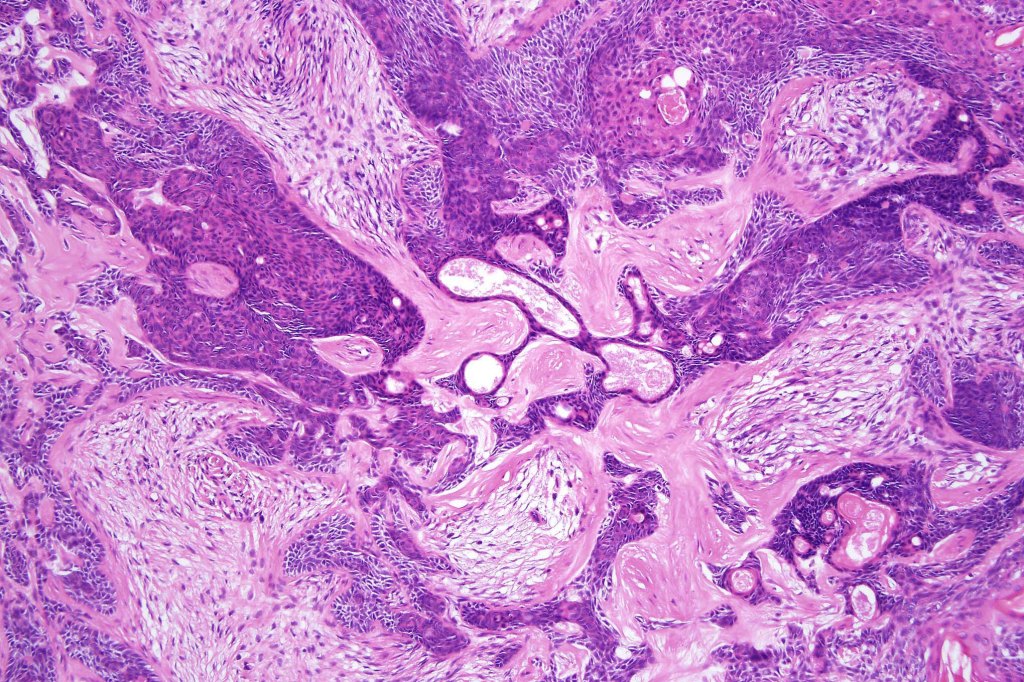
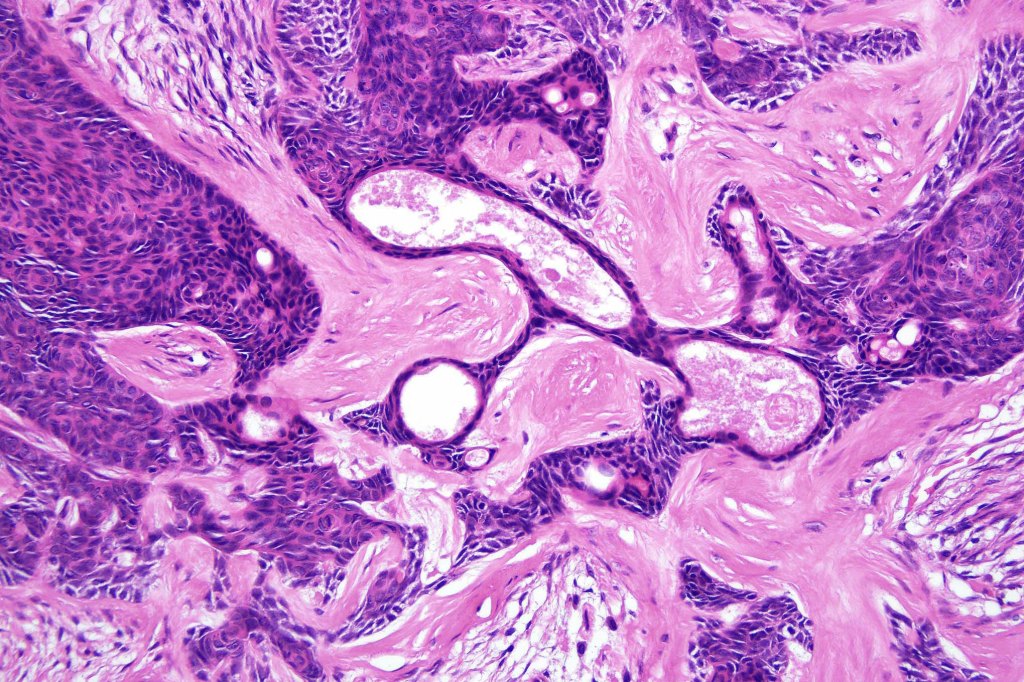
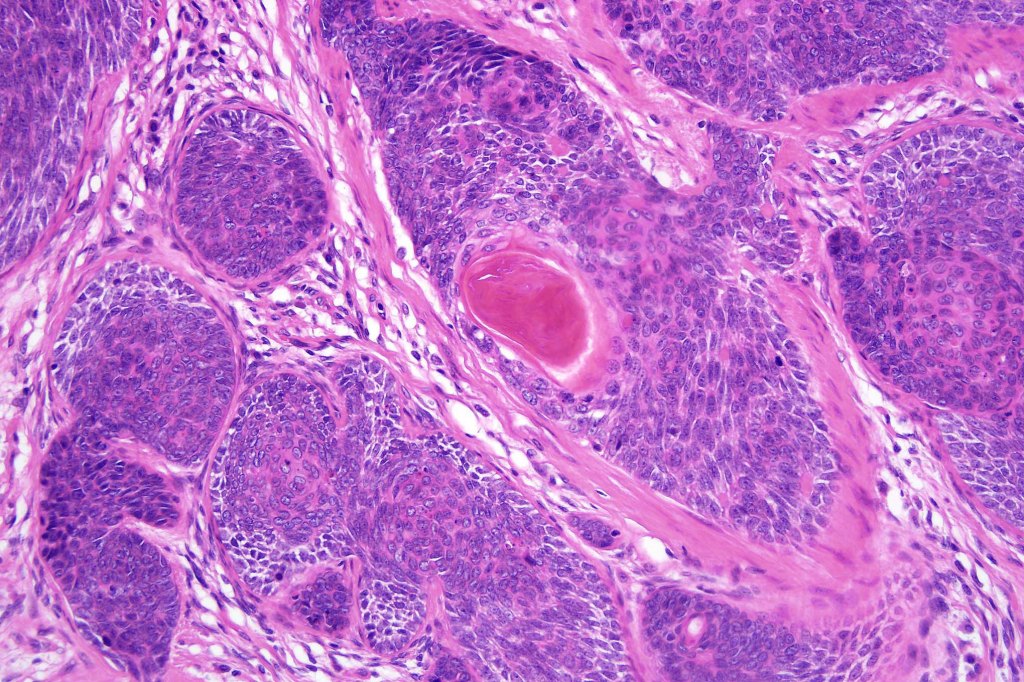
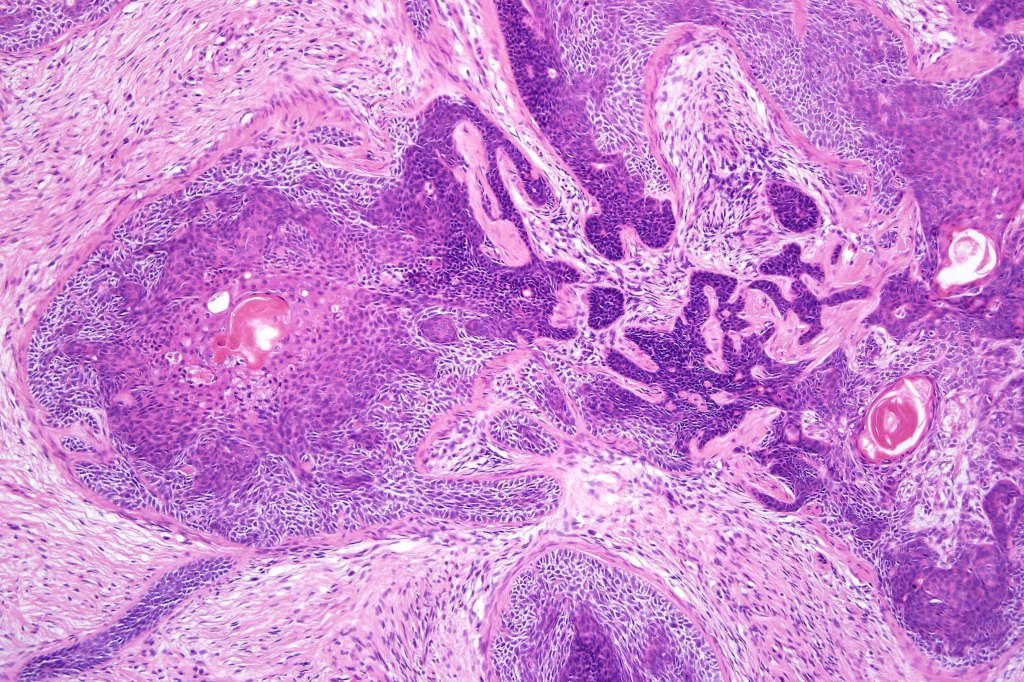
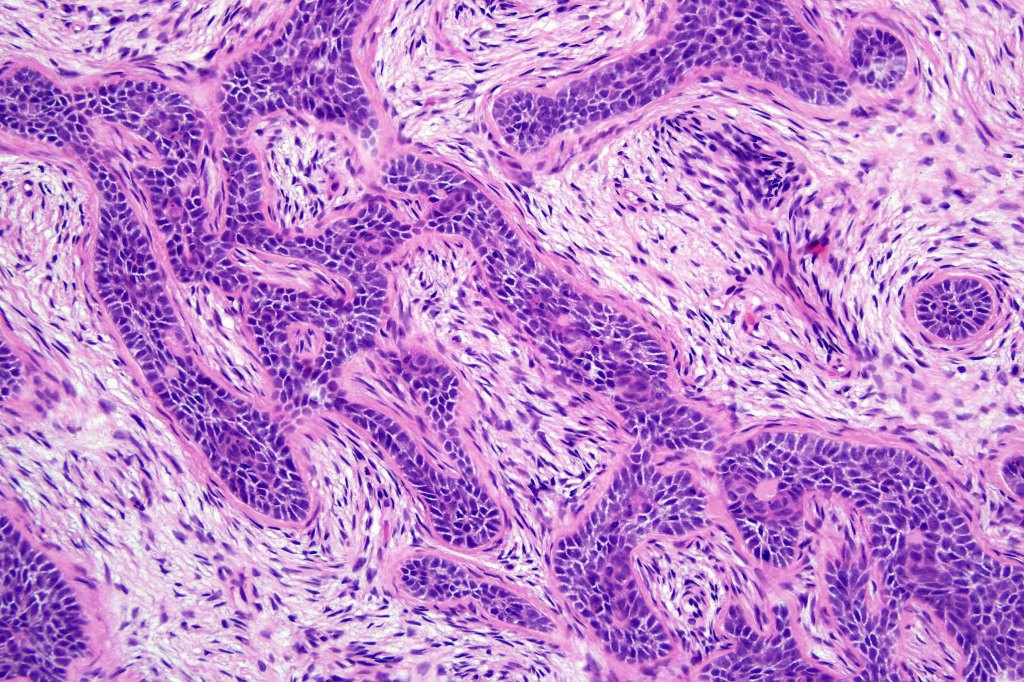
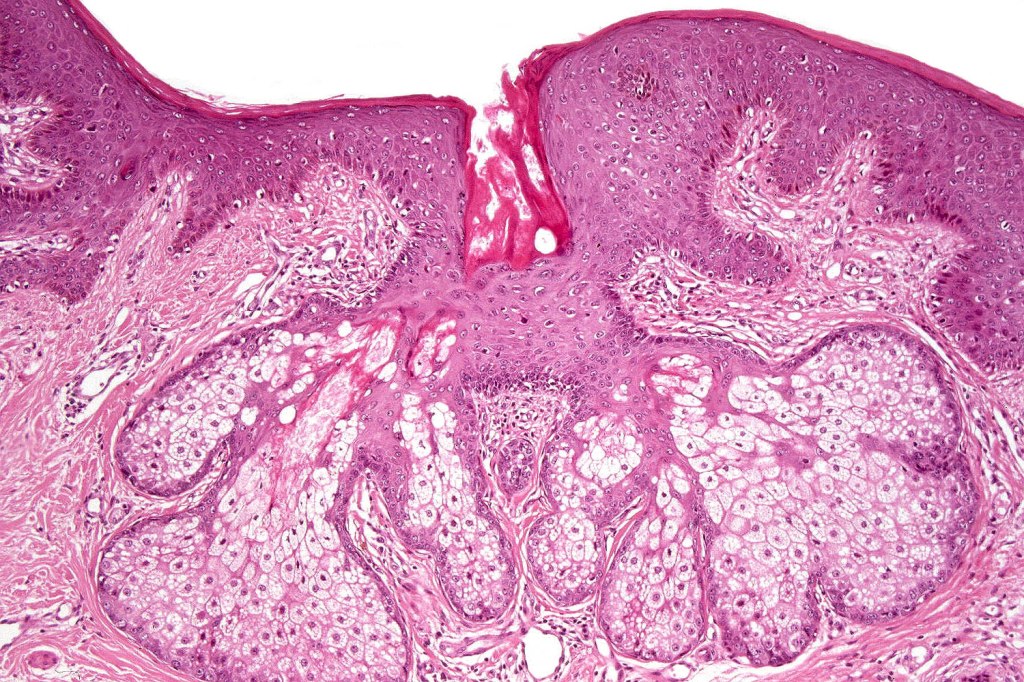
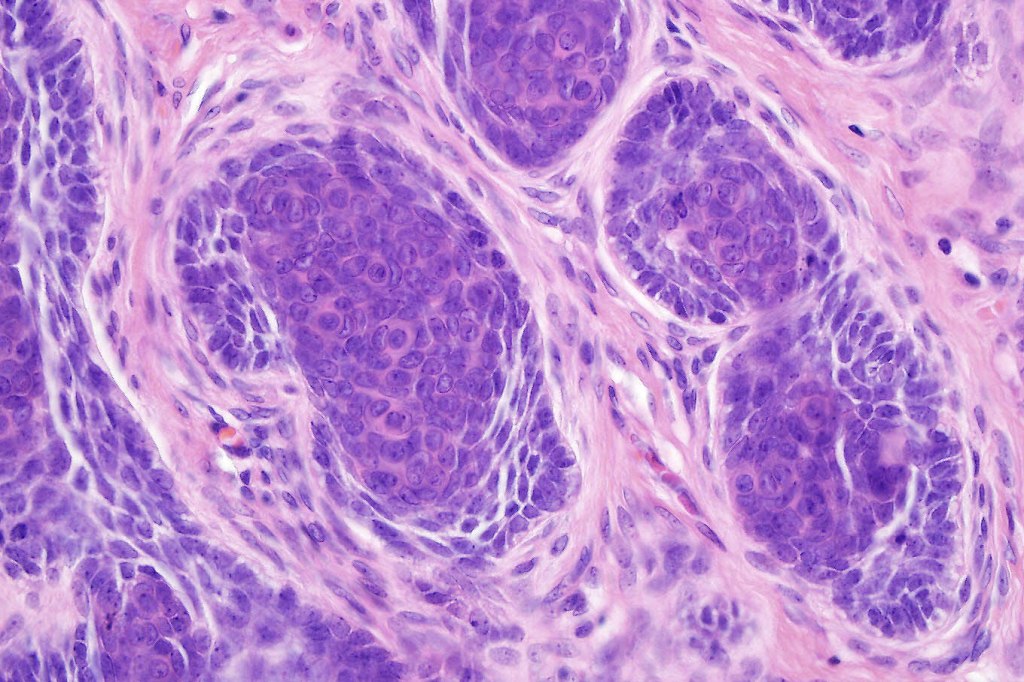
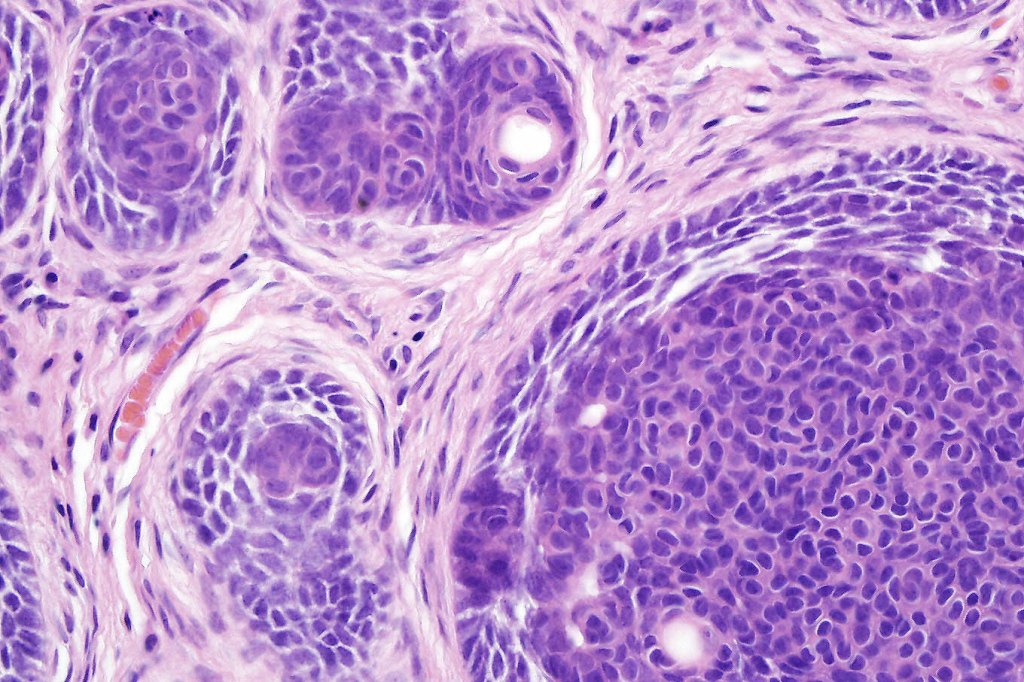
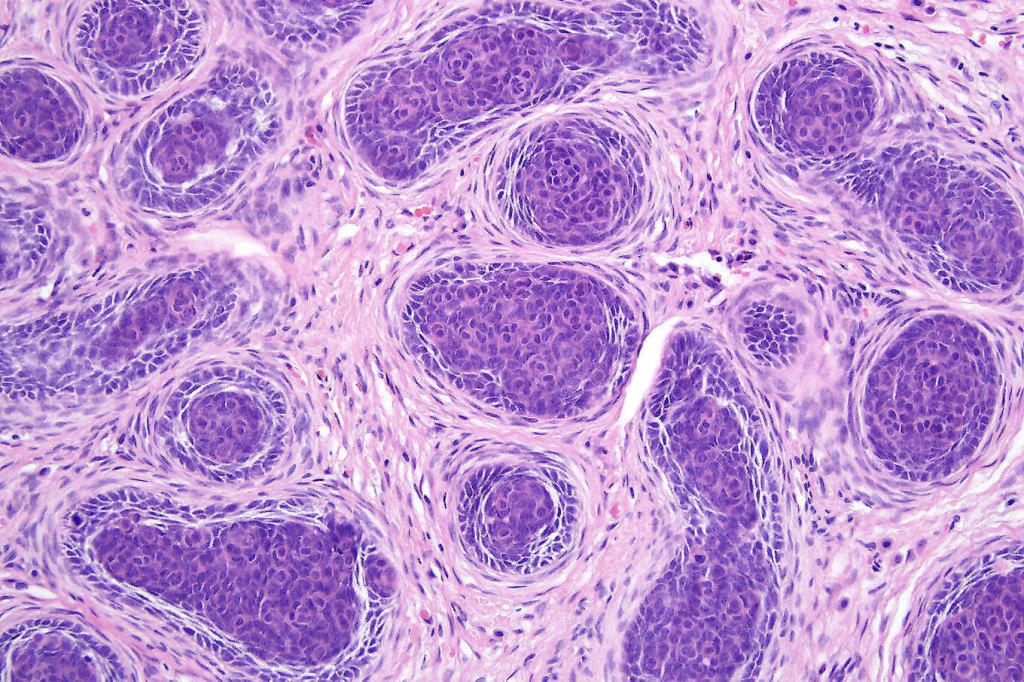
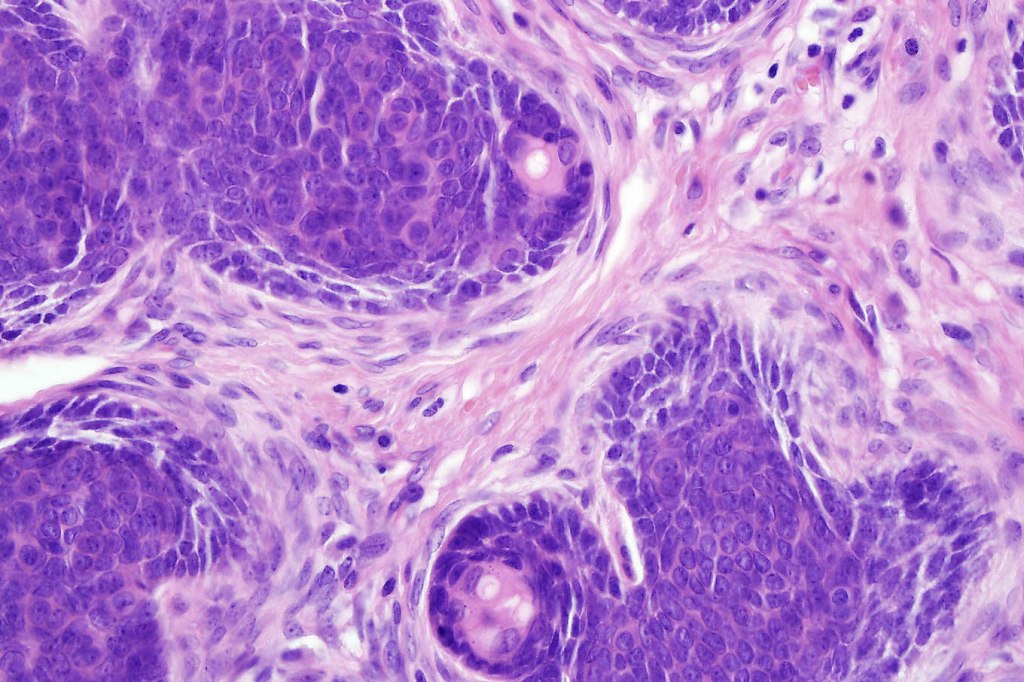
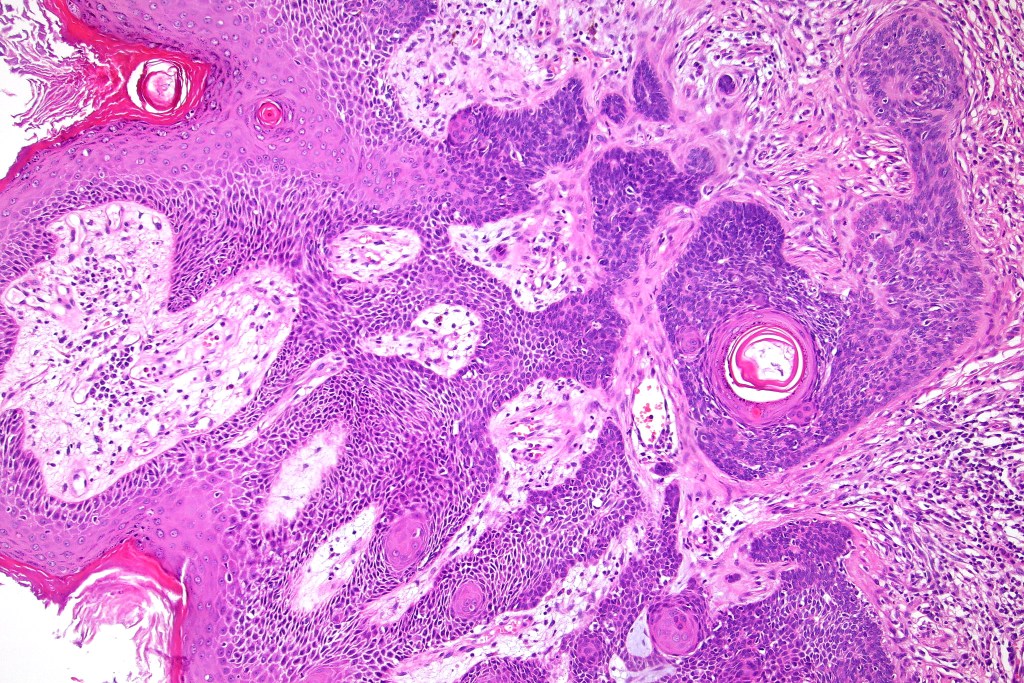
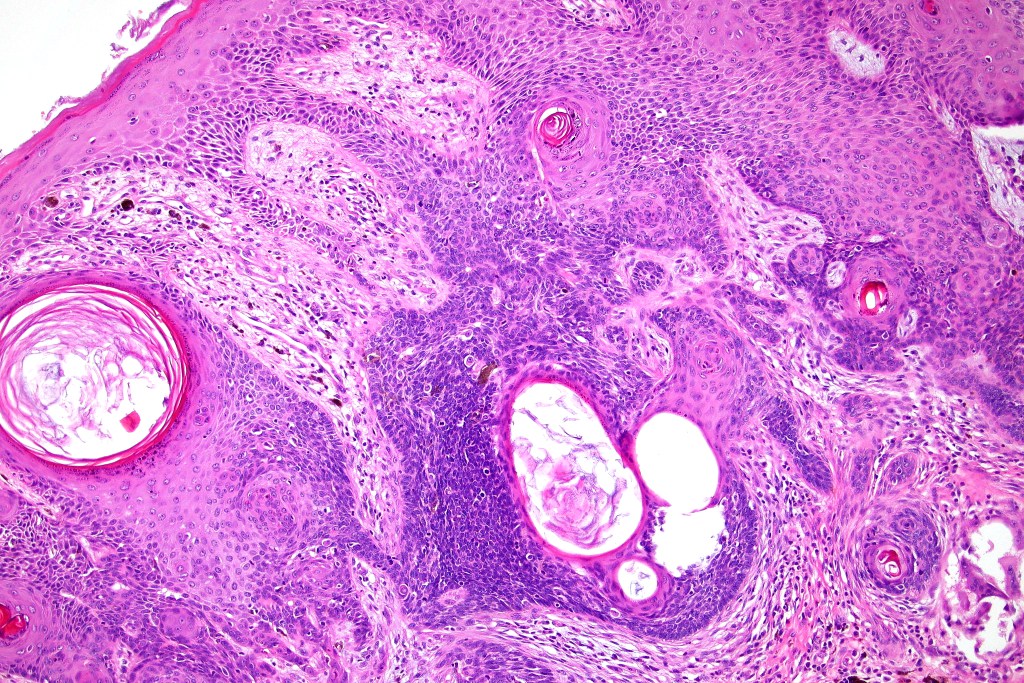
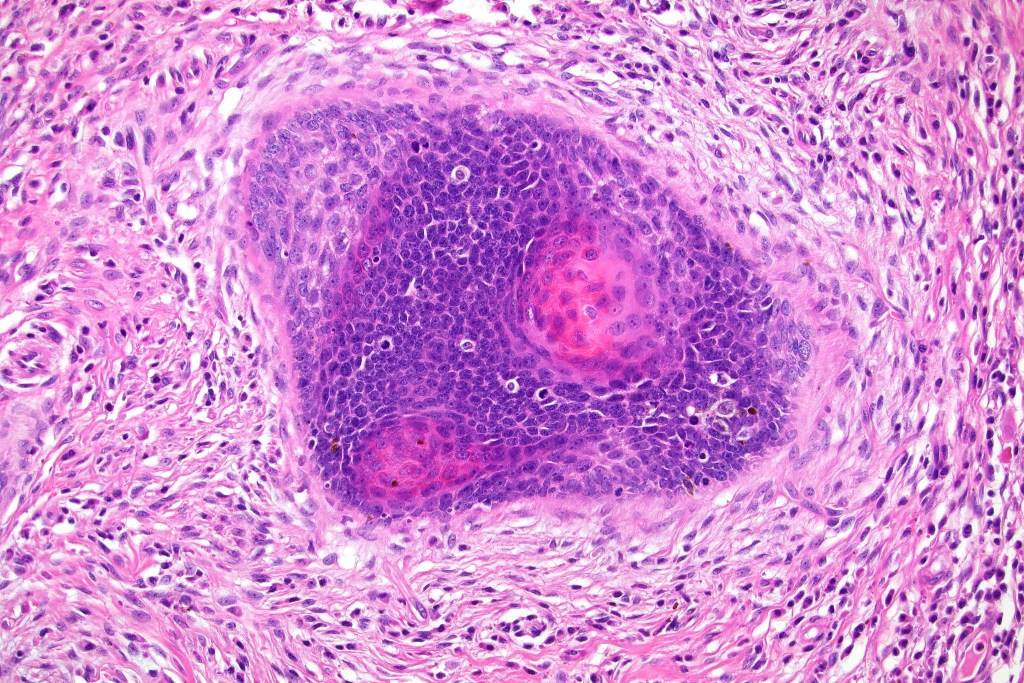
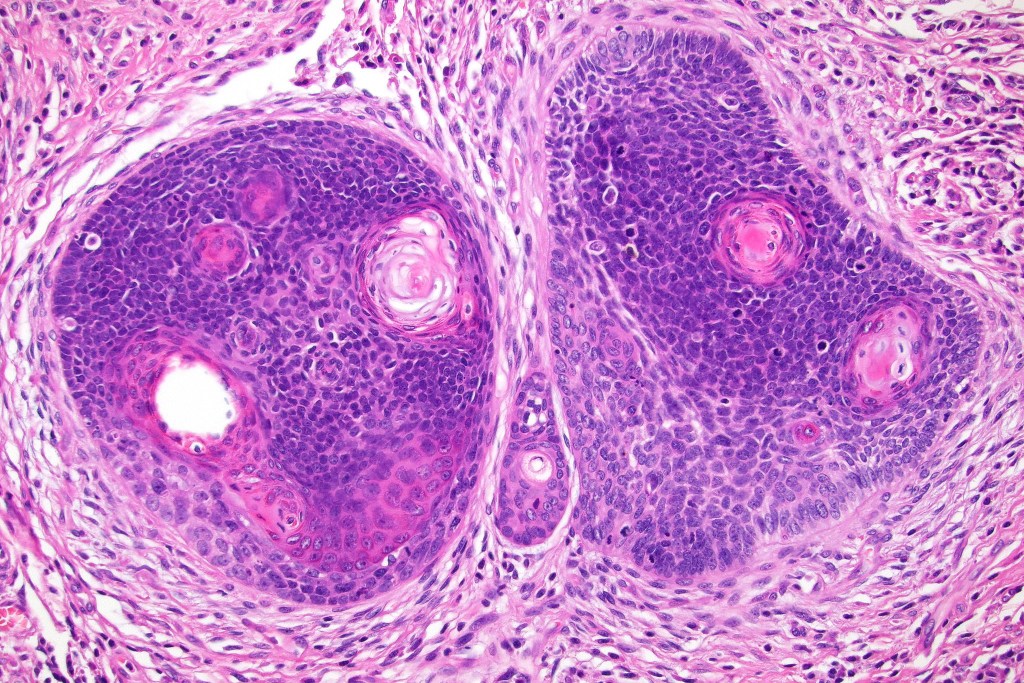
Histological features
