Clinical features
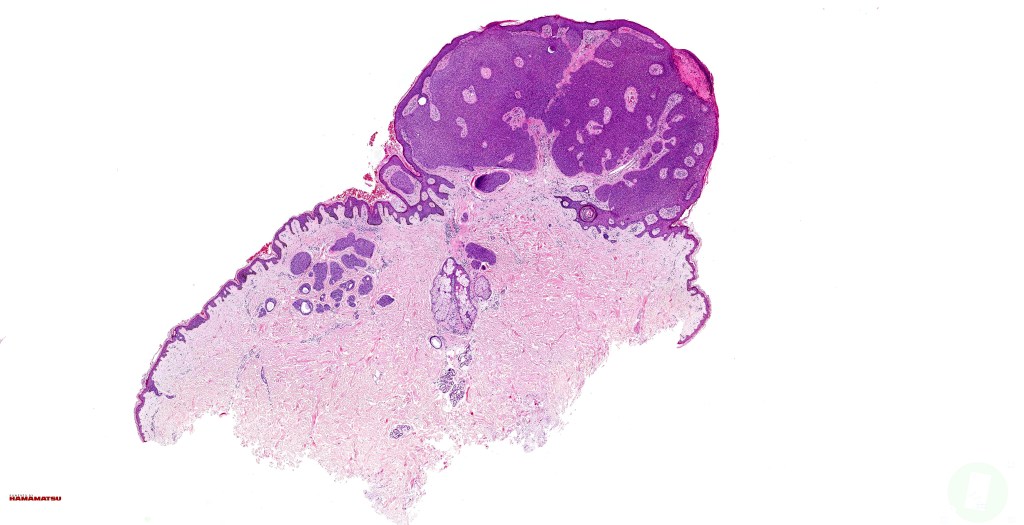
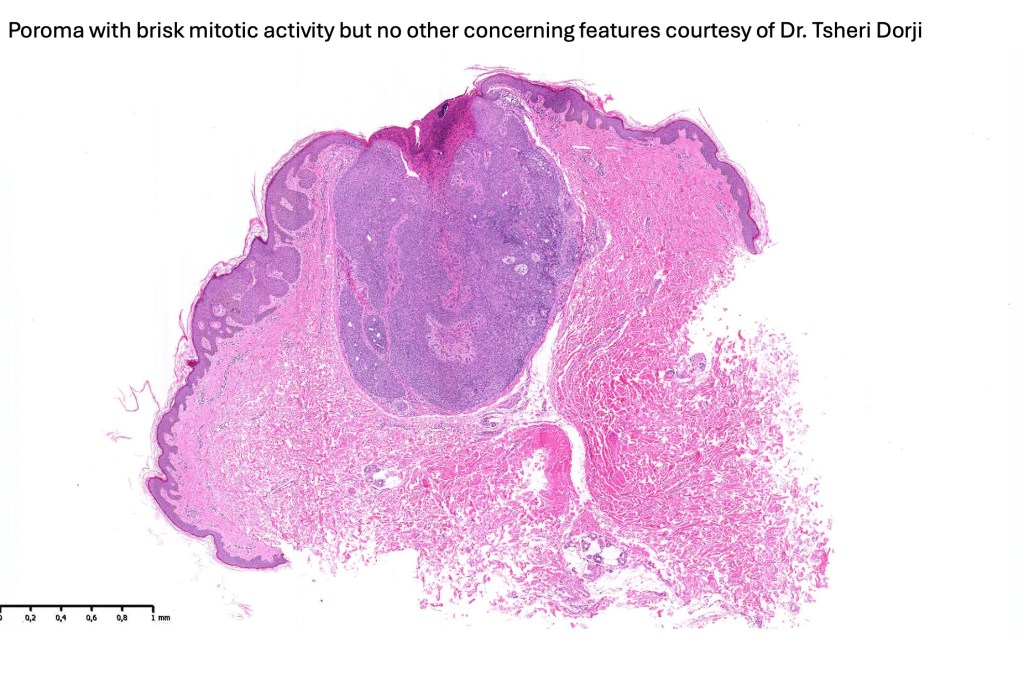
•May present as an intraepidermal lesion (hidroacanthoma simplex, a dermal tumor (dermal duct tumor) or as both with epidermal continuity (poroma); some tumors overlap hidradenoma & poroma (poroid hidradenoma overlap)
