Clinical features
•Rare, aggressive variant of SCC
•Should be distinguished from mucoepidermoid carcinoma
•Head (particularly the face & scalp) & neck are most affected but acral lesions are documented in addition to tumors on the penis
•Elderly patients
•Presents as an indurated, erythematous raised plaque
•Tumors often very thick at presentation
•Recurrences are common & the tumor has significant metastatic potential to nodes, less often distant spread

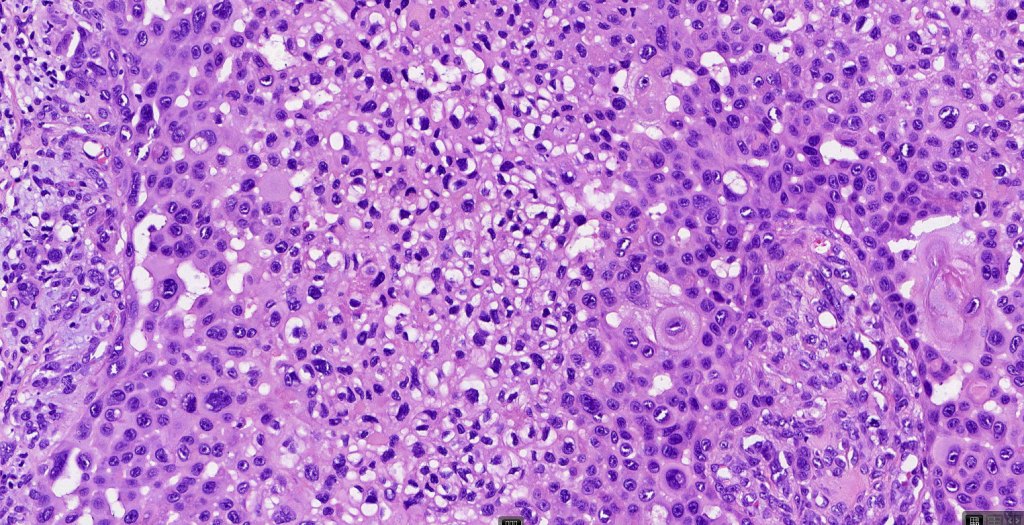
Histological features
•Should be distinguished from pseudoglandular (acantholytic) SCC & metastatic adenosquamous carcinoma e.g. respiratory tract, bile duct, prostate, colon, cervix etc
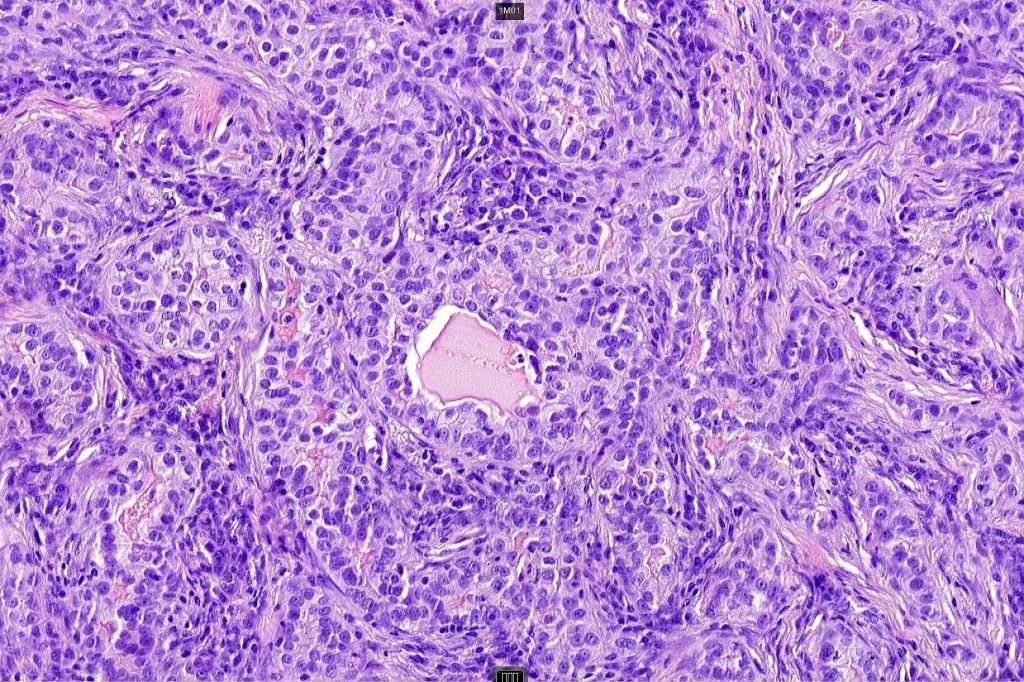