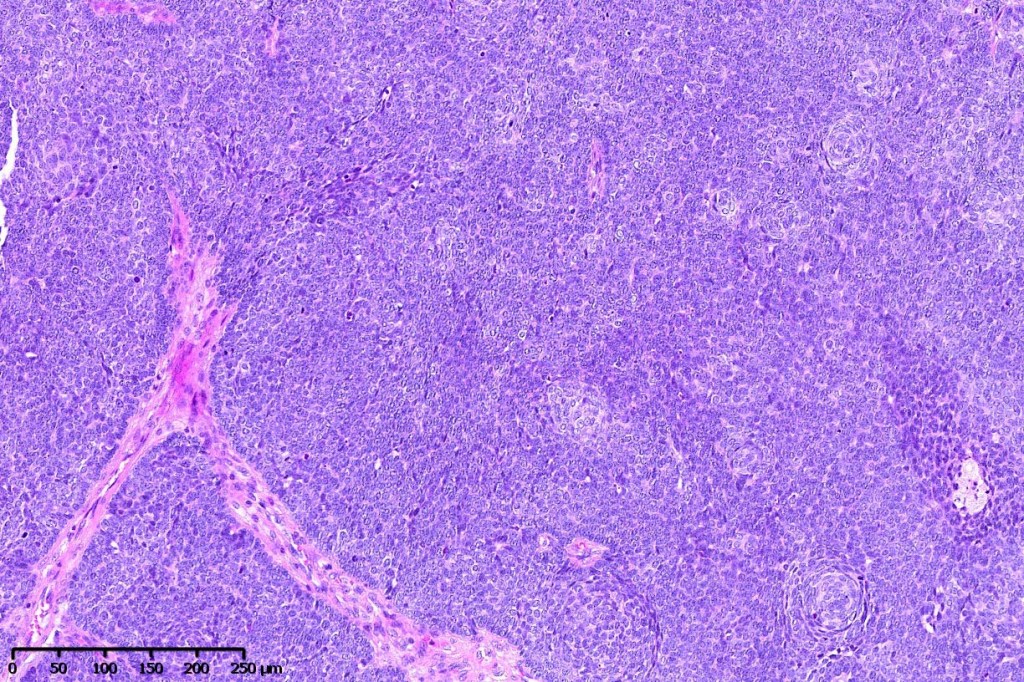
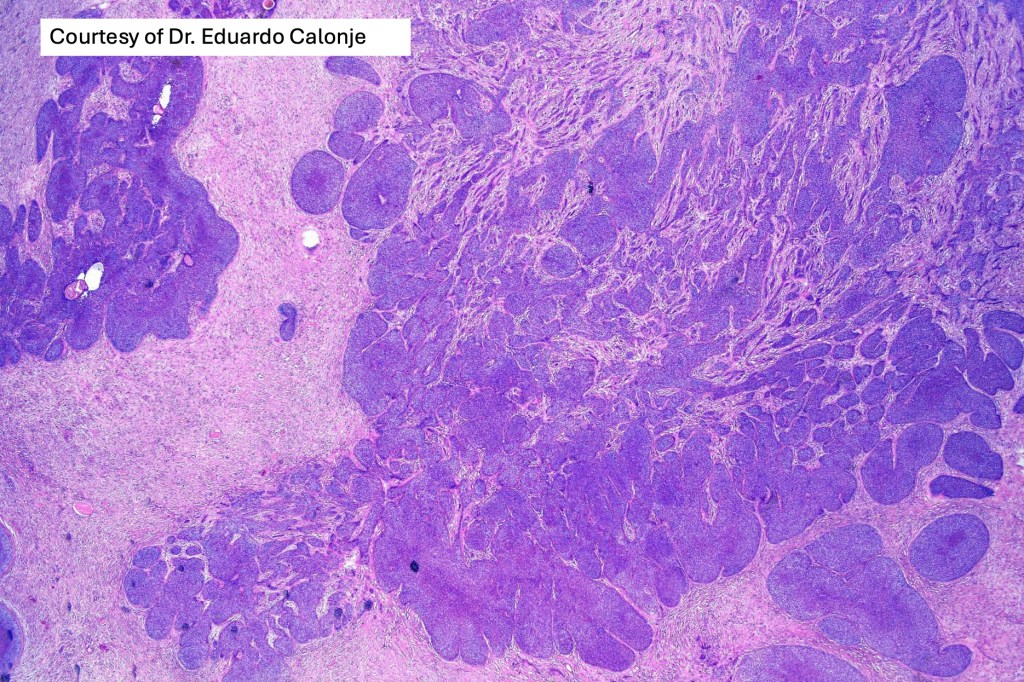
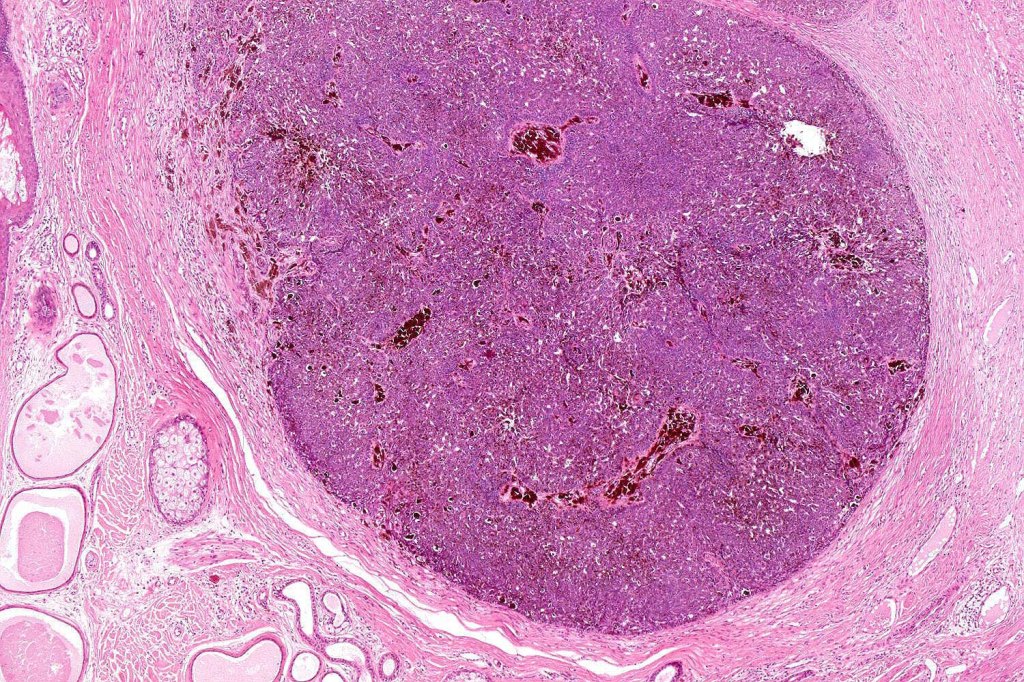
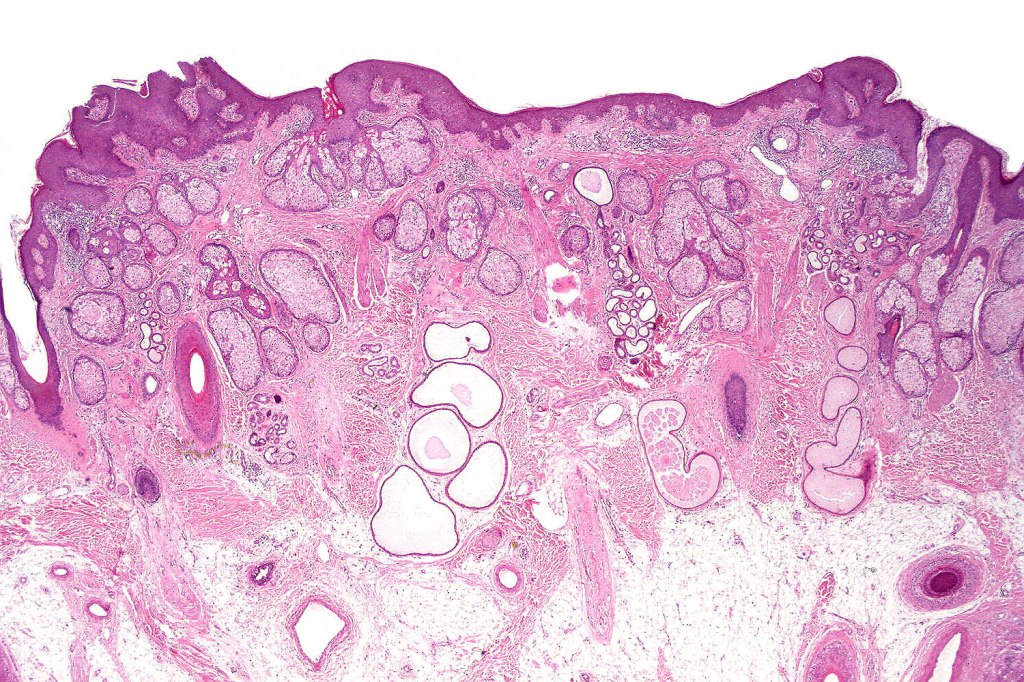
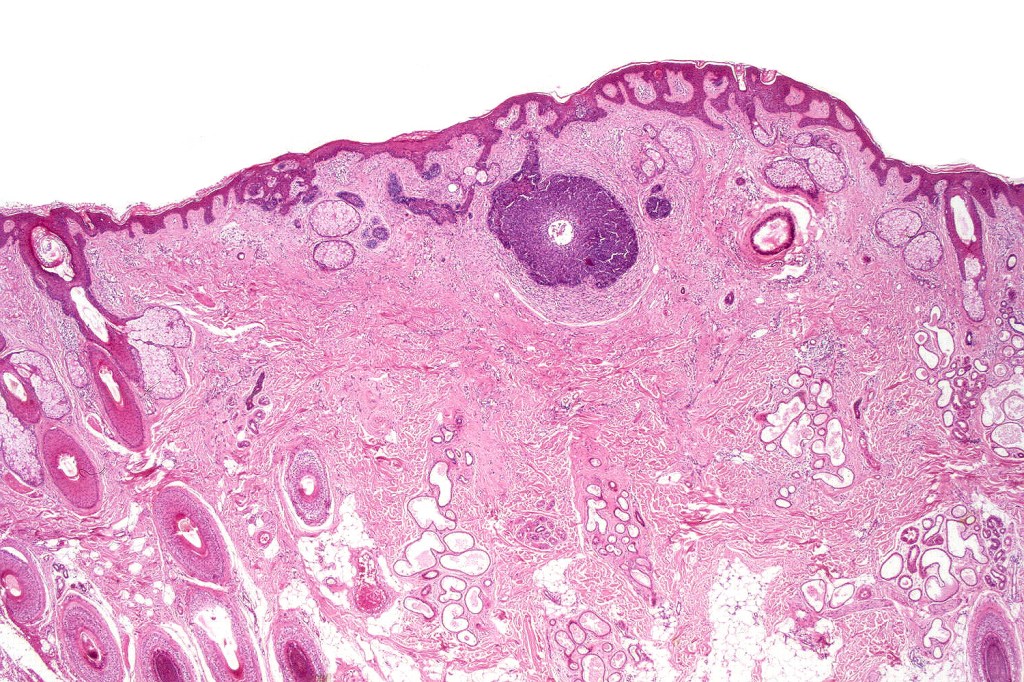
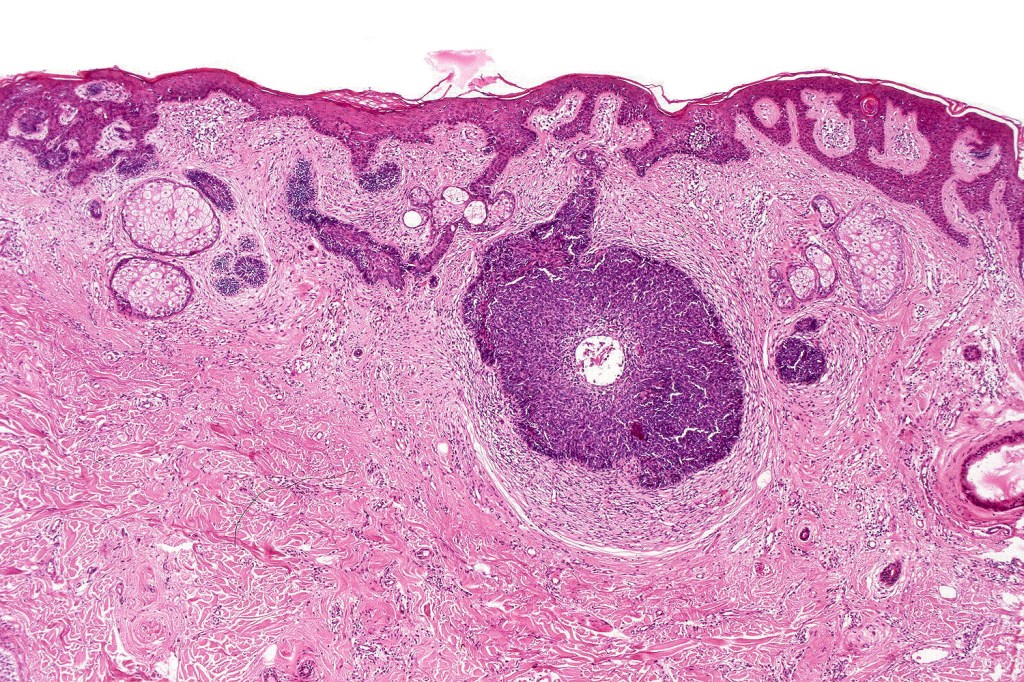
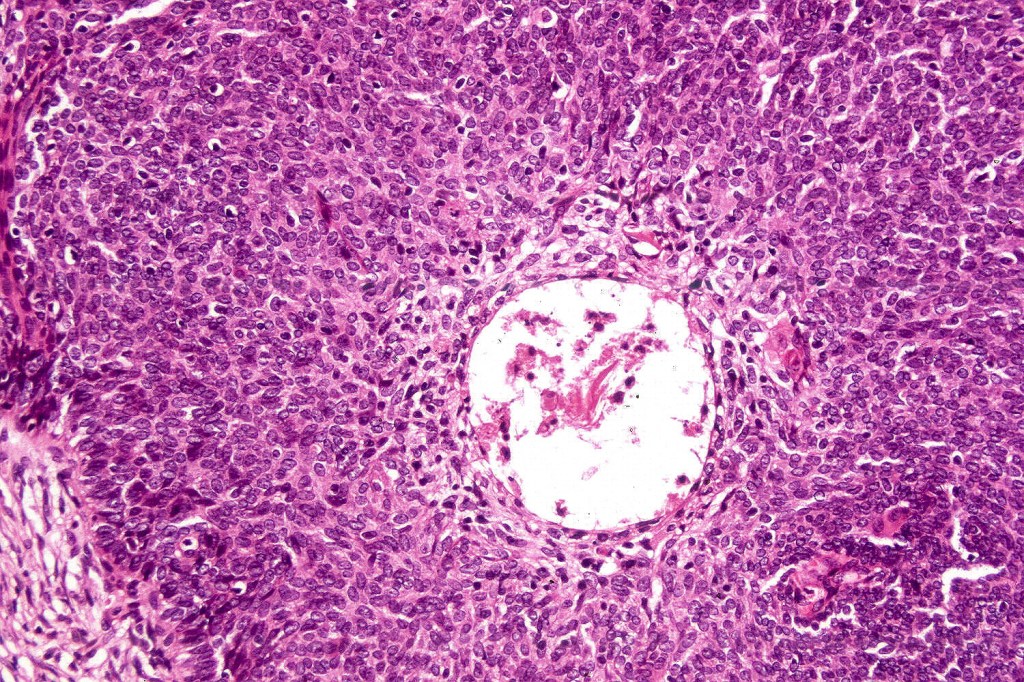
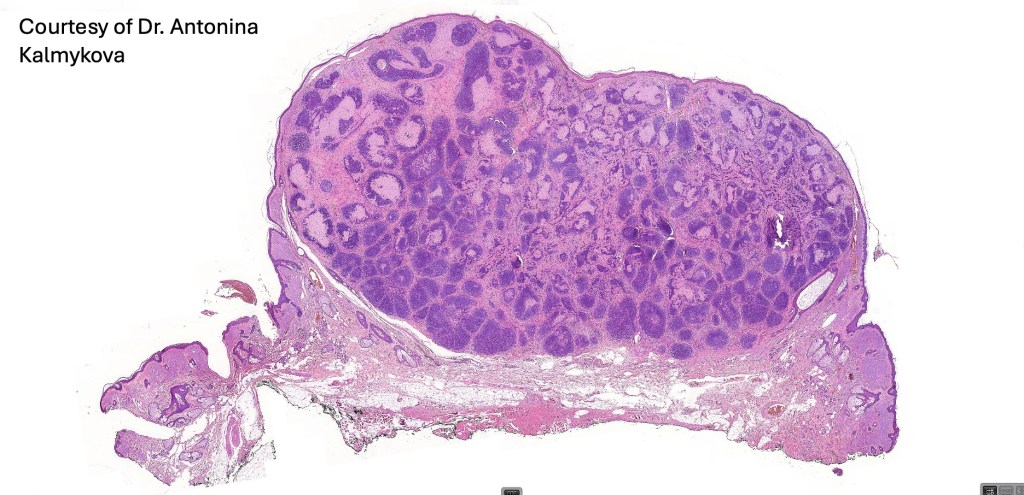
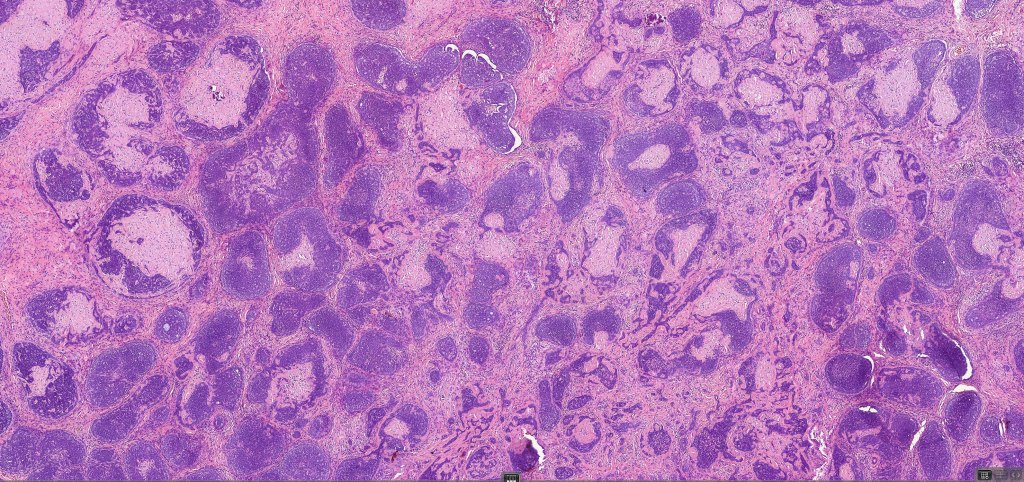
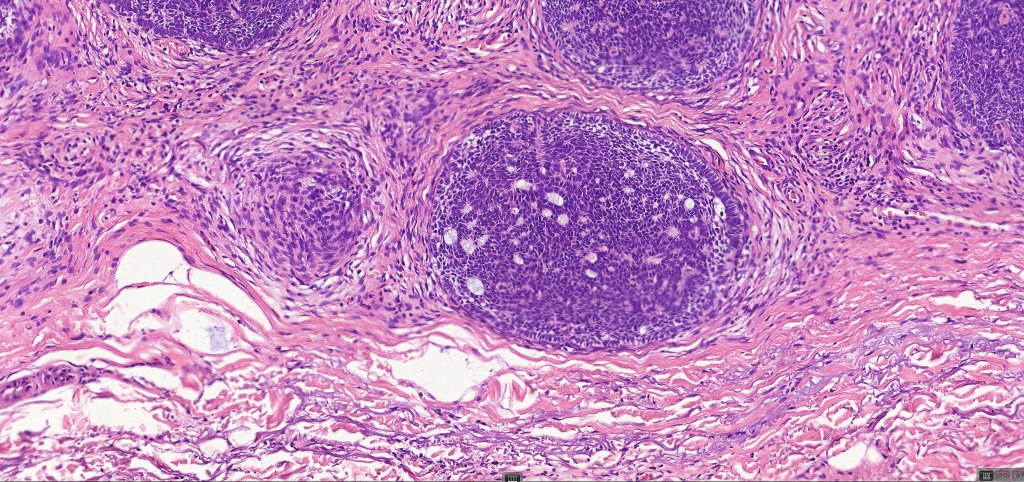
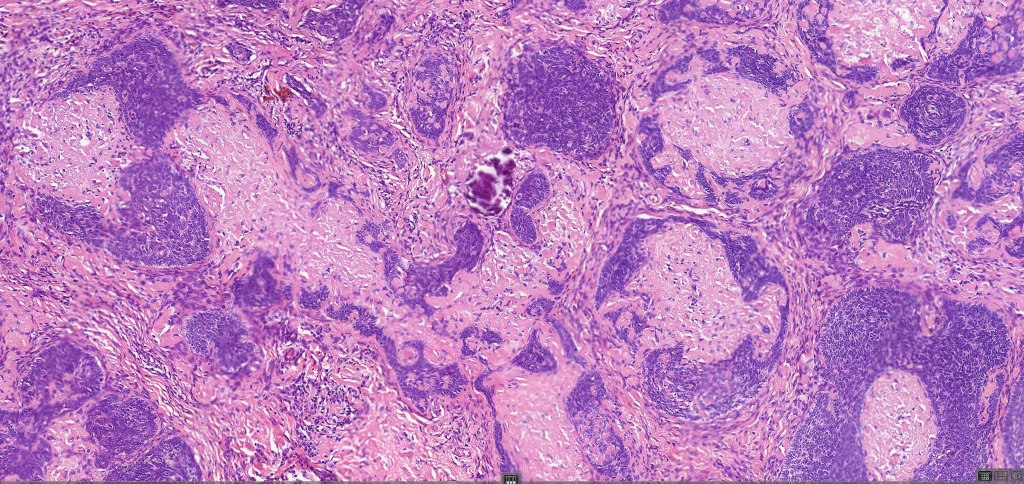
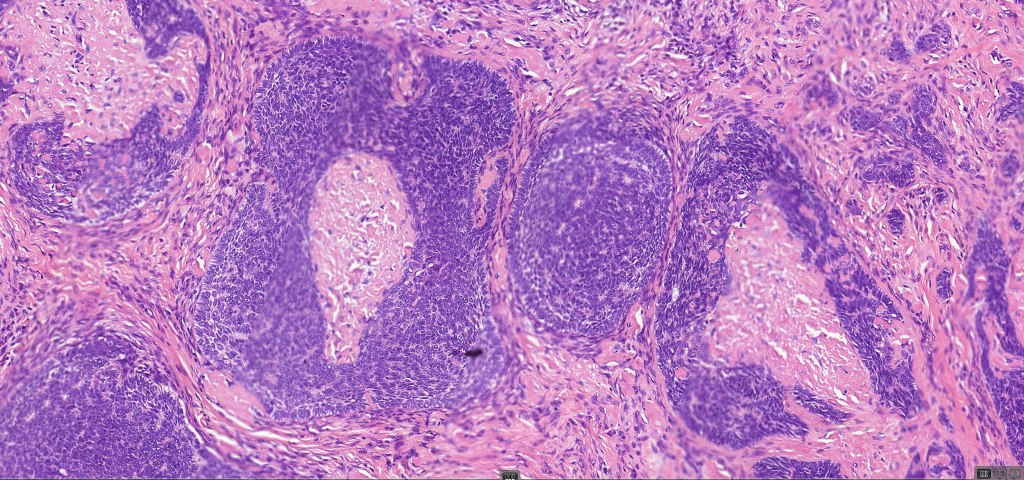
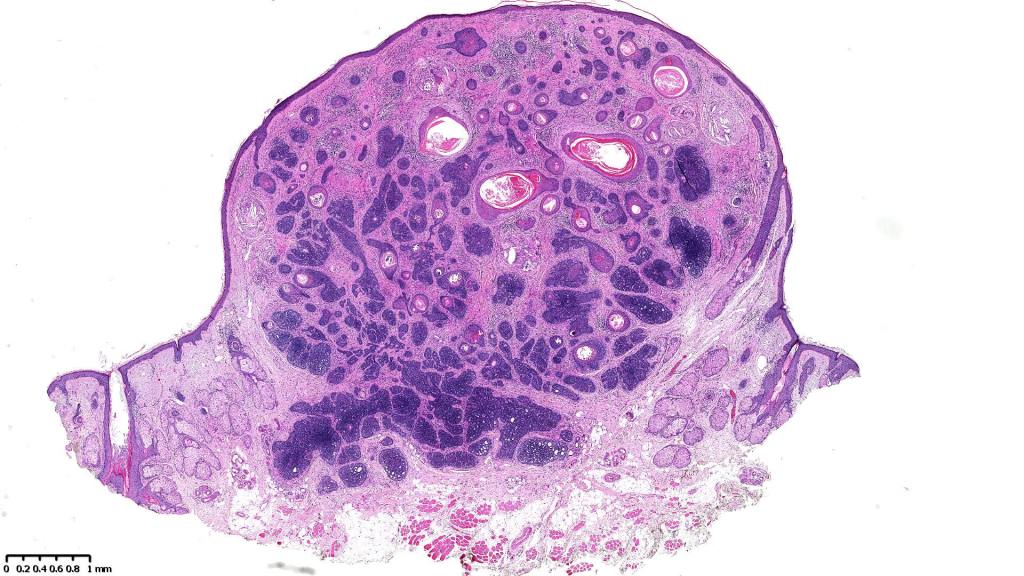
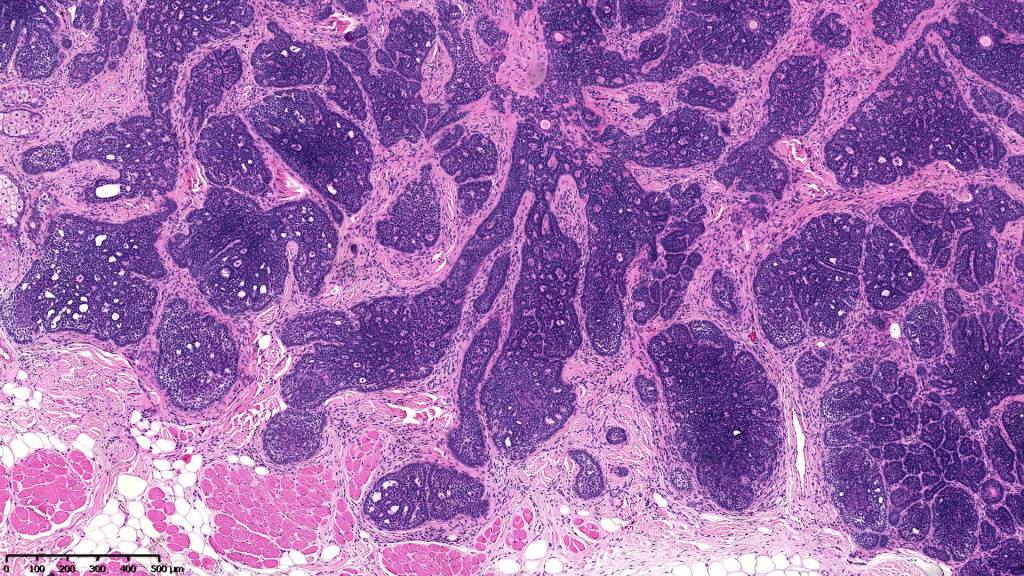
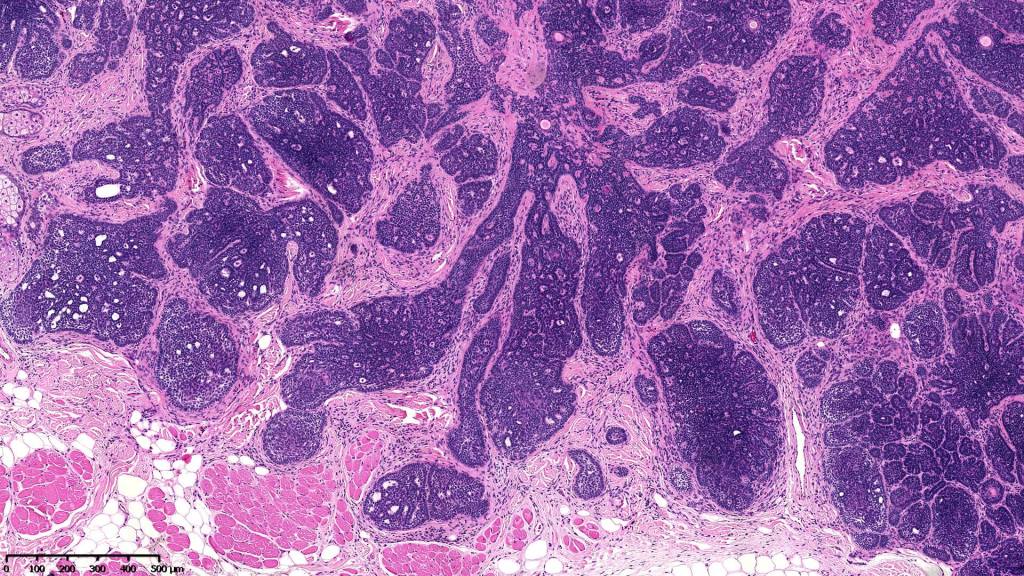