•Solitary skin colored, erythematous or pigmented, generally asymptomatic nodule with a predilection for the foot but it may occur just about anywhere
•M=F
•Adults
•Rarely multiple clustered lesions (poromatosis) may follow radiotherapy or chemotherapy
•Linear nevoid variant
•Hidroacanthoma is similar although it generally presents in the elderly
•Dermal duct tumor is similar but shows a predilection for the head, neck & limbs & presents mostly in elderly females



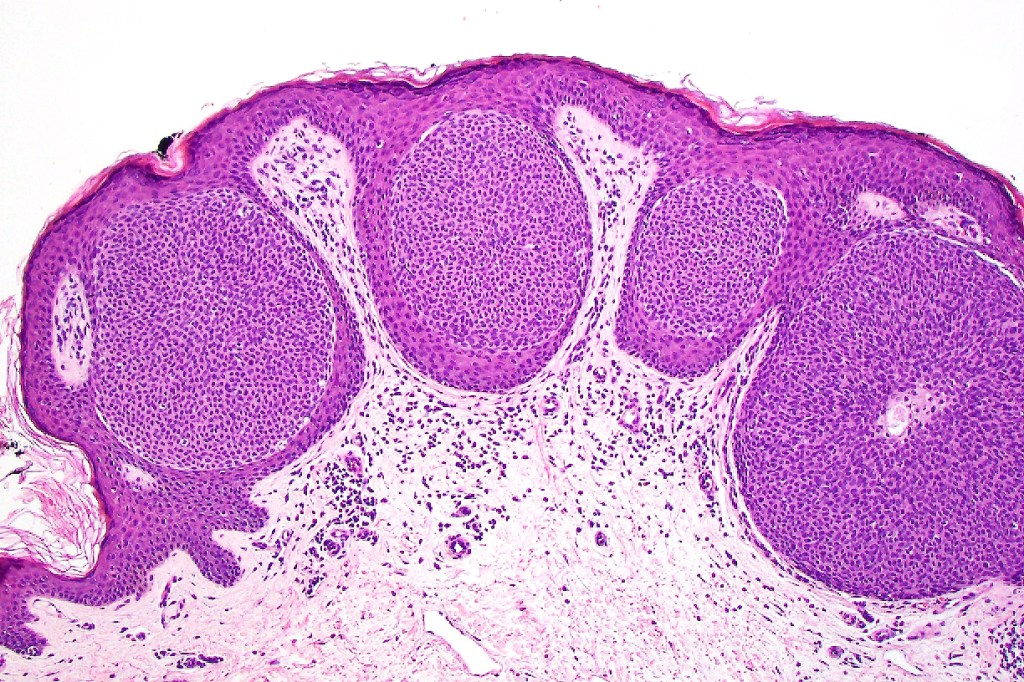
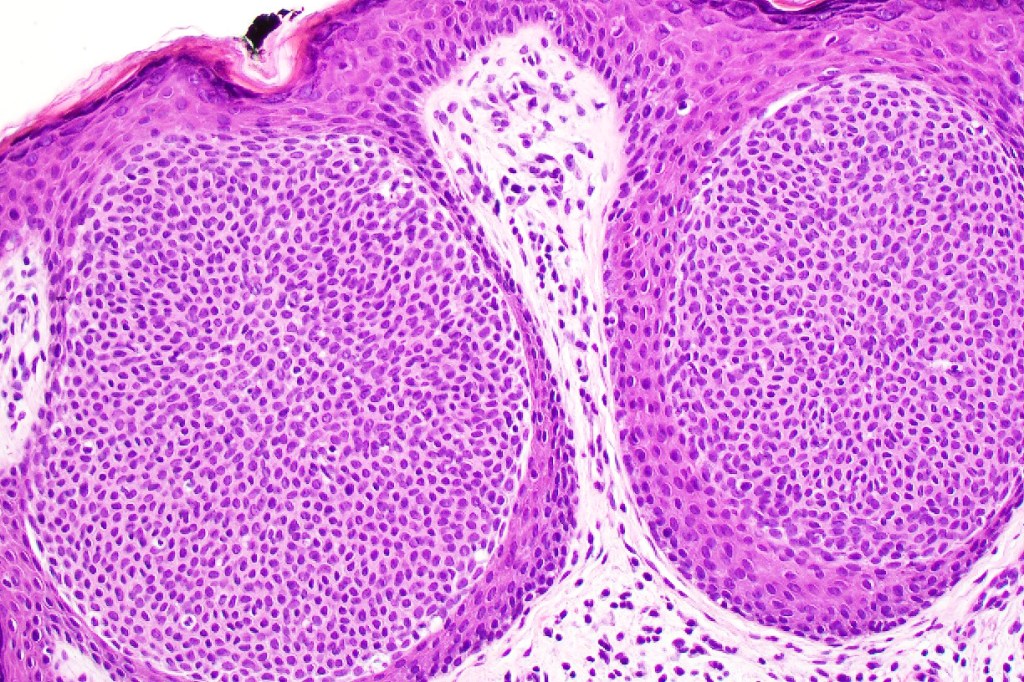
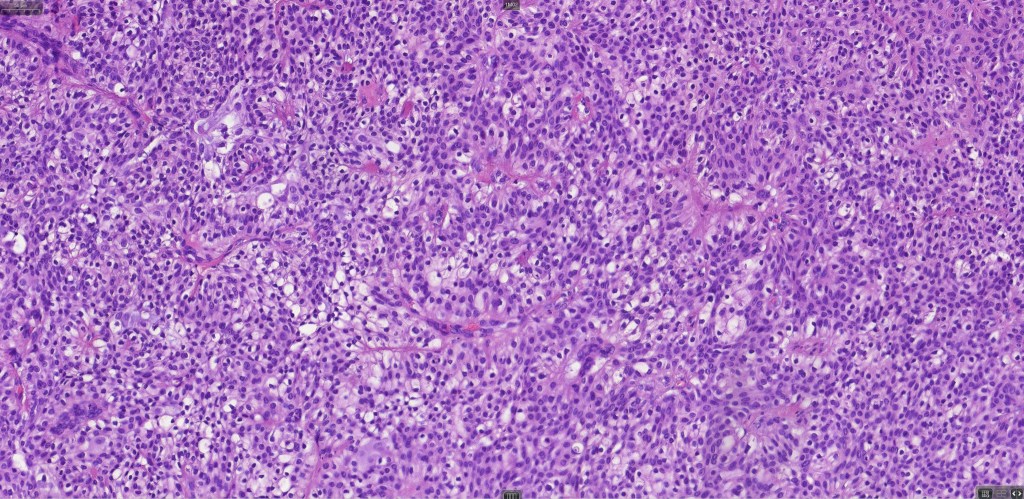
Histological features
•Poromas harbor activating mutations in HRAS, or fusions of