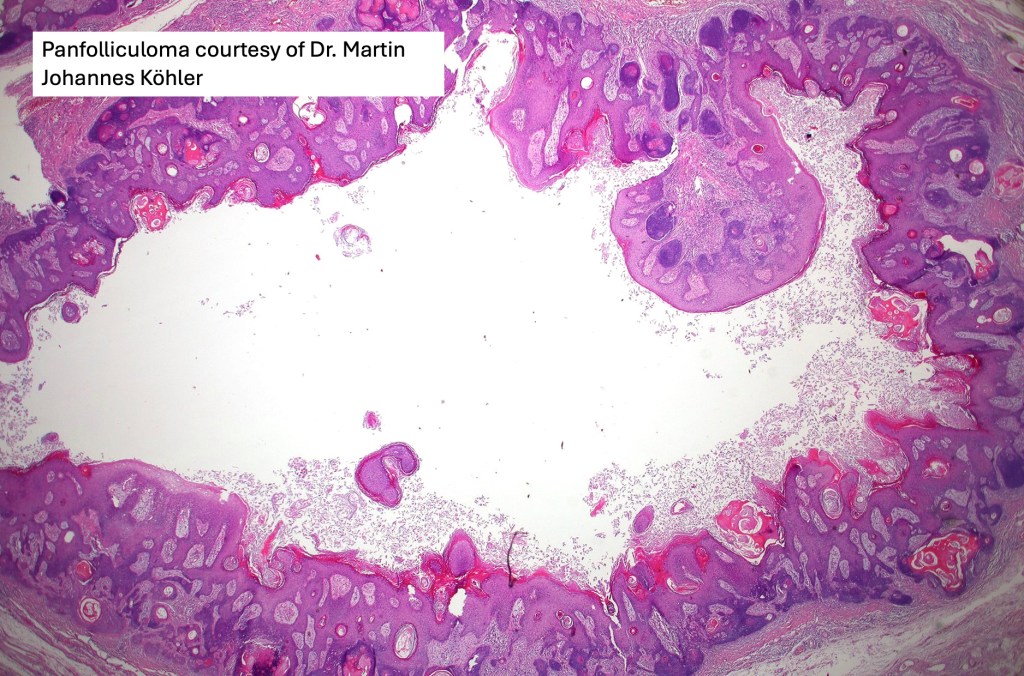
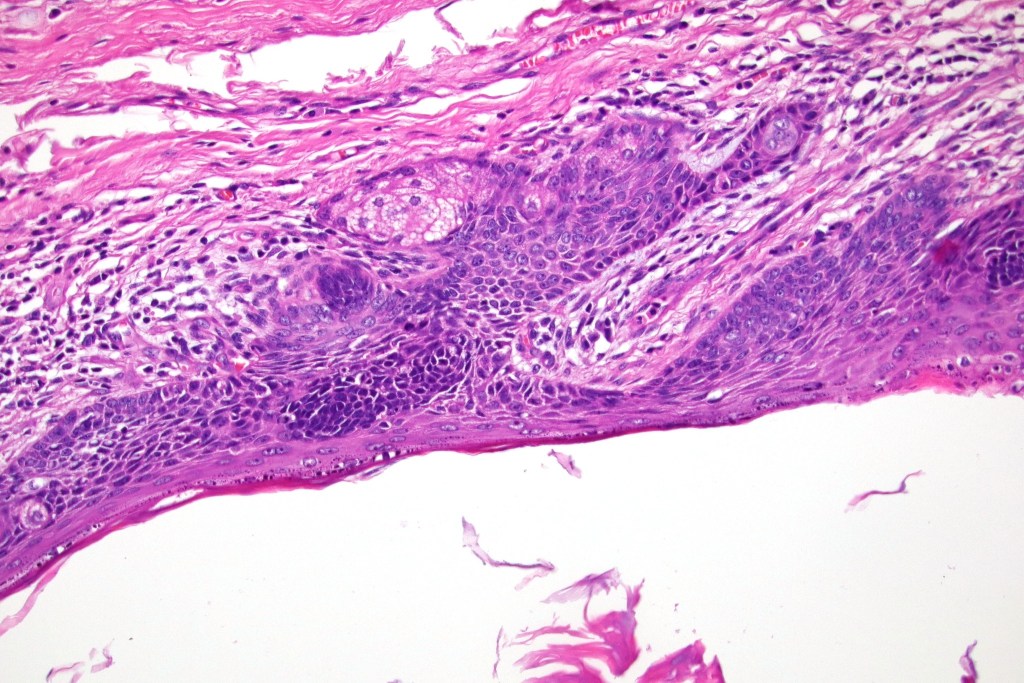
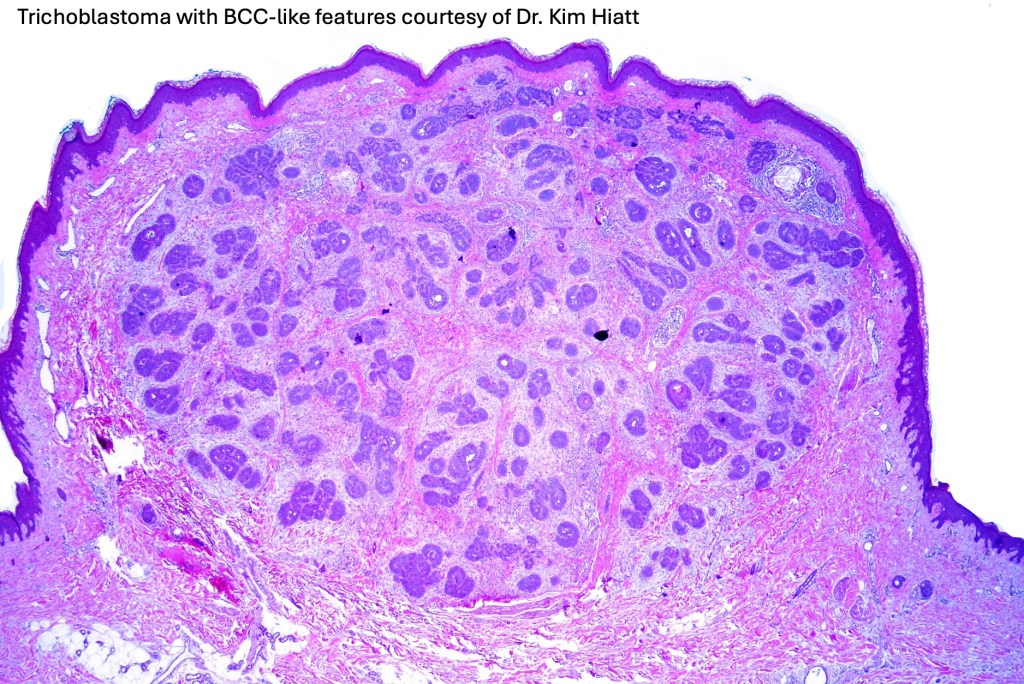
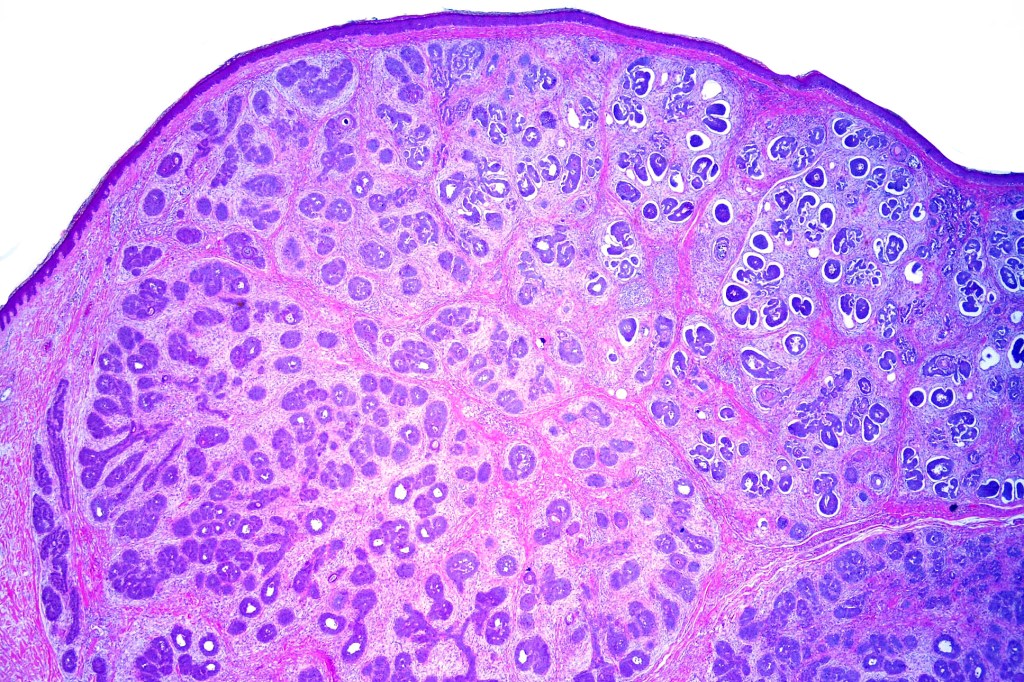
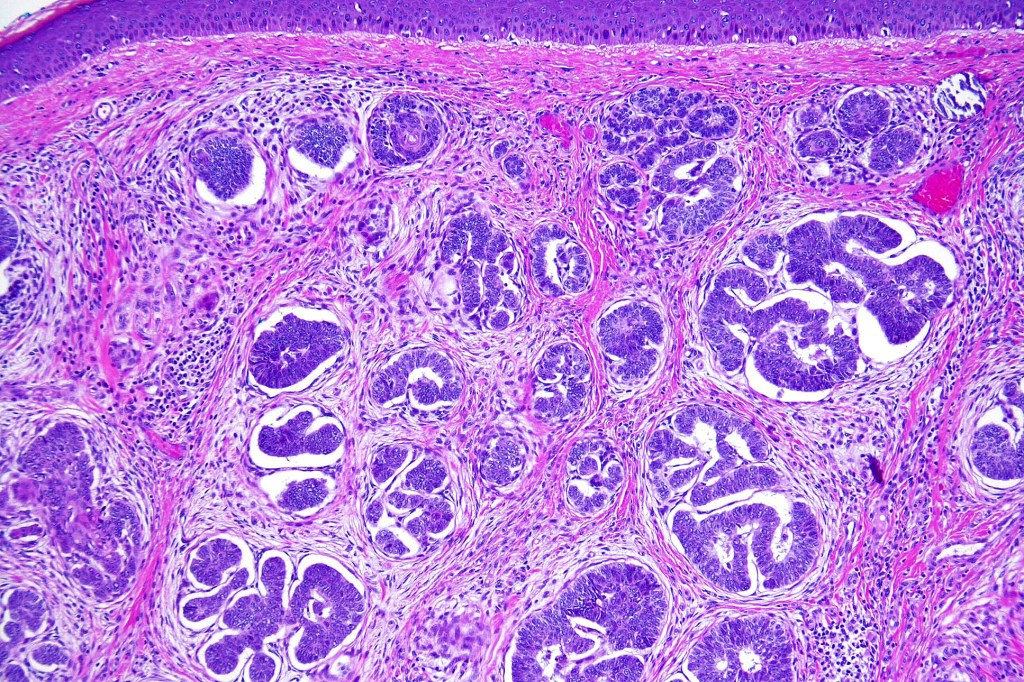
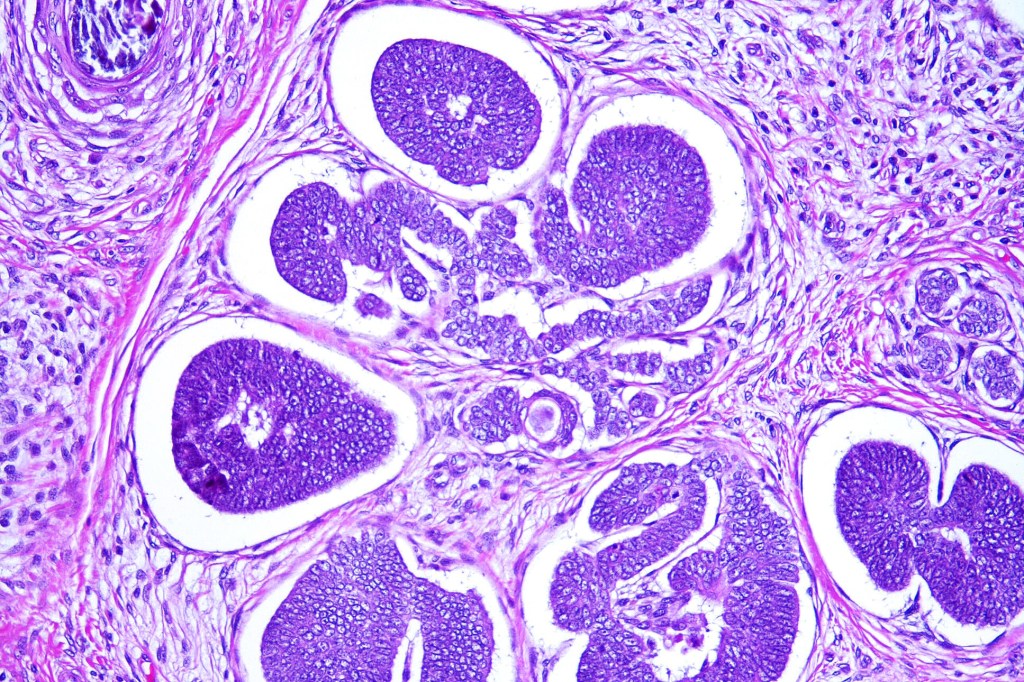
•Sharply circumscribed, unencapsulated nodule in deep dermis +/- subcutaneous fat or deeper (trichoepithelioma is much more superficial)
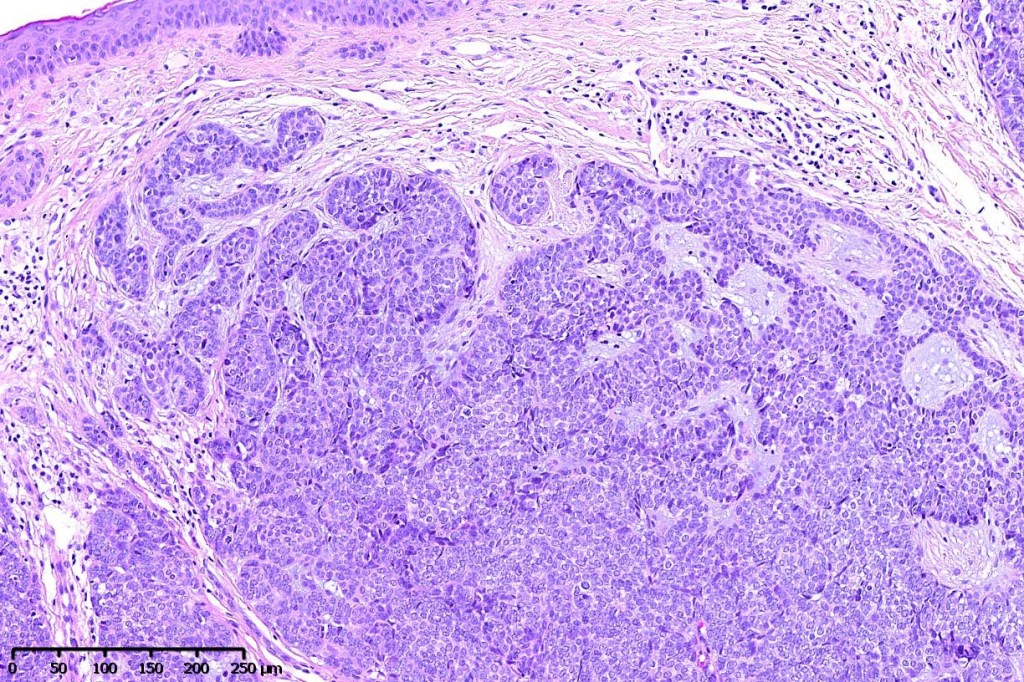
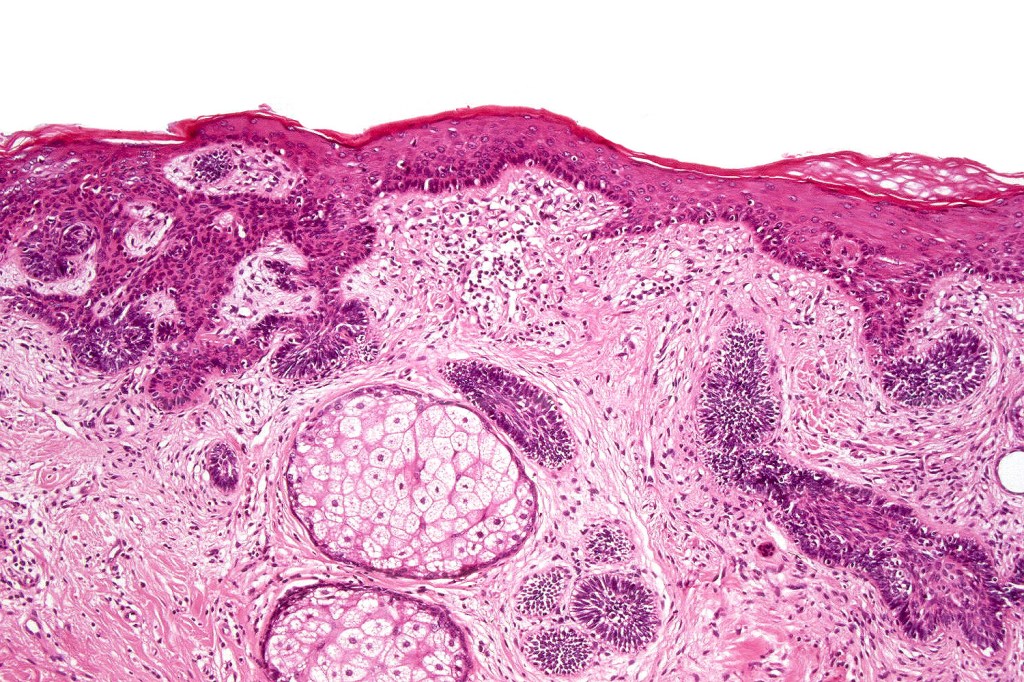
•Although many authors state that an epidermal origin/connection is not a feature of trichoblastoma, my own experience is that this