YAP/TAZ, YAP1-MAML2, YAP1-NUTM1, or WWTR1_NUTM1. (Airini Kyrmanidoe et al, 2023)
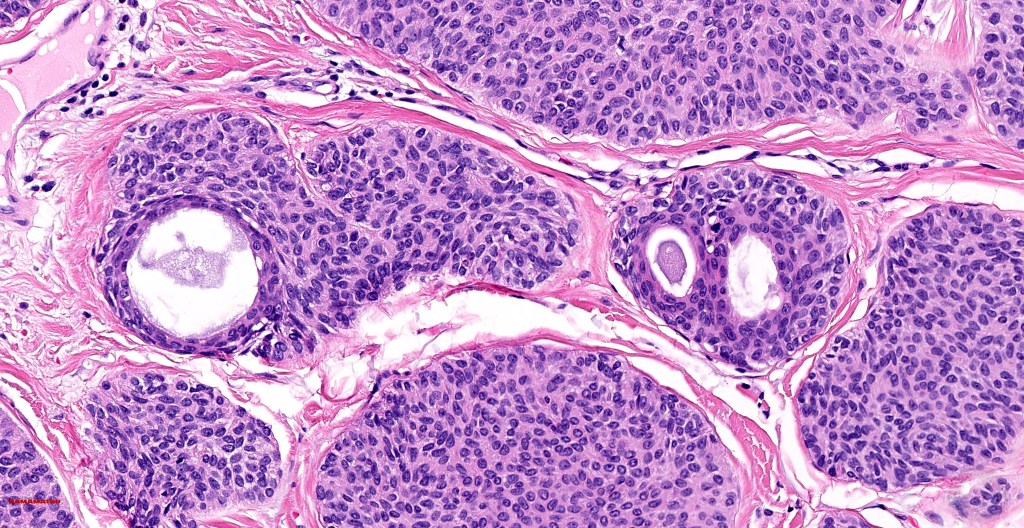
•Variably derived from the acrosyringium, the dermal duct or both
•Hidroacanthoma represents a wholly intraepidermal population of small poroid cells sharply delineated from the adjacent larger keratinocytes