can often be present particularly in those examples where a superficial dermal component is present in addition to the deep dermal/subcutaneous element
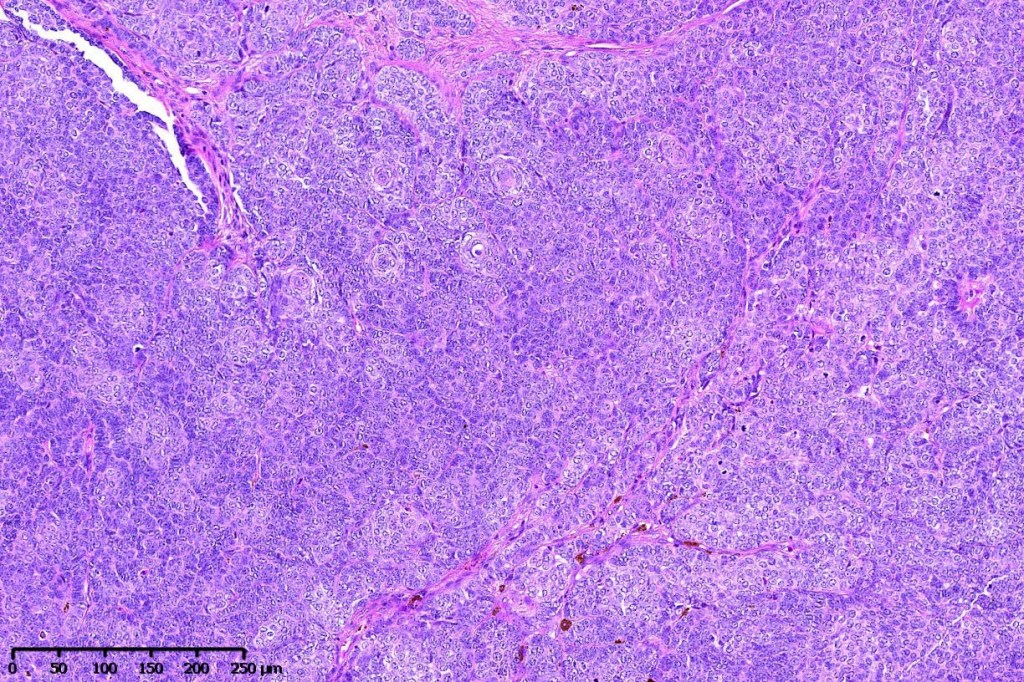
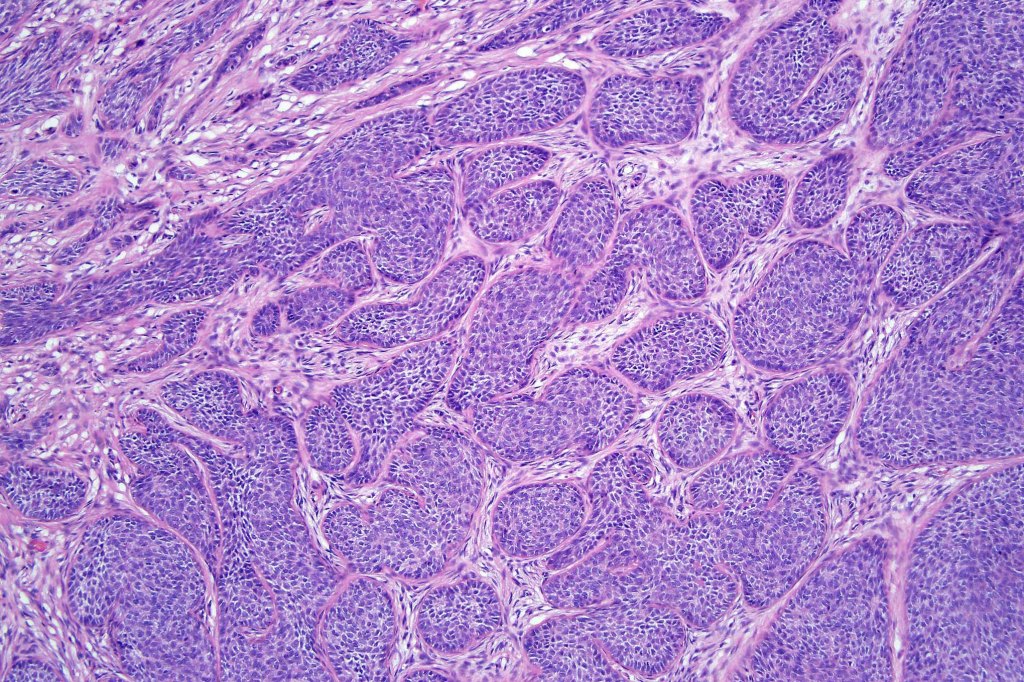
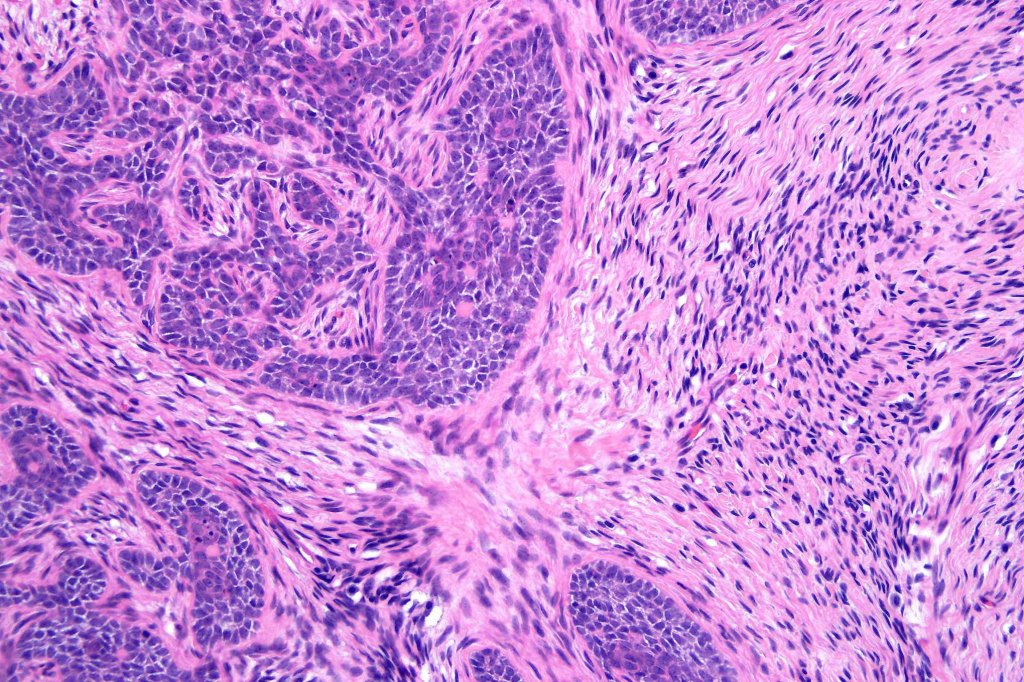
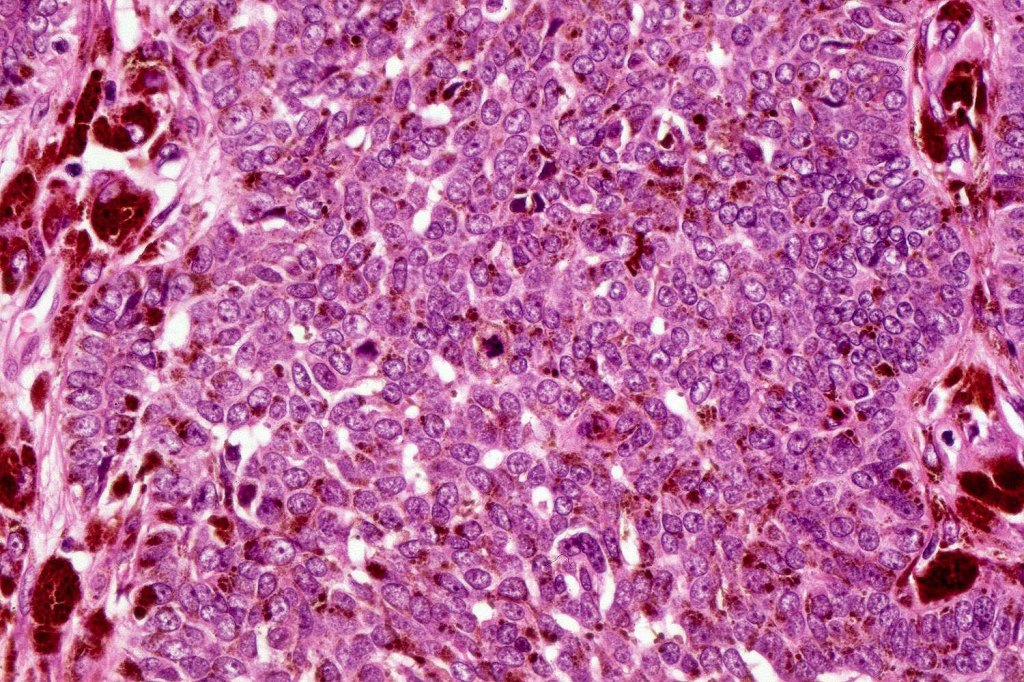
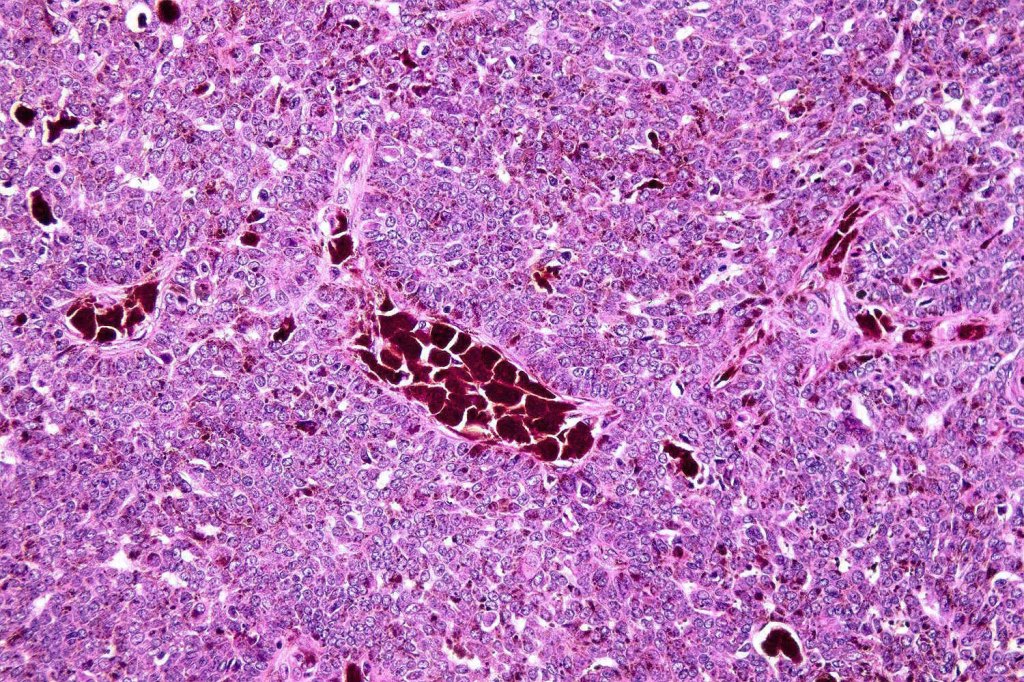
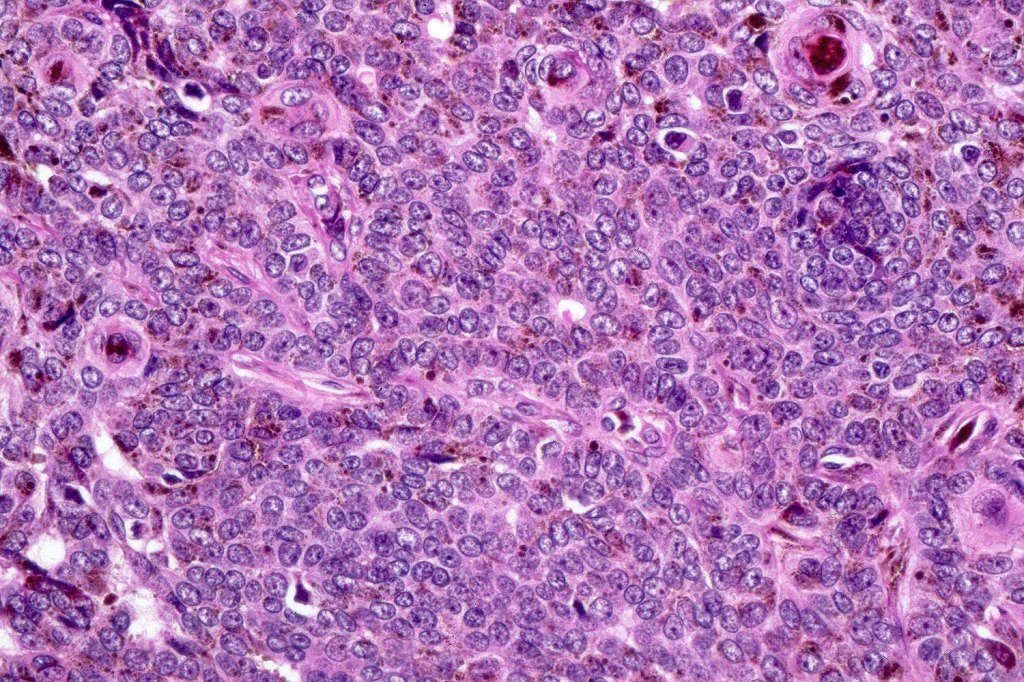
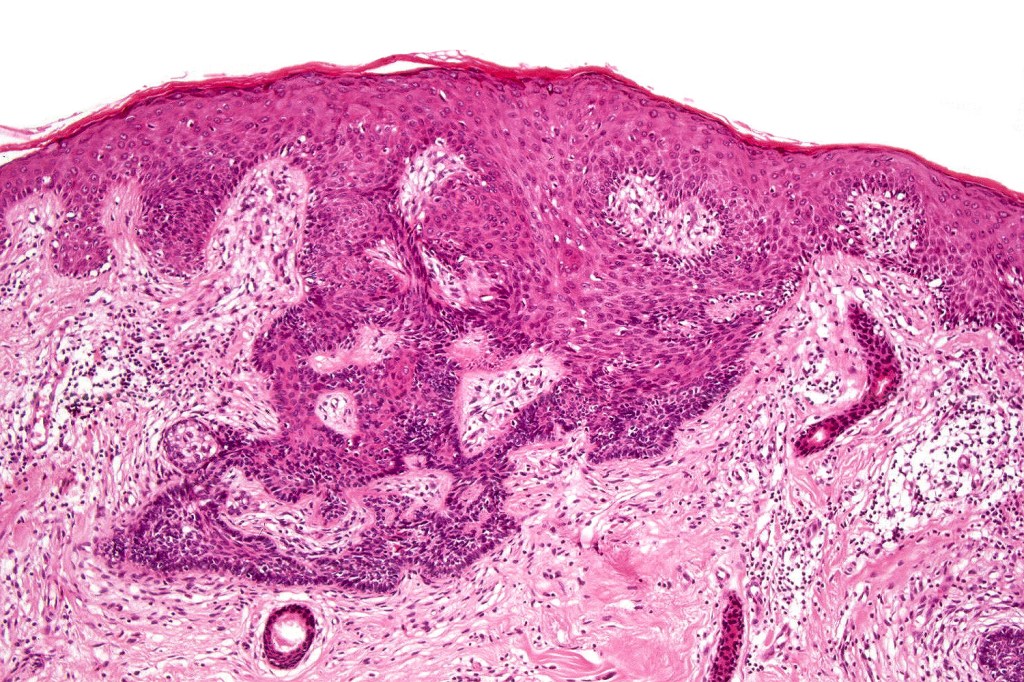
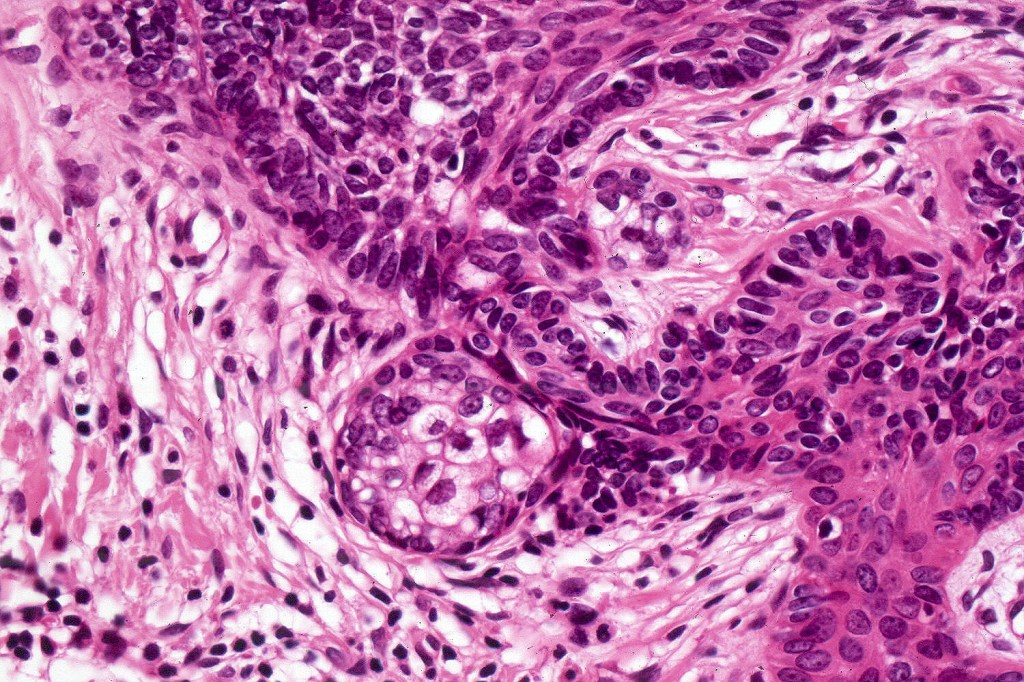
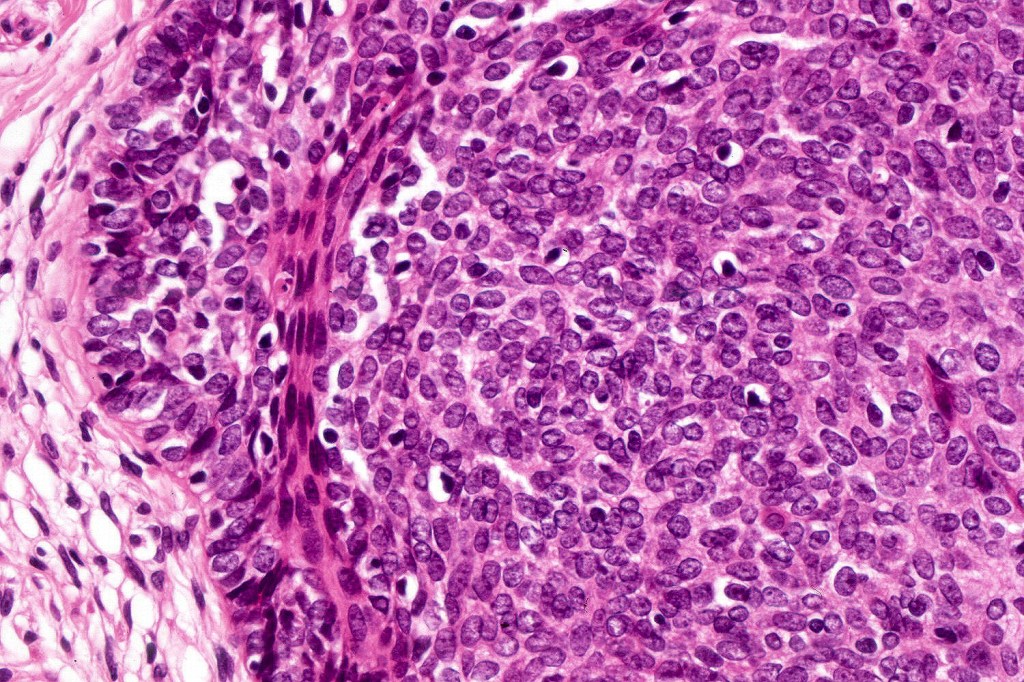
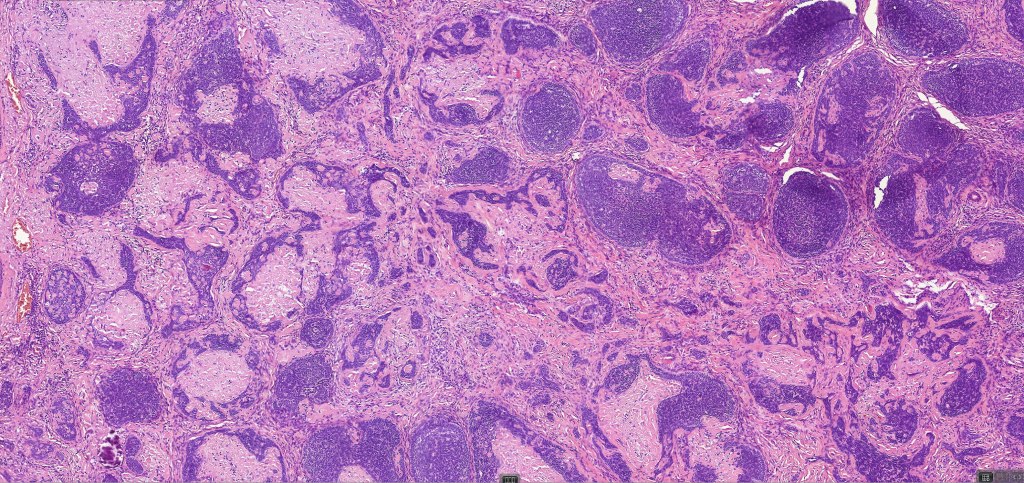
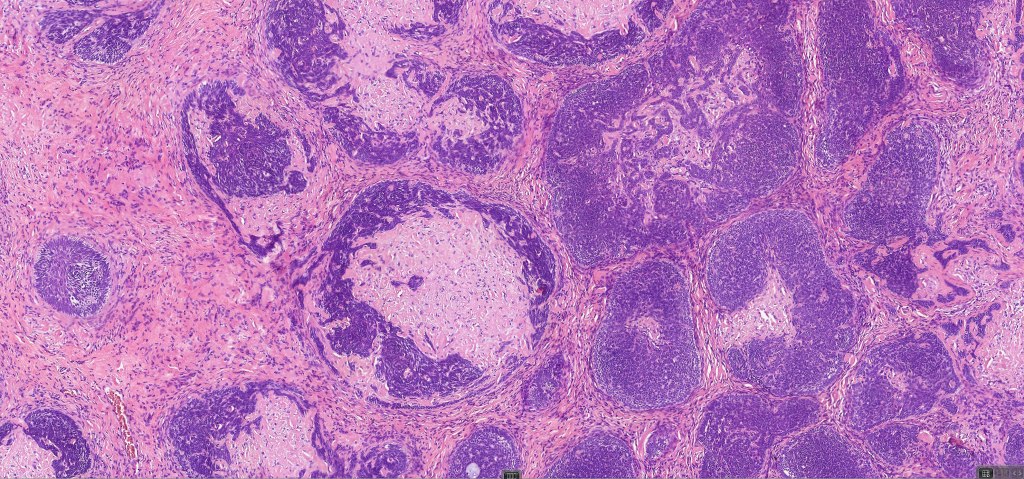