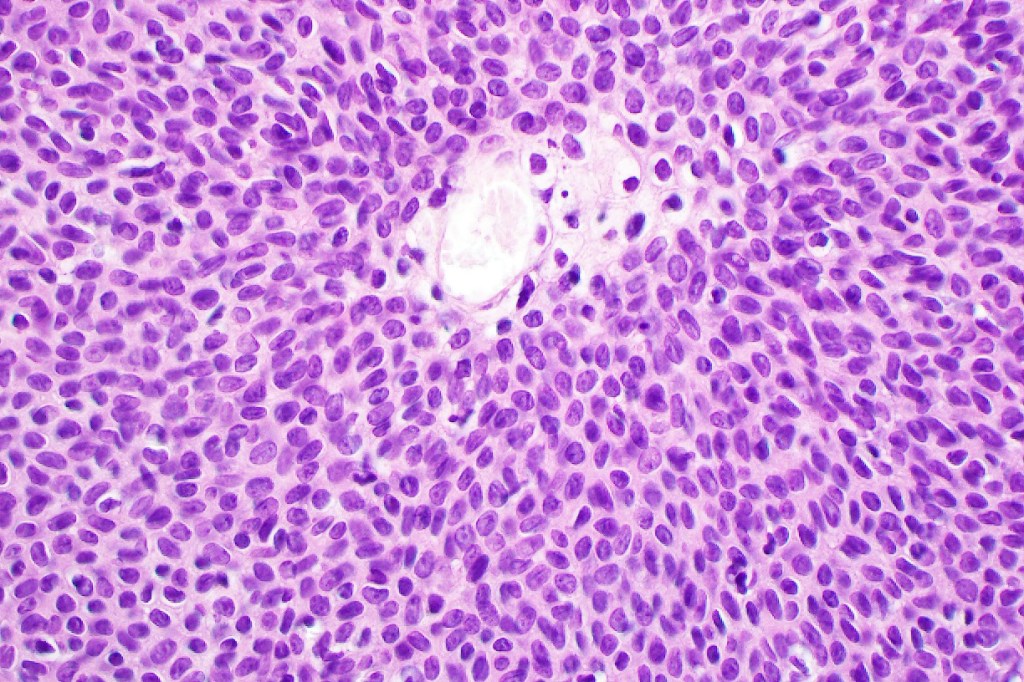
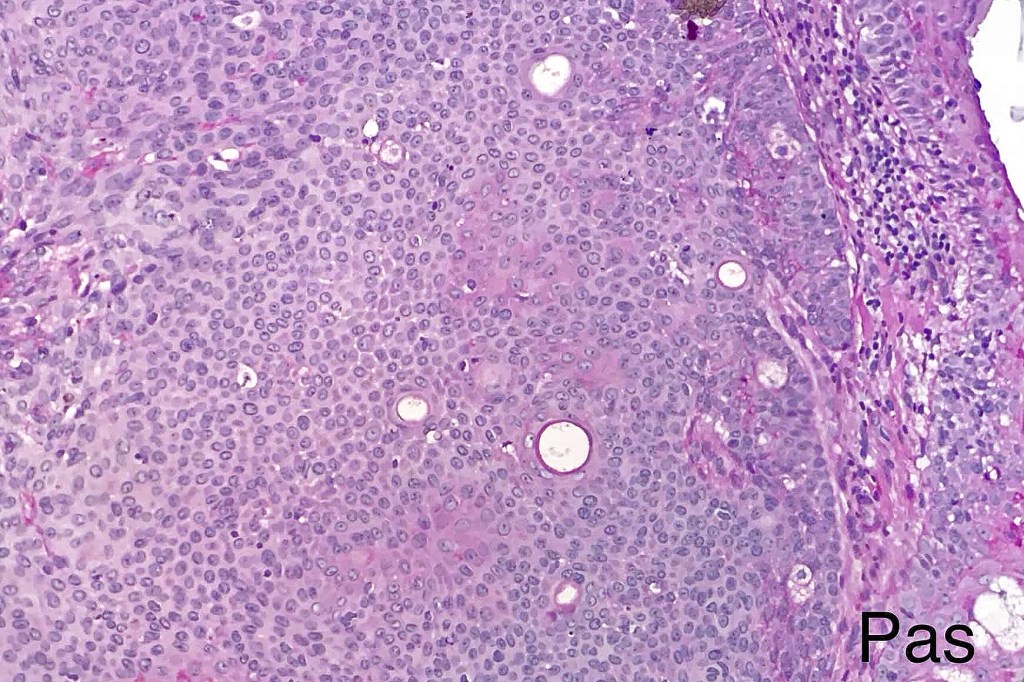
•Careful scrutiny and often levels are required to reveal intracytoplasmic lumina or ductal differentiation
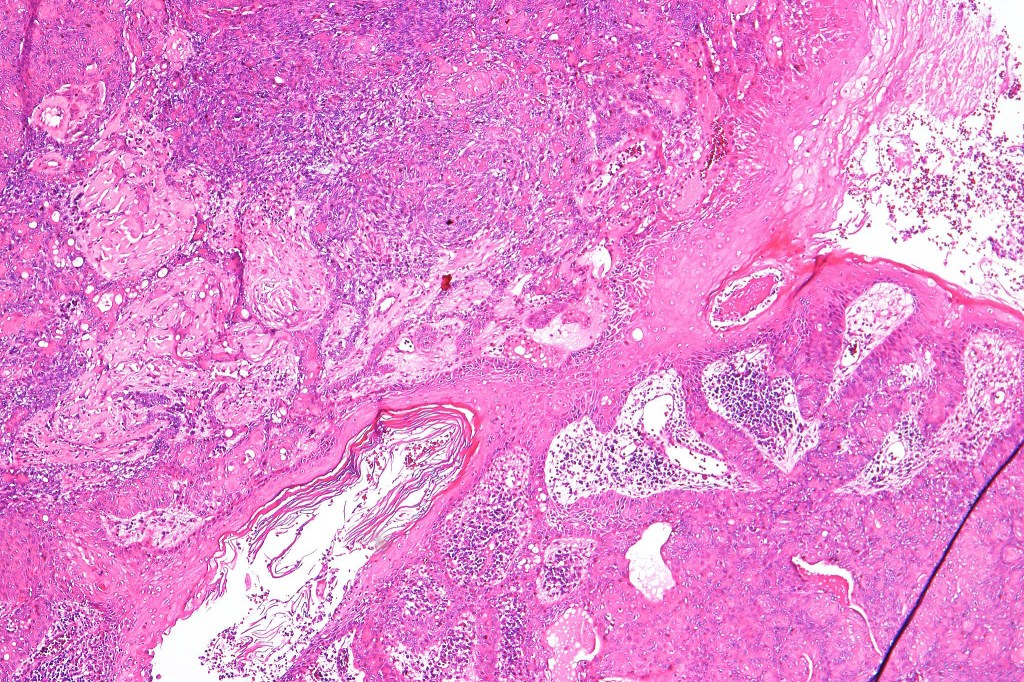
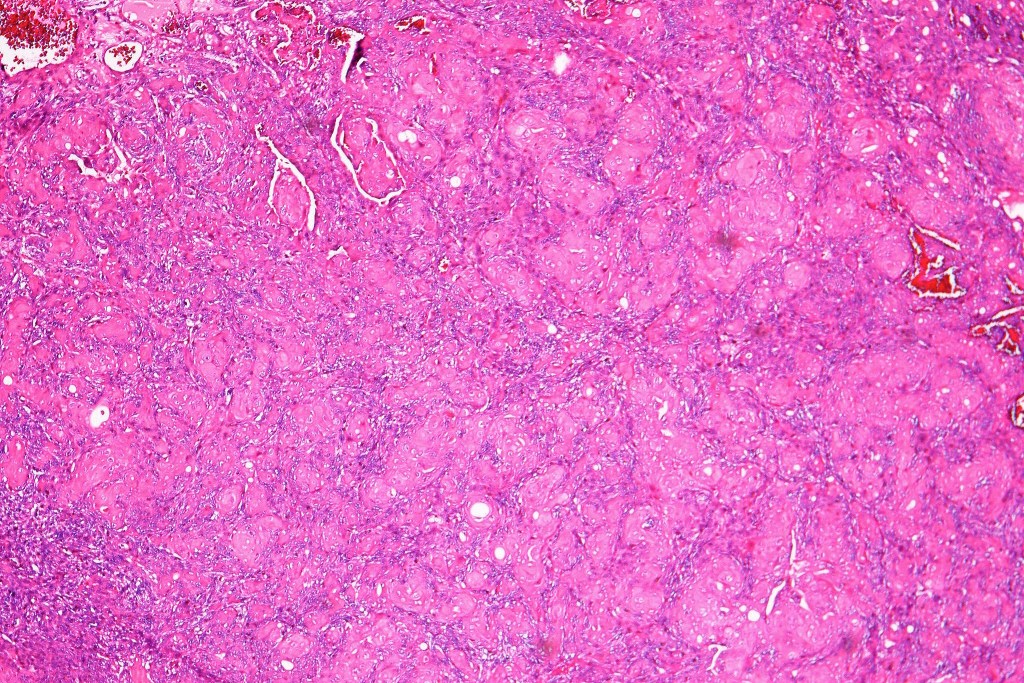
•Dermal duct tumor comprises dermal nodules composed of poroid cells showing