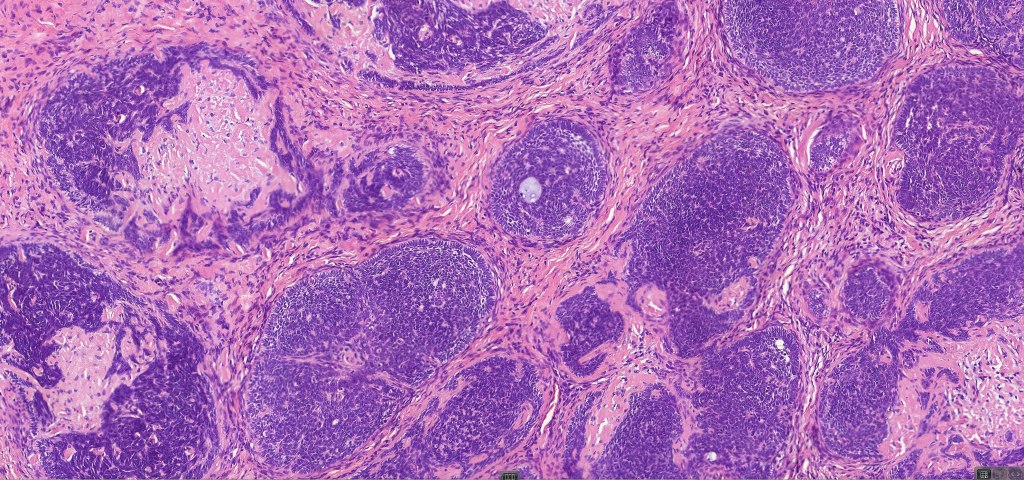
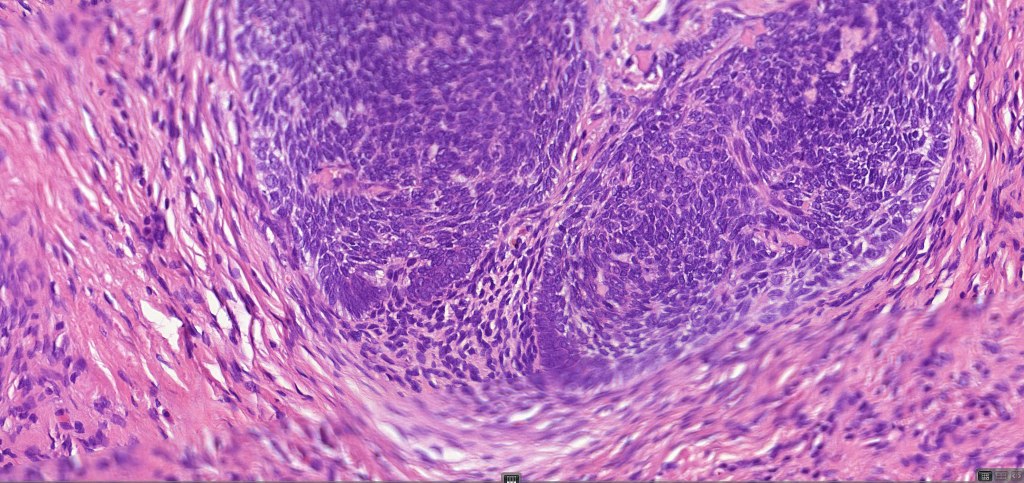
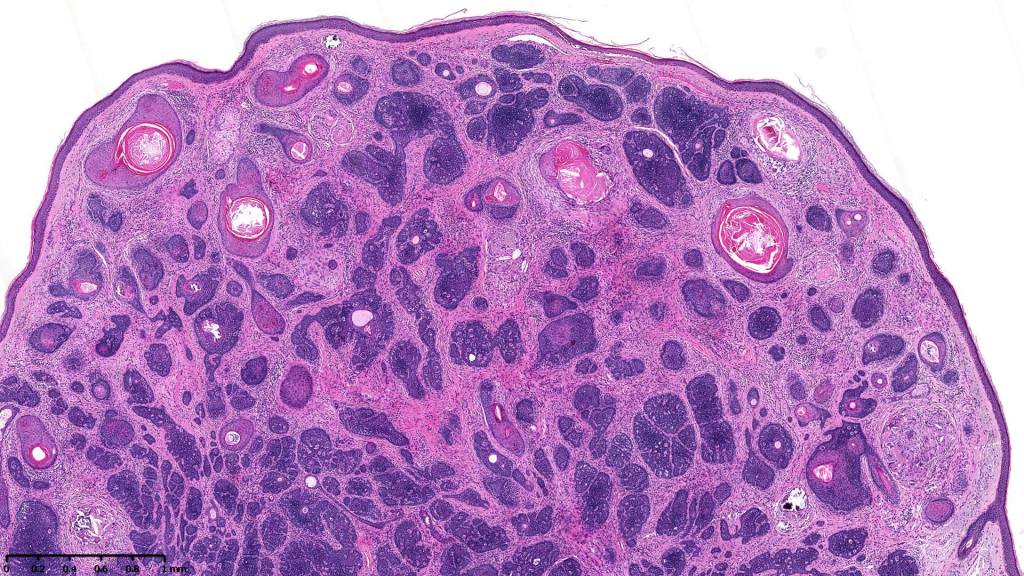
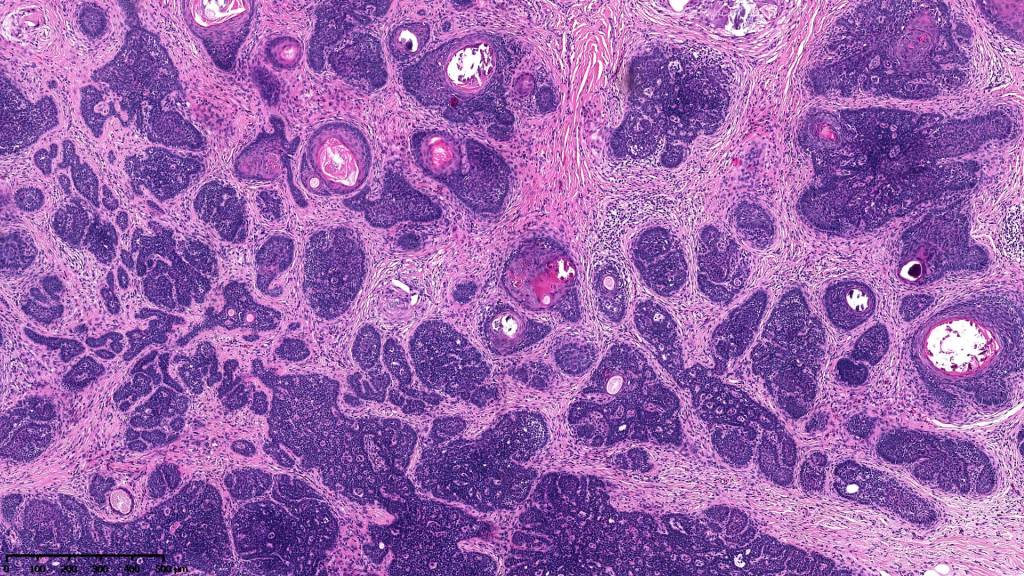
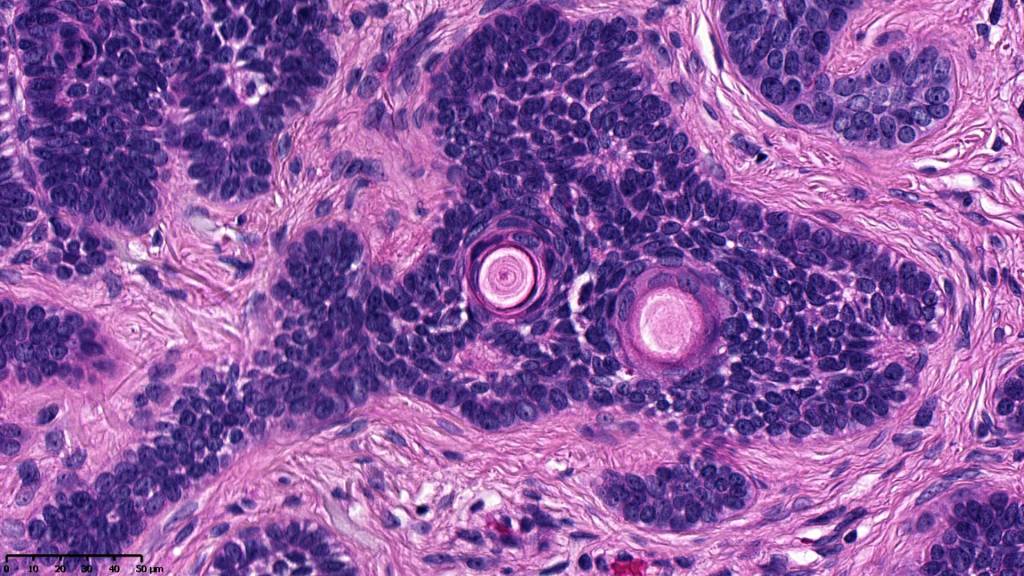
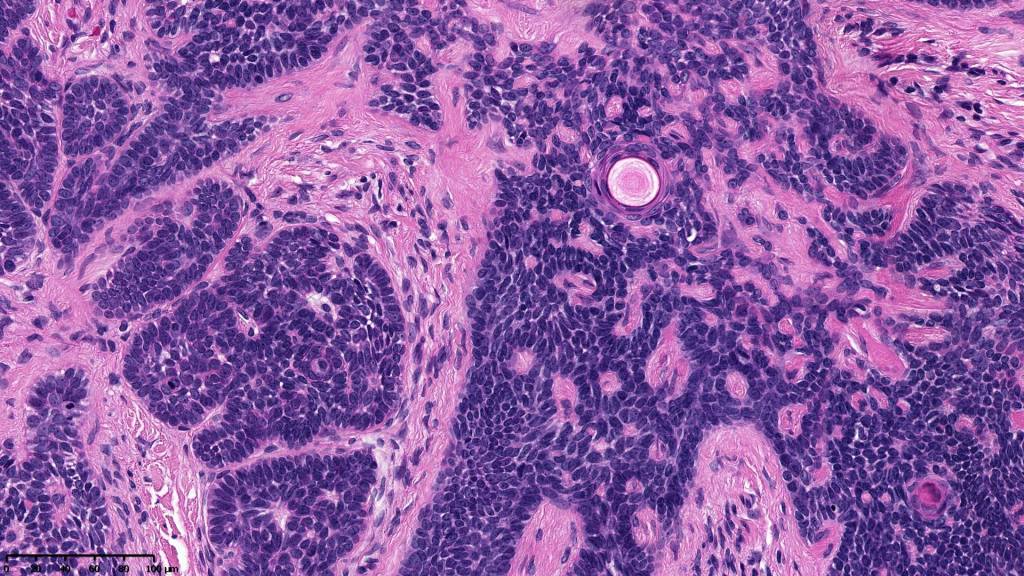
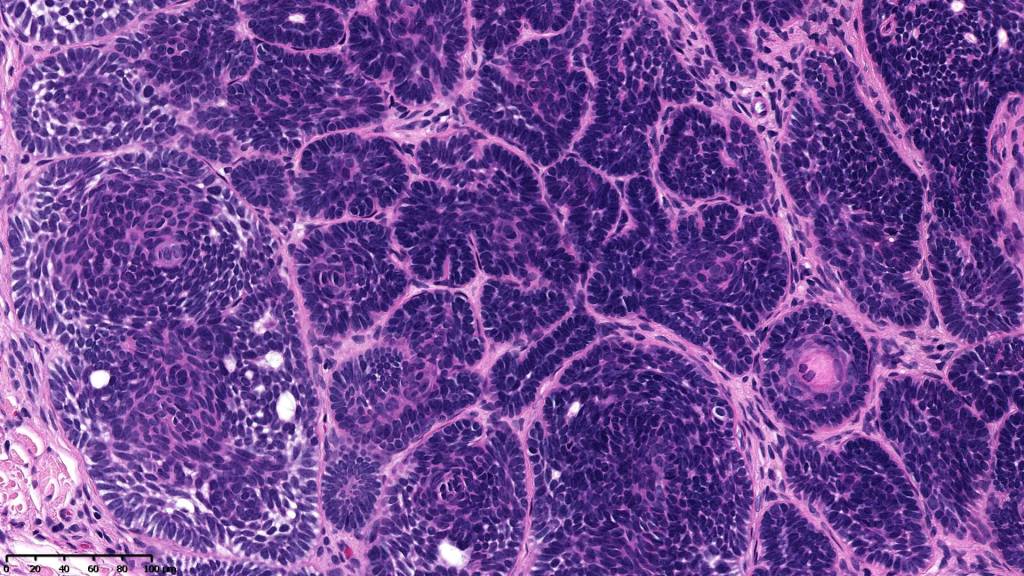
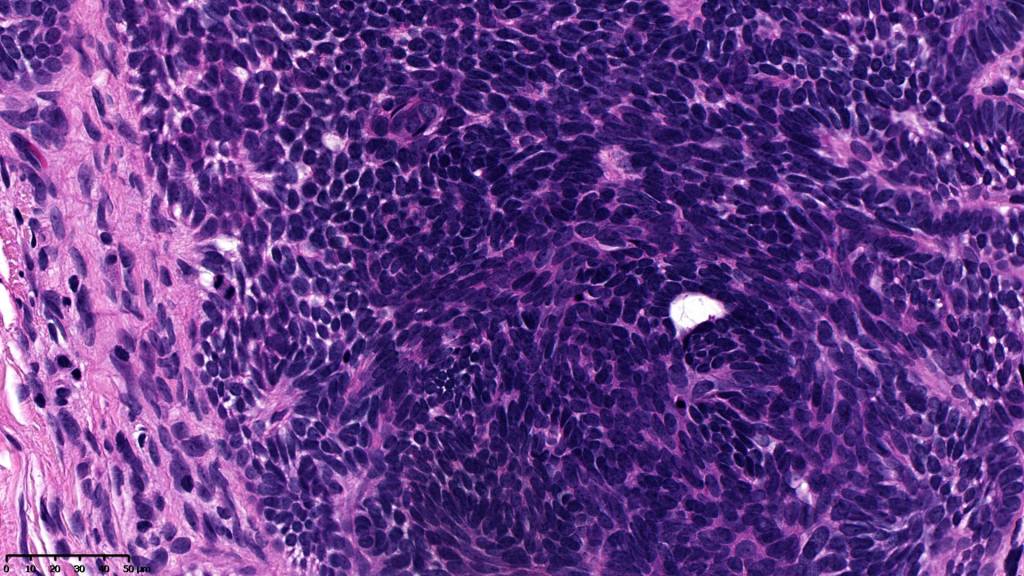
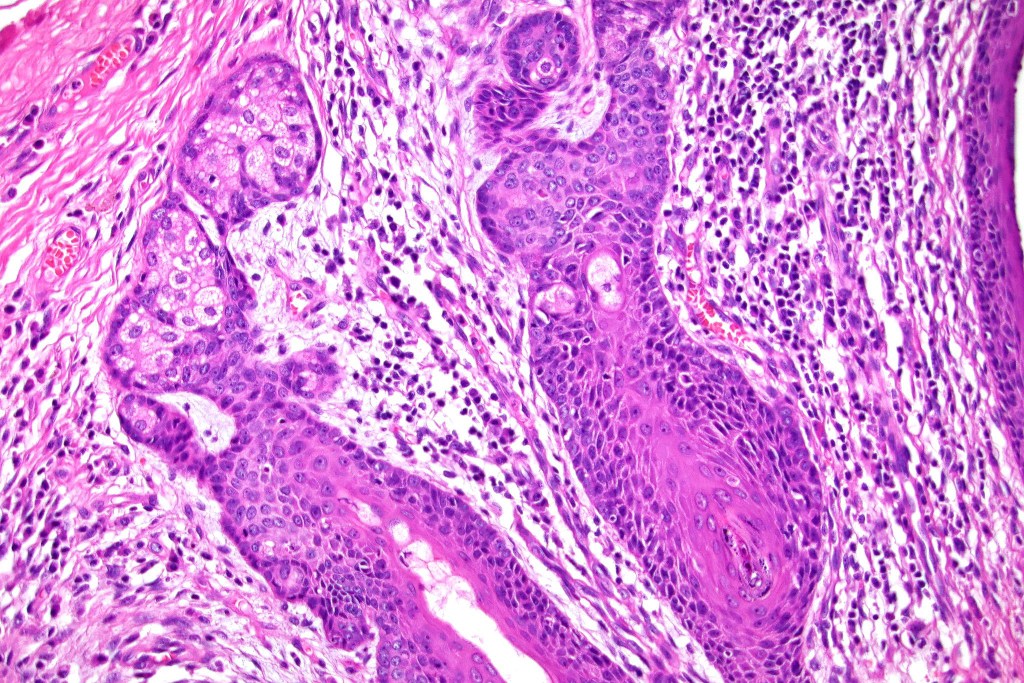
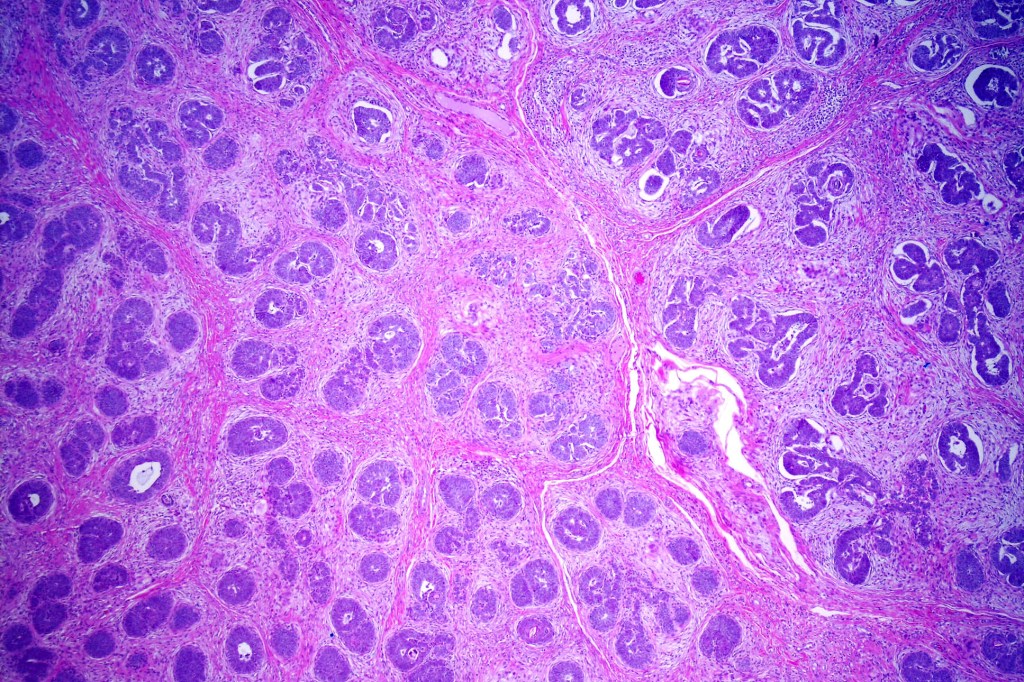
•Variably sized but generally large, basophilic tumor nodules composed of small uniform basaloid cells with minimal cytoplasm
•Variable mitotic activity, can be brisk
•No pleomorphism or abnormal mitoses