ductal differentiation & intracytoplasmic lumina with variable cyst formation
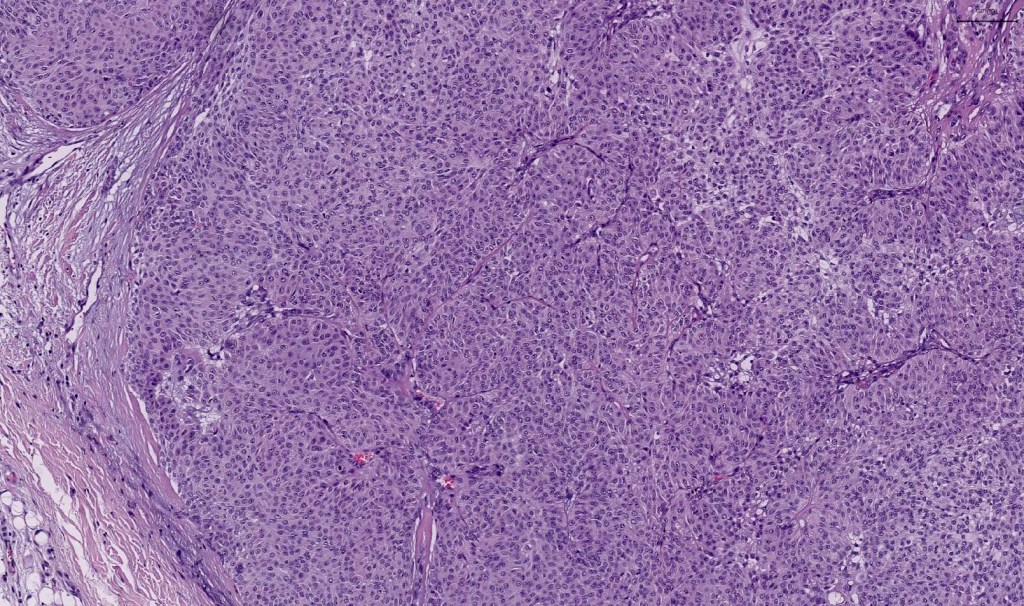
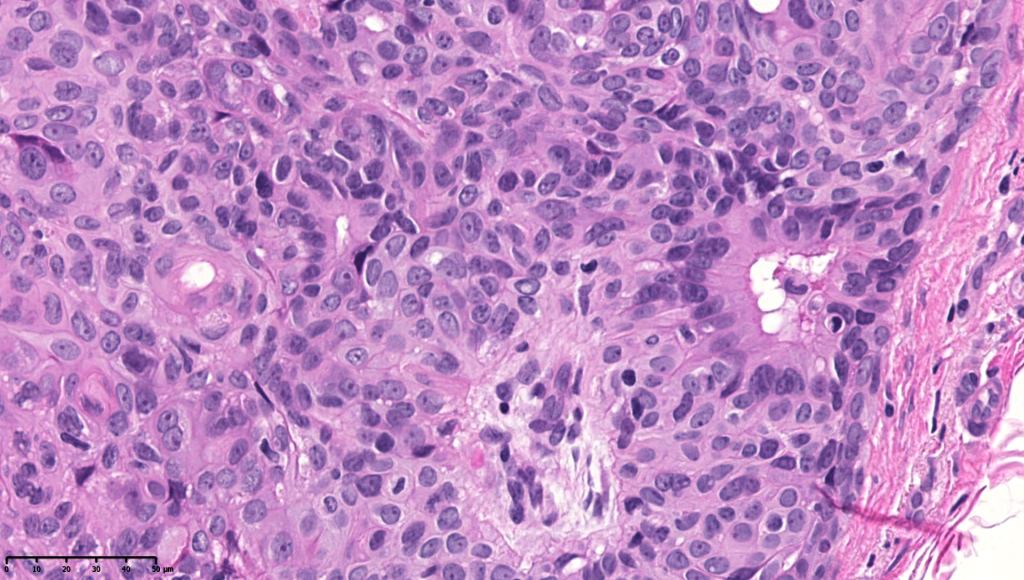
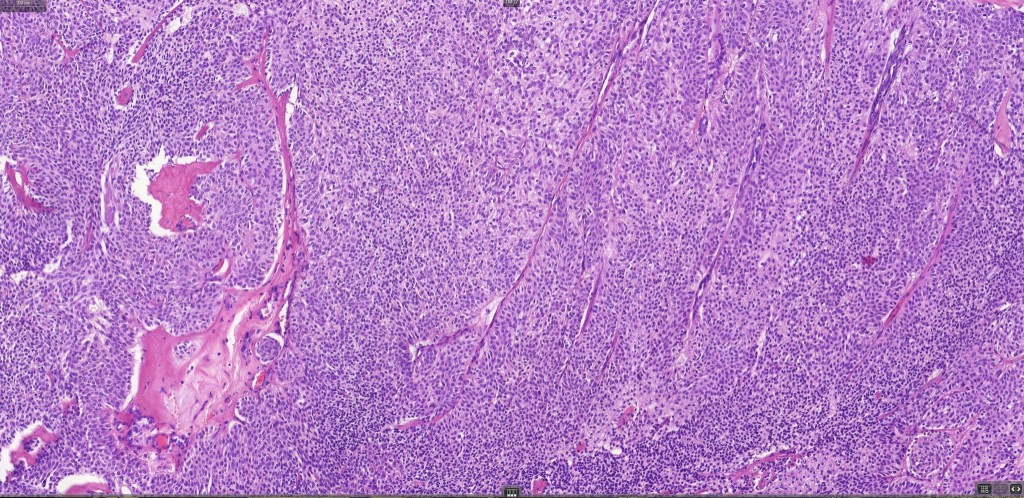
•In poroma, a dermal-centric tumor is associated with epidermal origin/continuity & is composed of small cells with vesical nuclei.