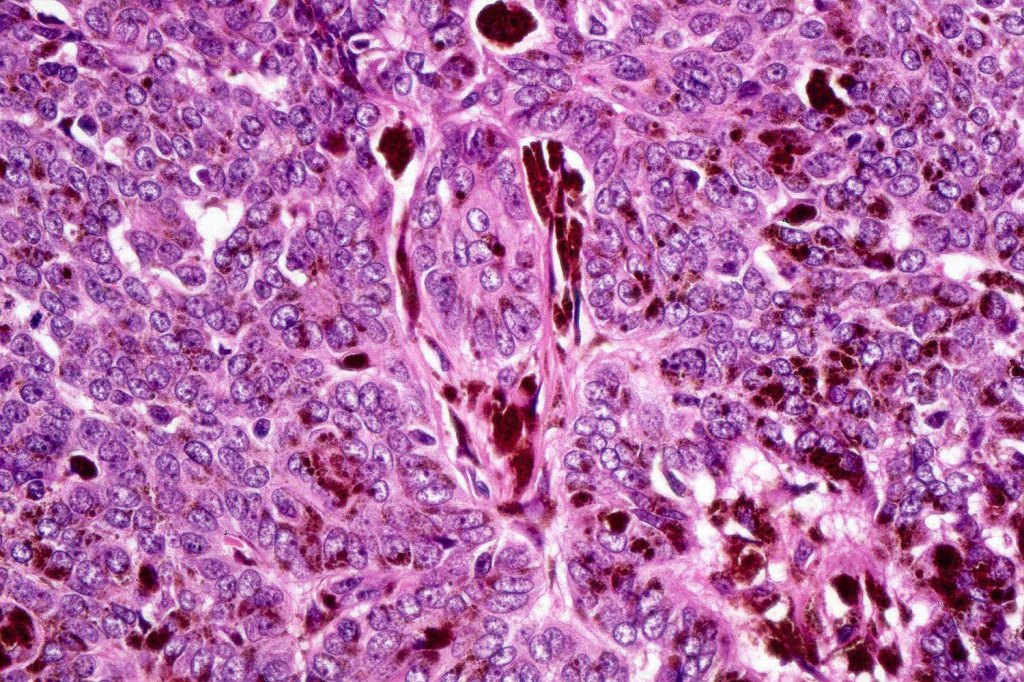
•Peripheral palisading but no retraction artifact or stromal mucin deposition
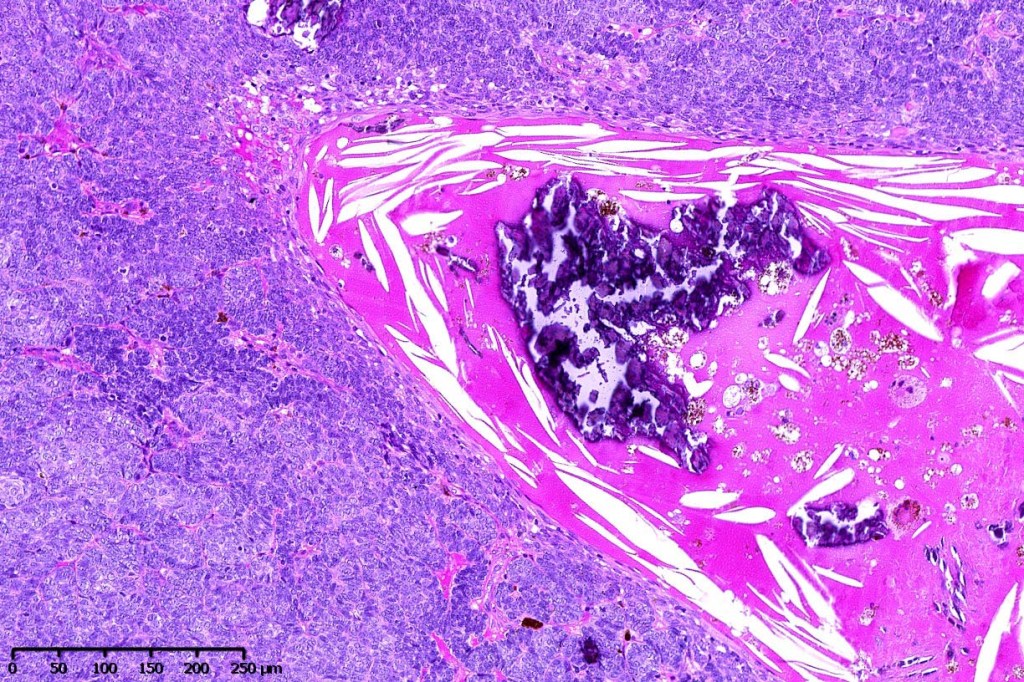
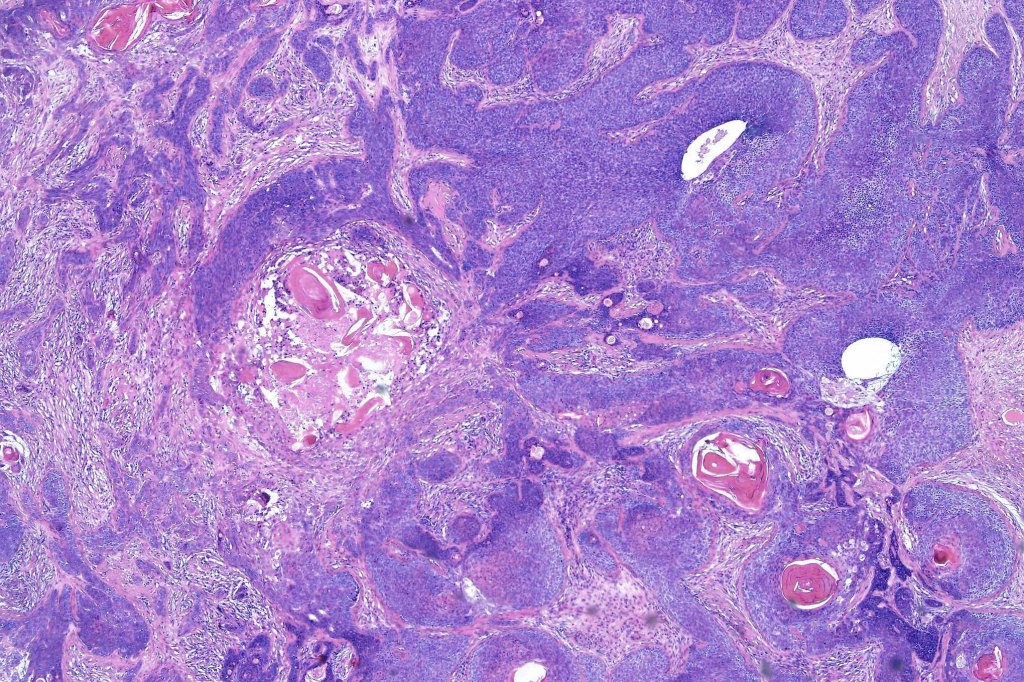
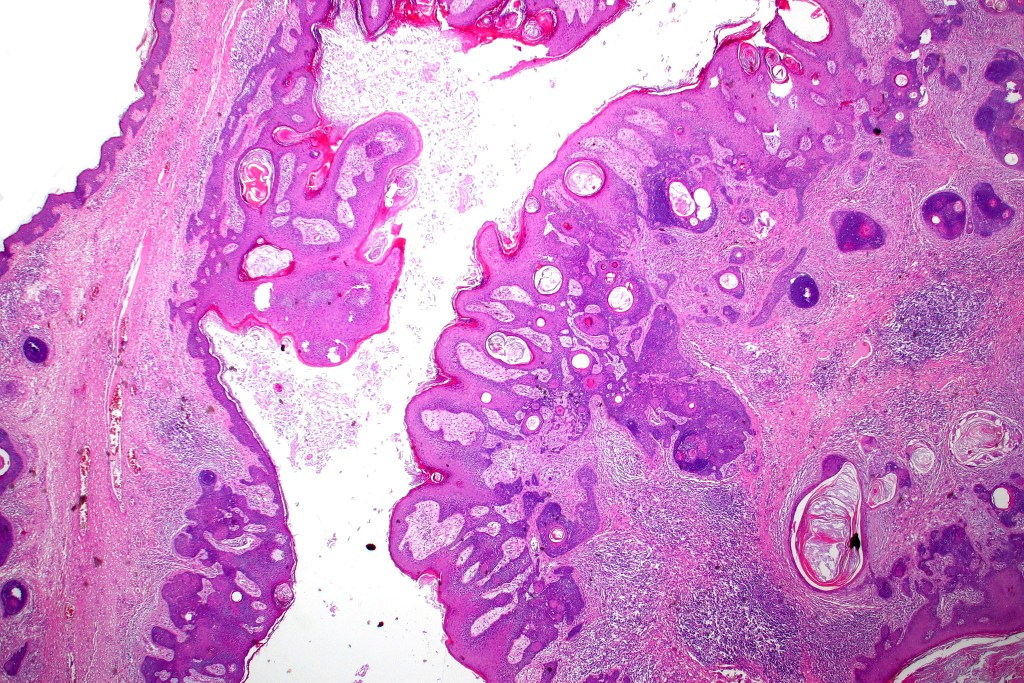
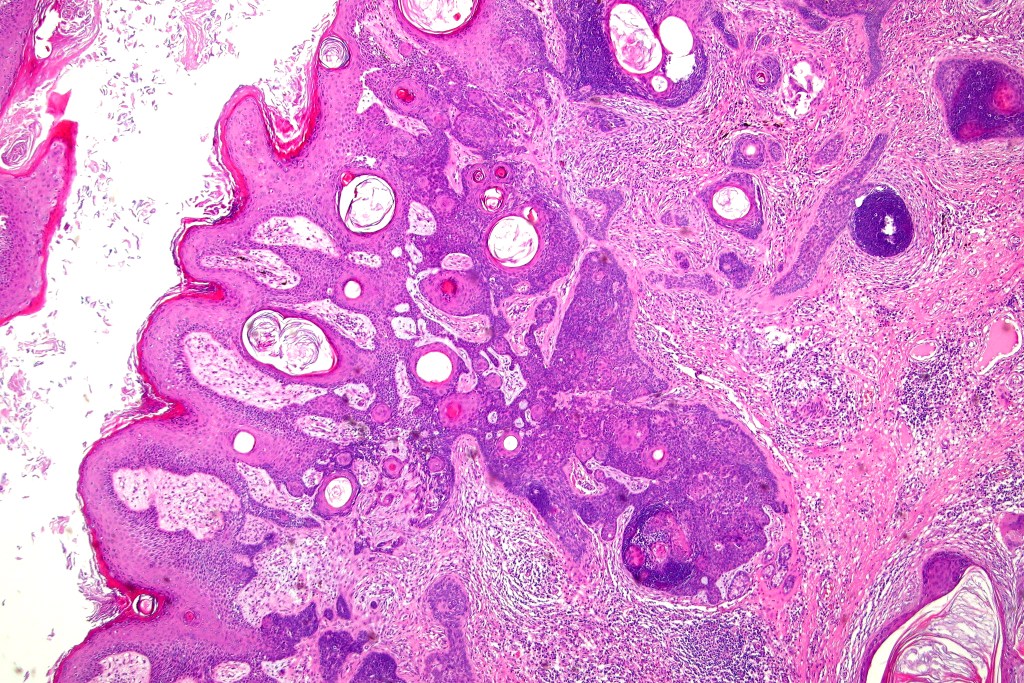
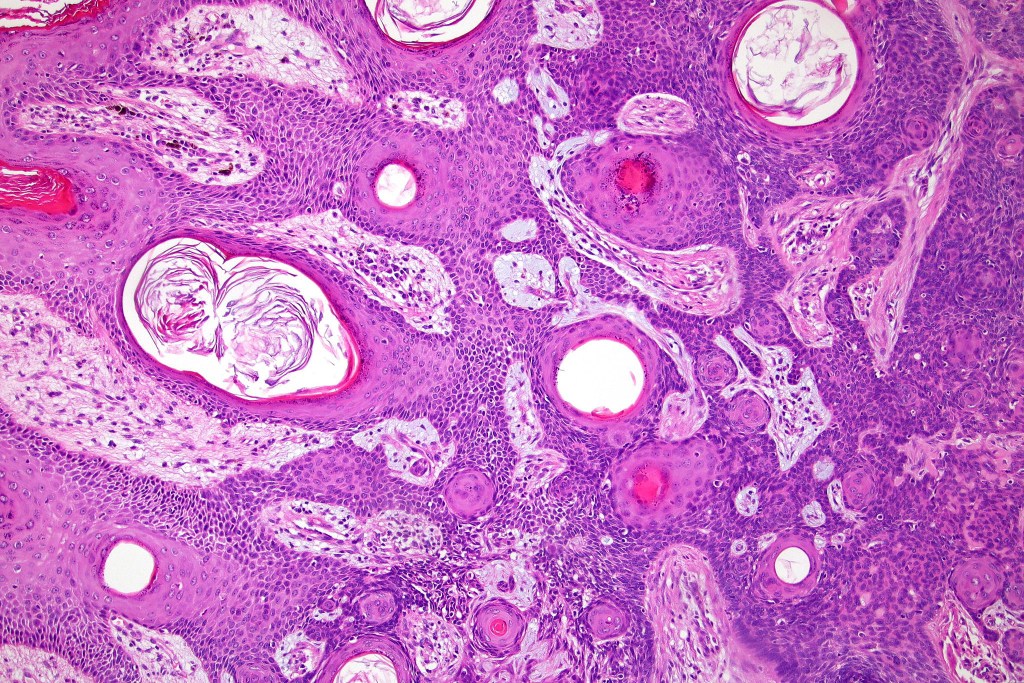
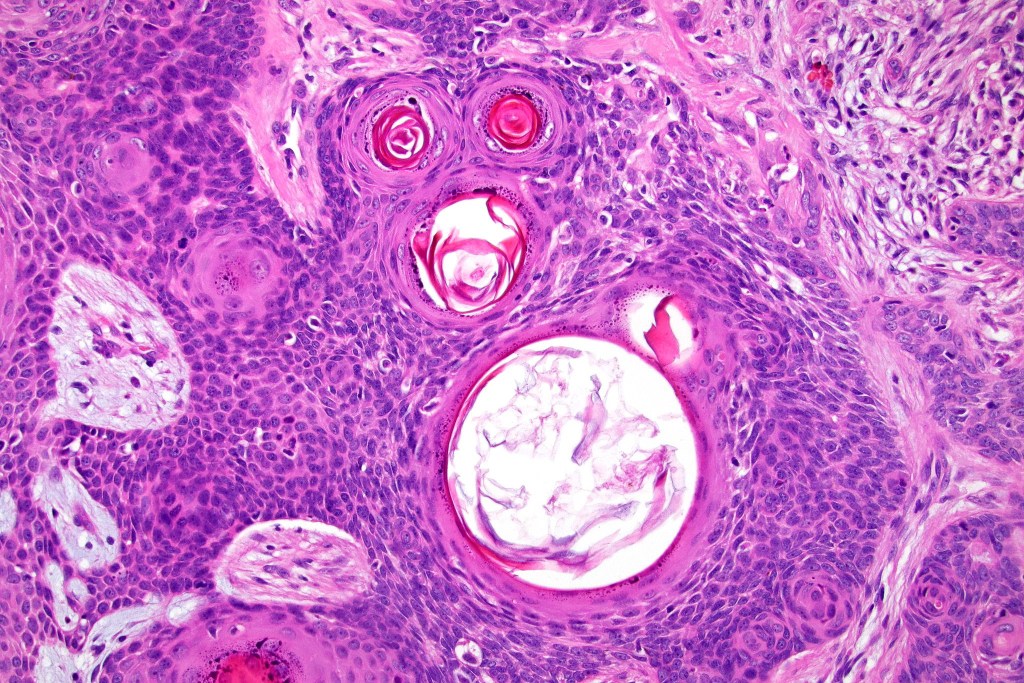
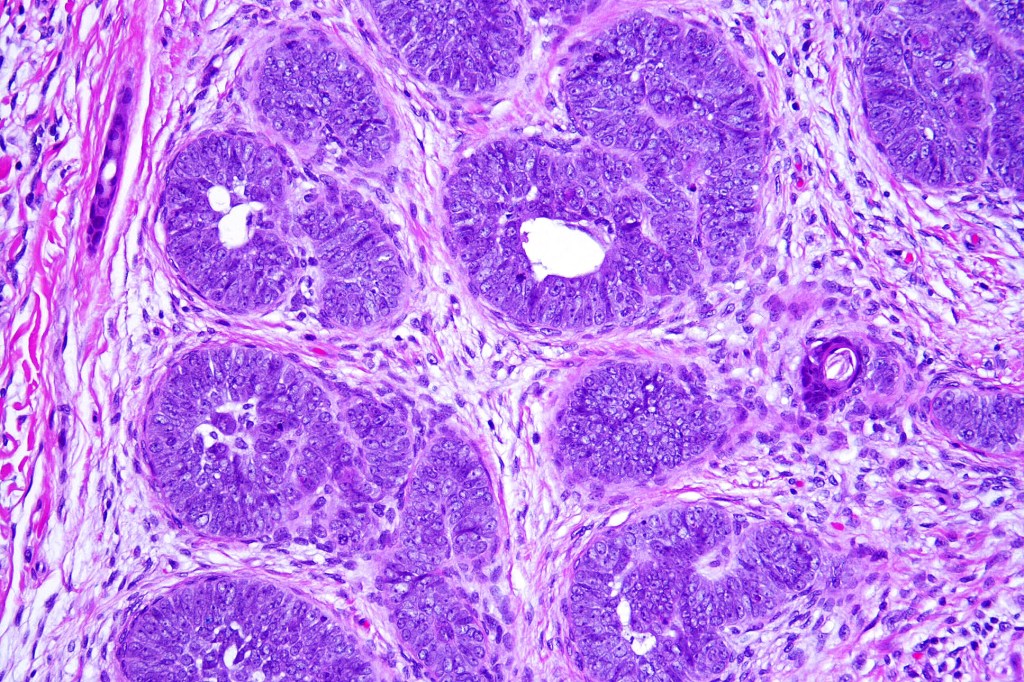
•Variable keratocysts
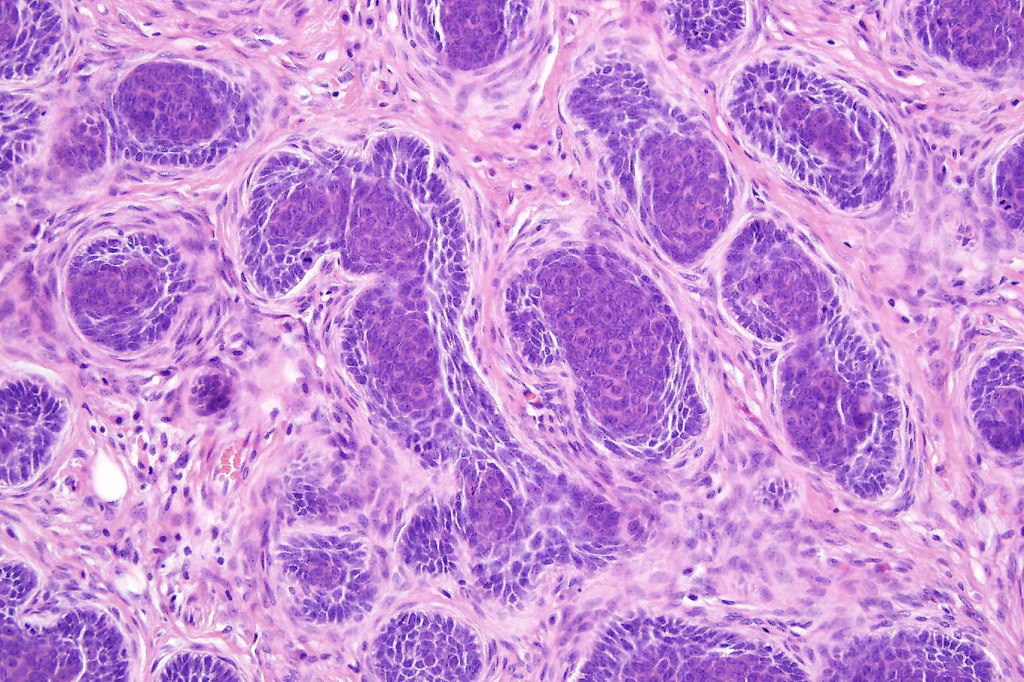
•A rich fibromyxoid mesenchymal stroma with variable papillary mesenchymal bodies (sometimes these are absent)
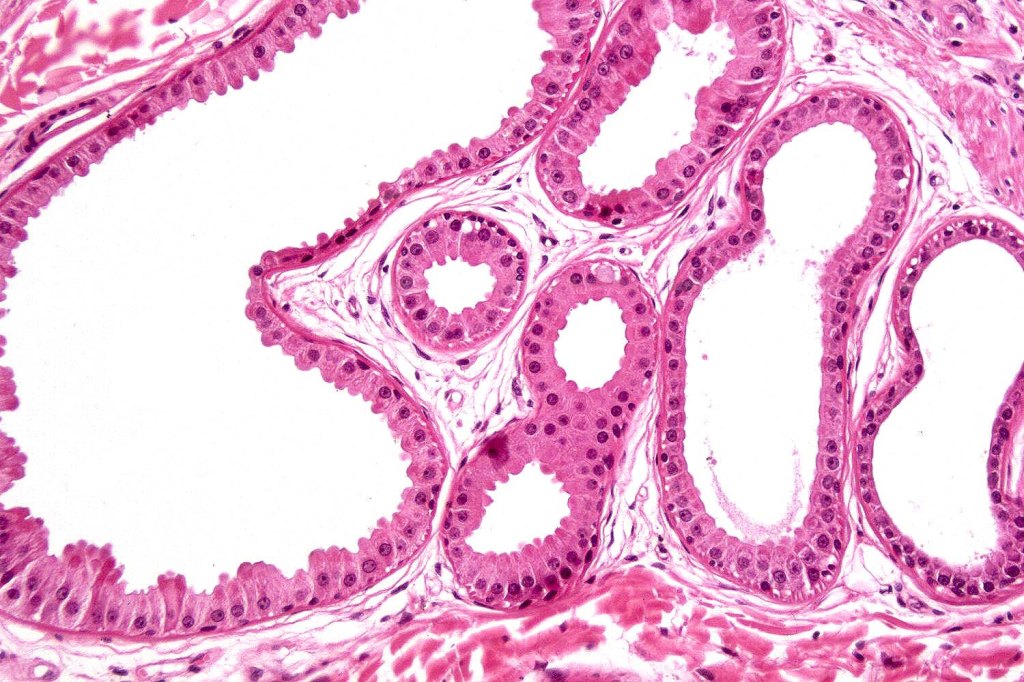
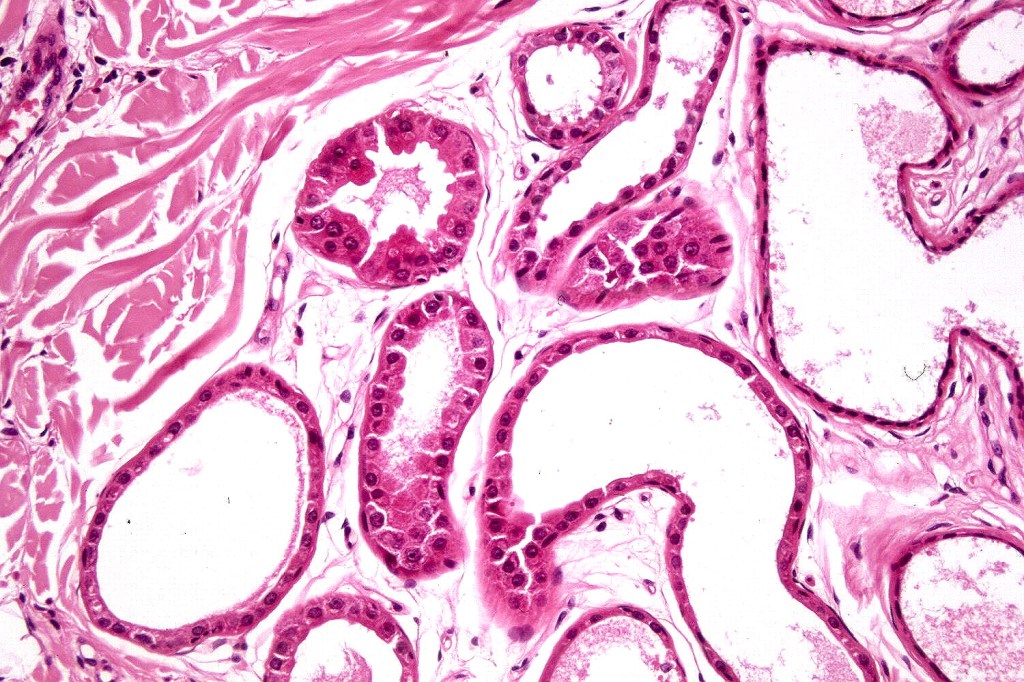
•Variants include cystic, rippled pattern, pigmented, clear cell, trichoblastoma with ductal differentiation & trichoblastoma with sebaceous differentiation
•Variable features include amyloid, focal granulomatous inflammation associated with free keratin & calcification
•Cutaneous lymphadenoma is considered in a separate blog
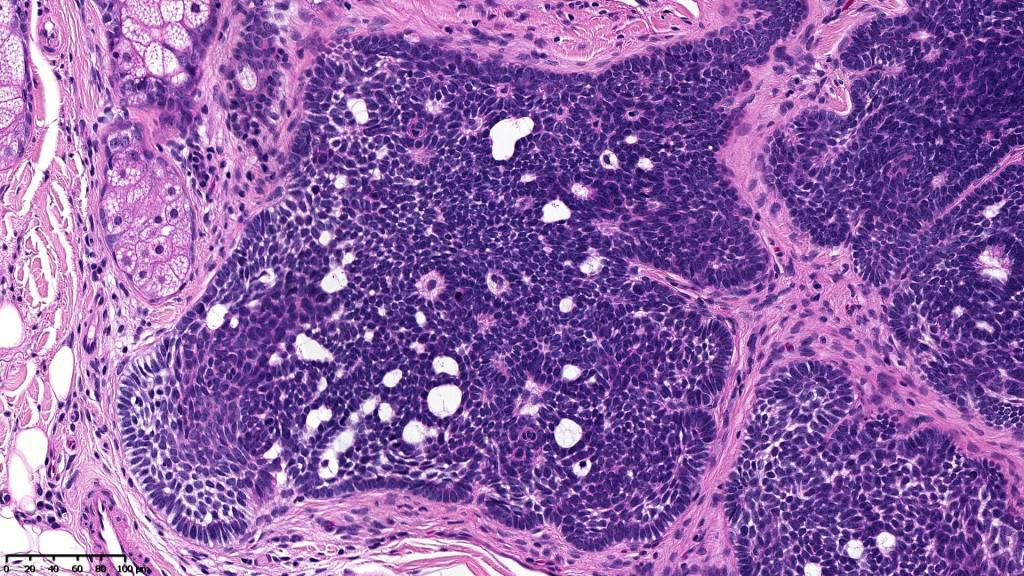
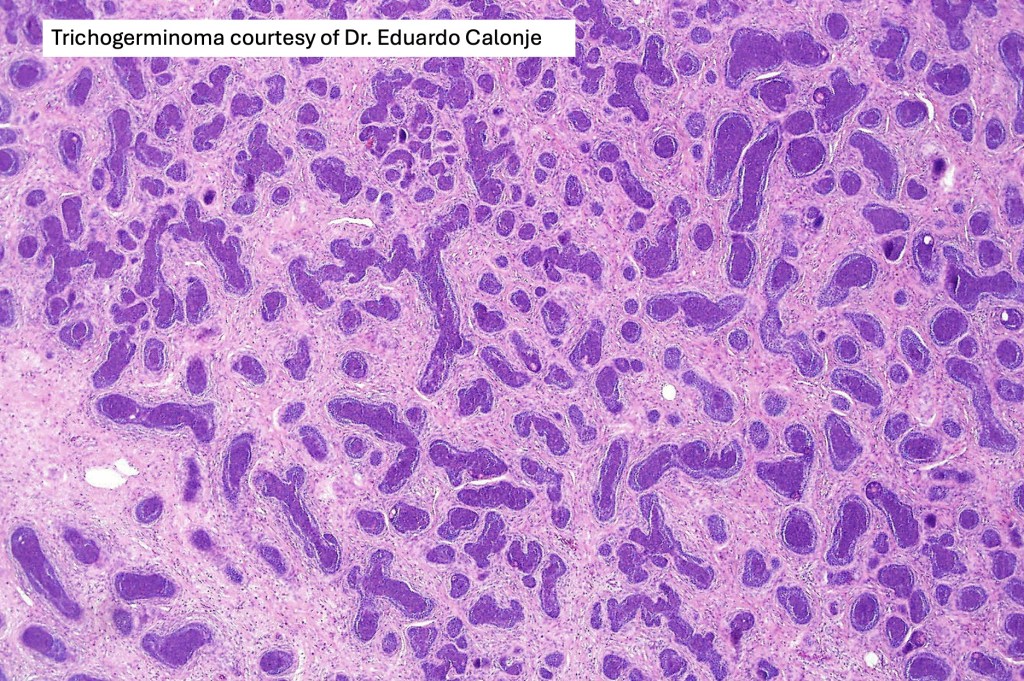
•Trichogerminoma is a distinctive variant being composed of tumor nodules with basaloid cells surrounding pale or eosinophilic micronodules (Zellballen)