•Desmosomes often prominent
•Clear cells (sometimes predominating- so-called clear cell variant)
•No peripheral palisading or retraction artifact
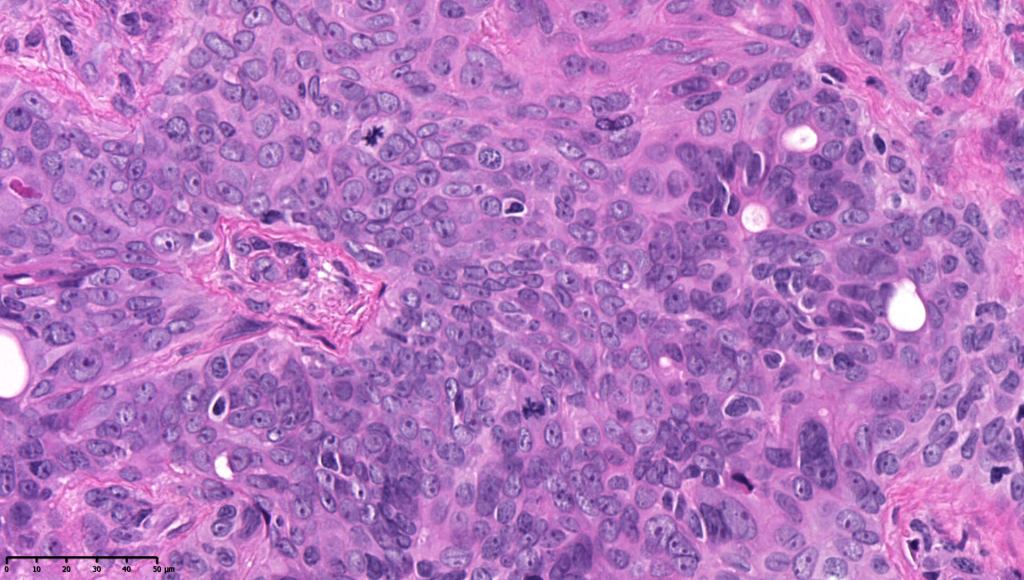
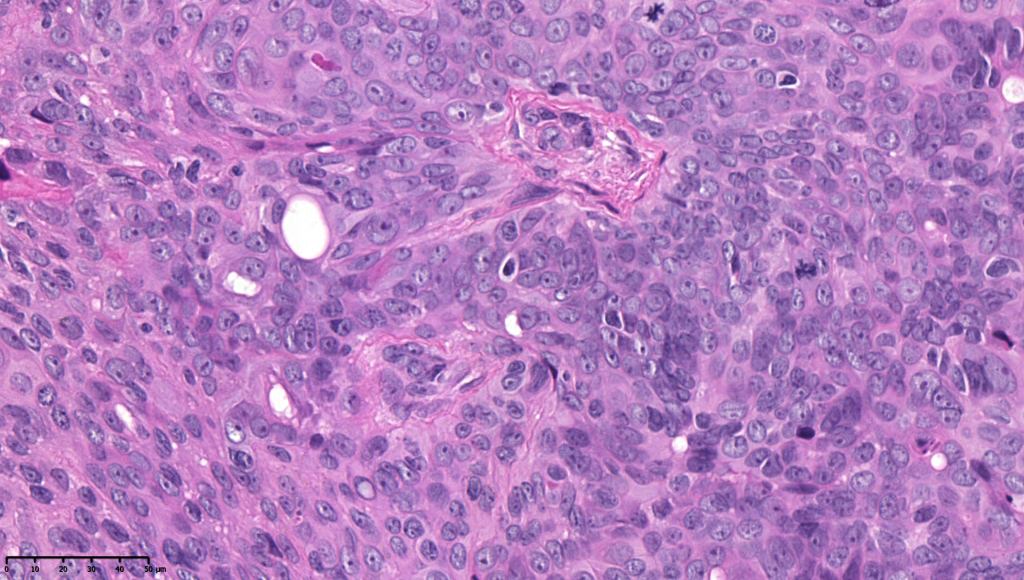
•Generally few mitoses but occasionally can be conspicuous. In the absence of other features of porocarcinoma, this should not be taken as necessarily implying maligant potential unless other worrying features sre also present (see case below)
•No pleomorphism or abnormal mitoses