•Panfolliculoma represents an often-cystic trichoblastoma showing differentiation toward all follicular elements
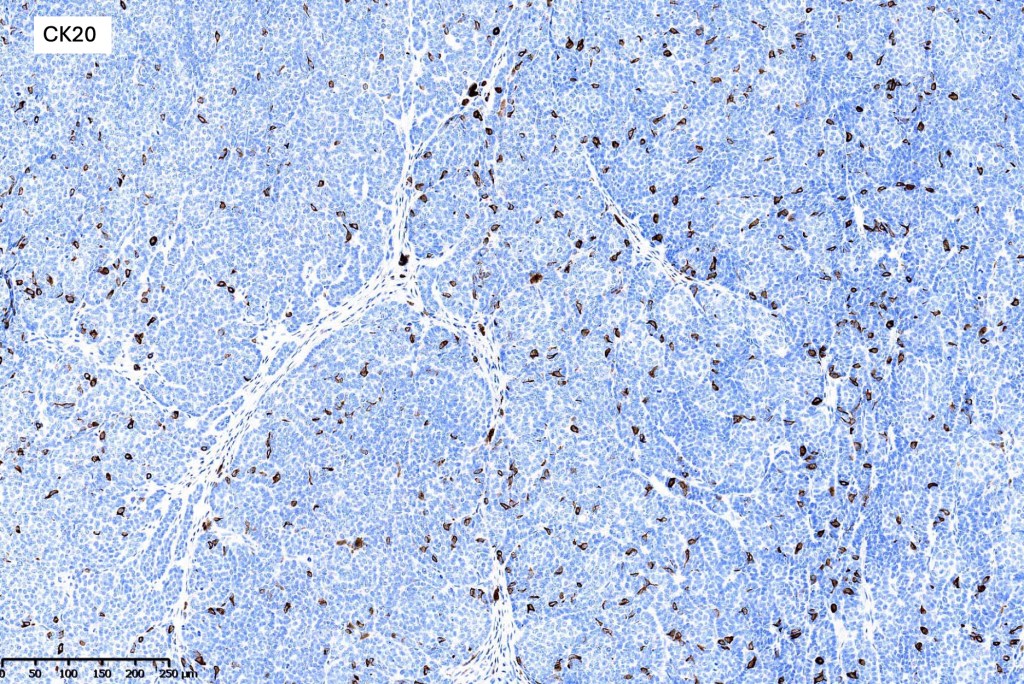
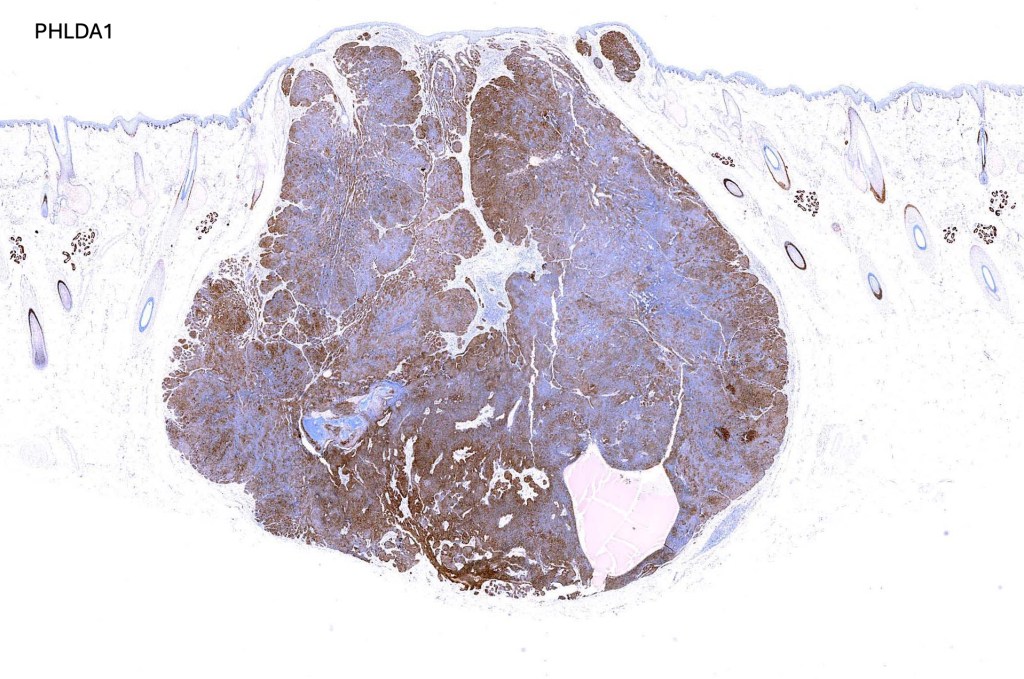
.Immunohistochemistry is included under differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
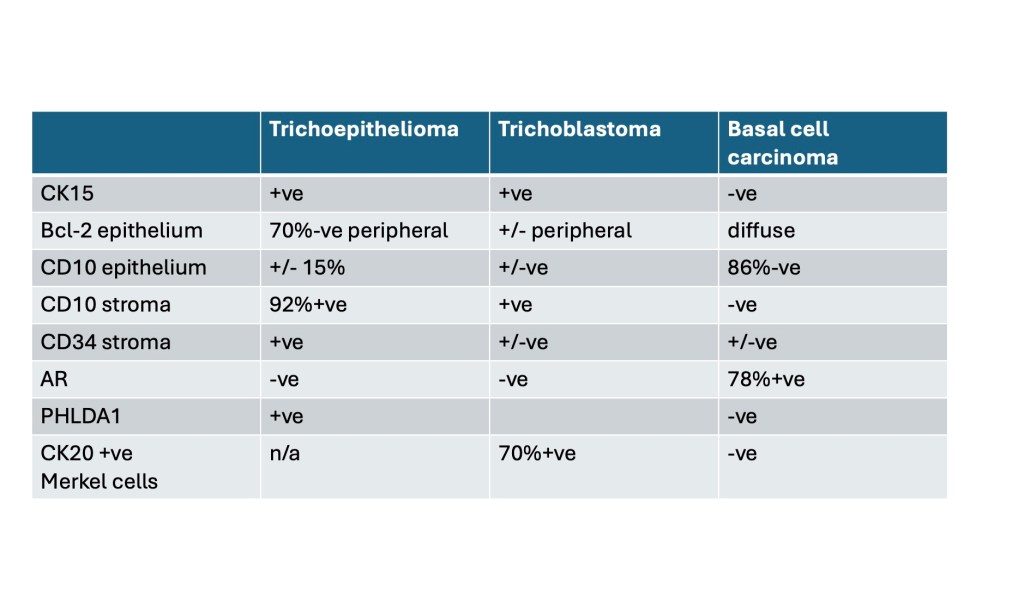
Trichoblastoma can be distinguished from BCC by the absence of retraction artifact and stromal mucin deposition. BCC does not show papillary mesenchymal bodies. Immunohistochemical differences are shown in the table below.
Leave a comment