•No lymphovascular involvement or perineural infiltration
•Variable squamous differentiation (can be marked)
•Spindle cell variant
•Pigmented variant
•Rarely acantholysis
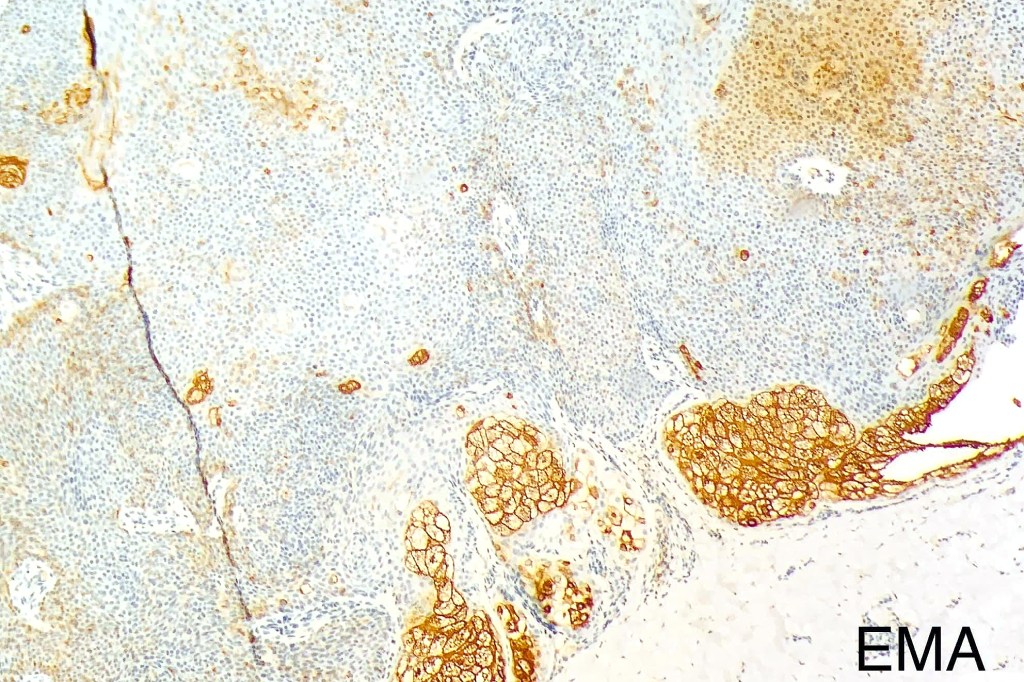
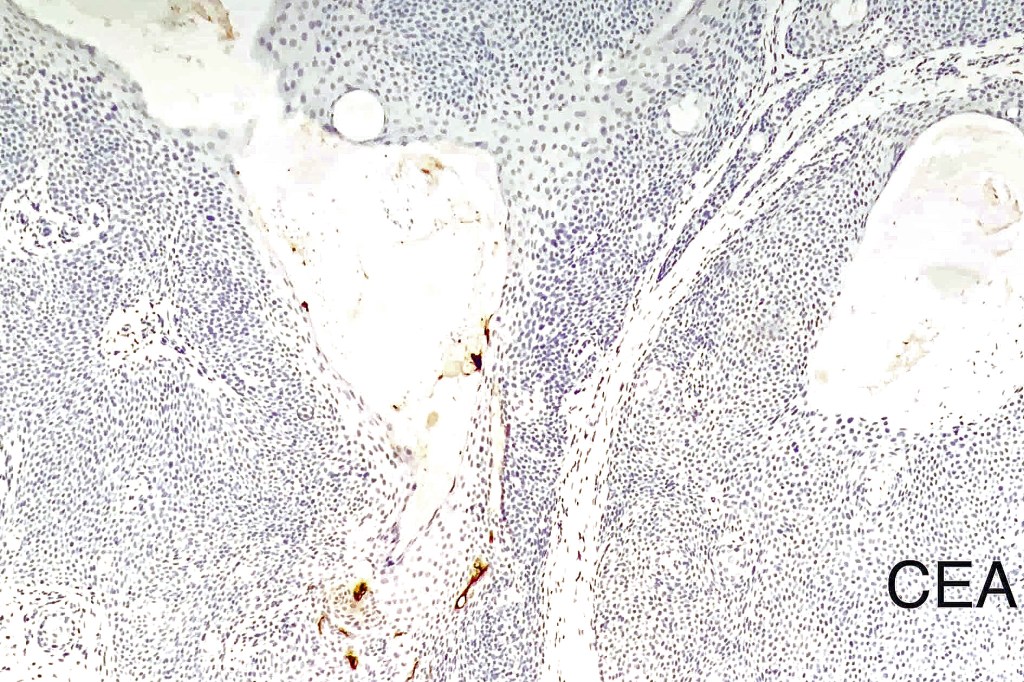
•Ducts highlighted with DPAS, EMA & CEA (best if all 3 are used as staining is very unpredictable)
•Apocrine poroma is characterized by a variable admixture of sebaceous, follicular & apocrine elements in addition to typical poroma




























Leave a comment