•Biphasic tumor combining squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; the latter showing ductal and glandular differentiation
•Glands are lined by cuboidal to columnar epithelium
•Intracytoplasmic lumina sometimes evident
•Glandular foci show mucin
•Variable pleomorphism & mitotic activity but can be marked
•Perineural infiltration is common (up to 15% of cases)
•DPAS, Alcian blue & mucicarmine +ve
•CEA, EMA & CK7 +ve
.CK20, p63, TTF-1, PSA, ER, PR -ve
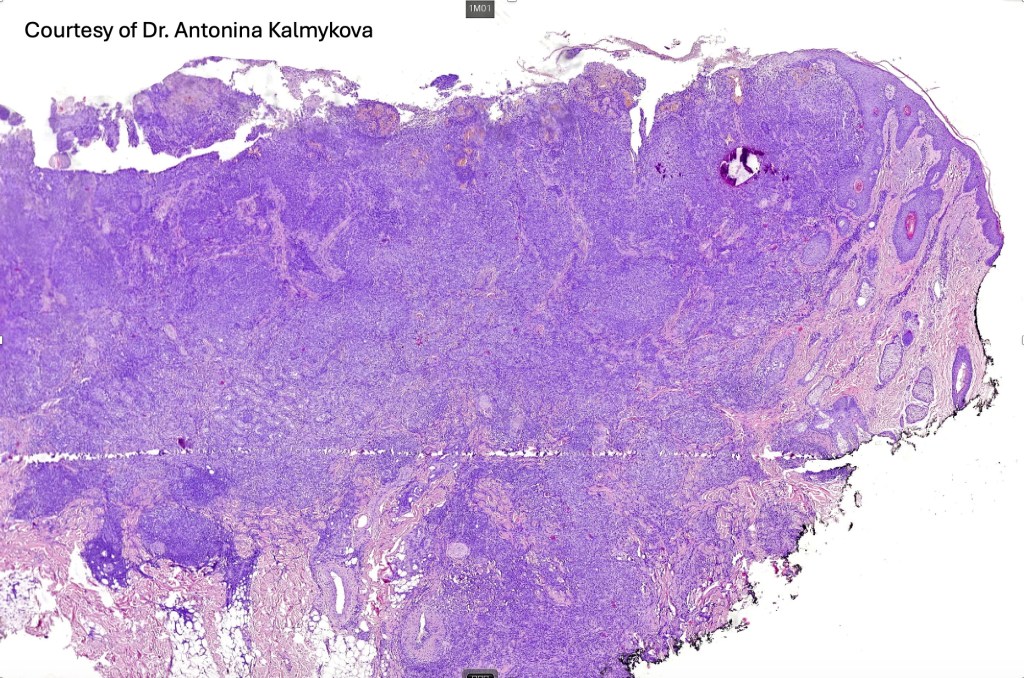

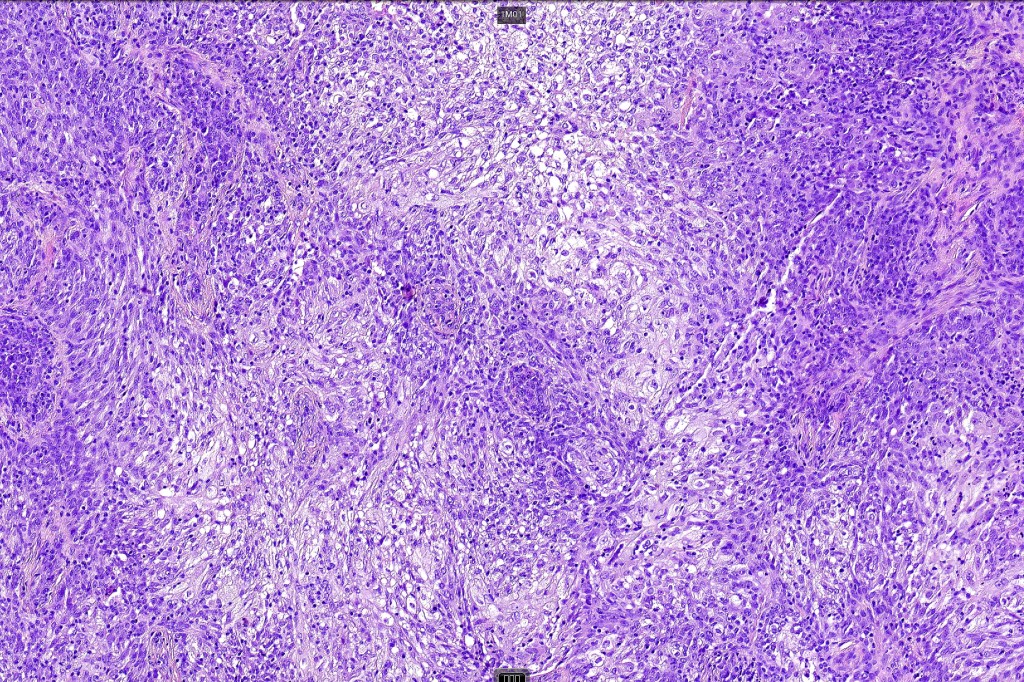
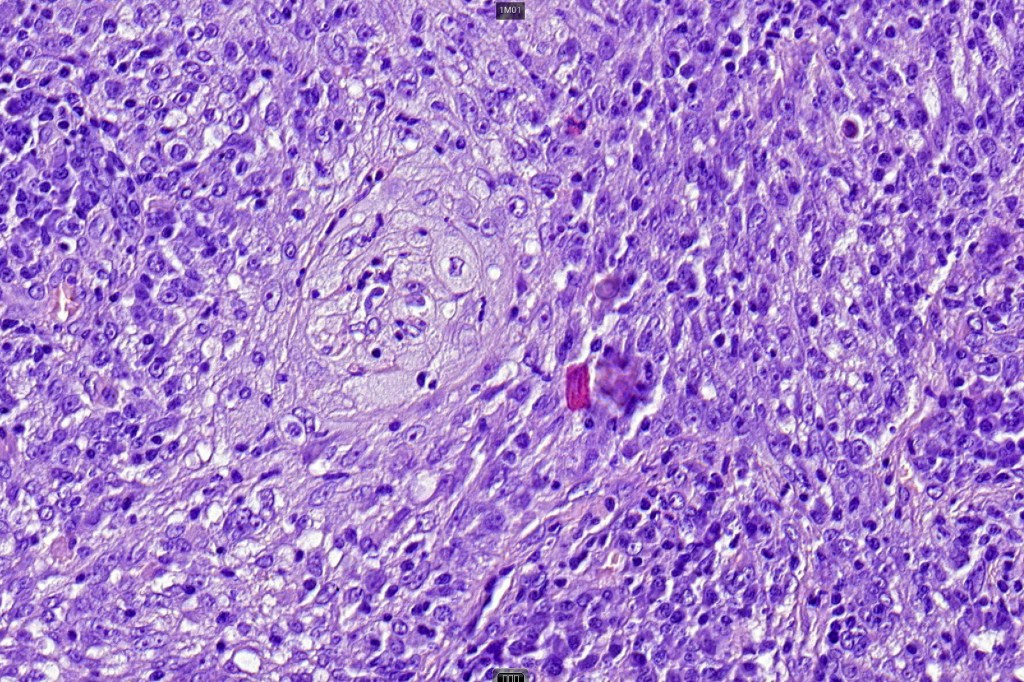

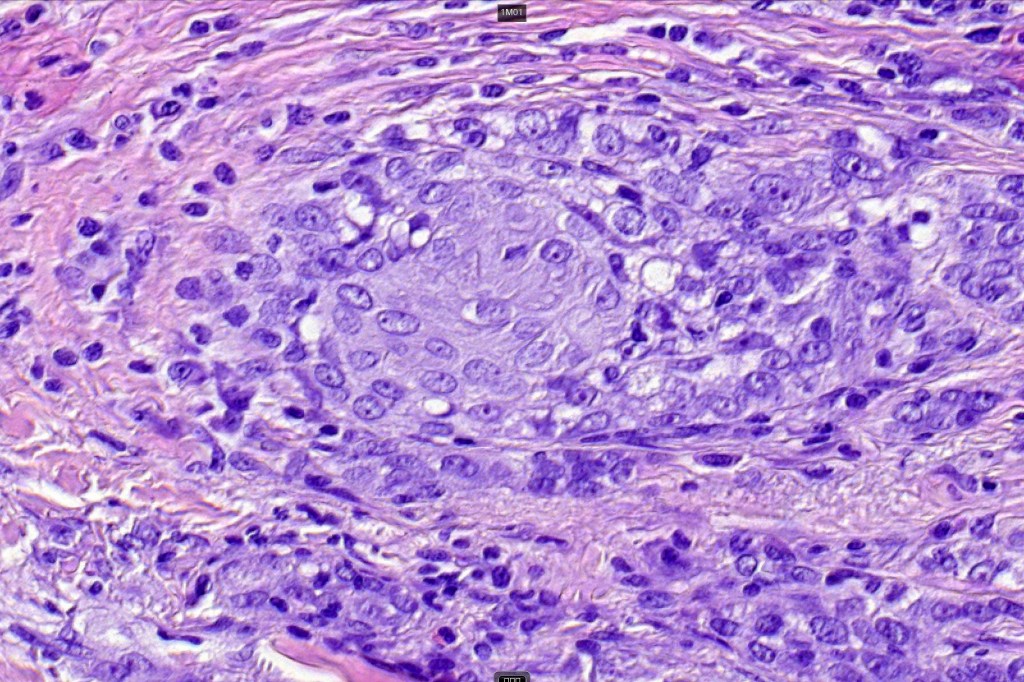











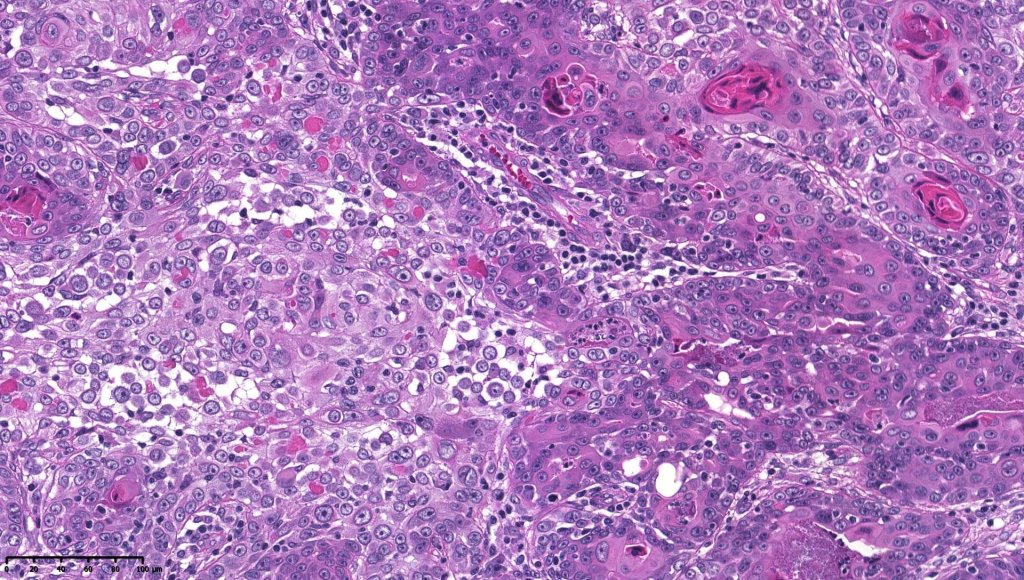




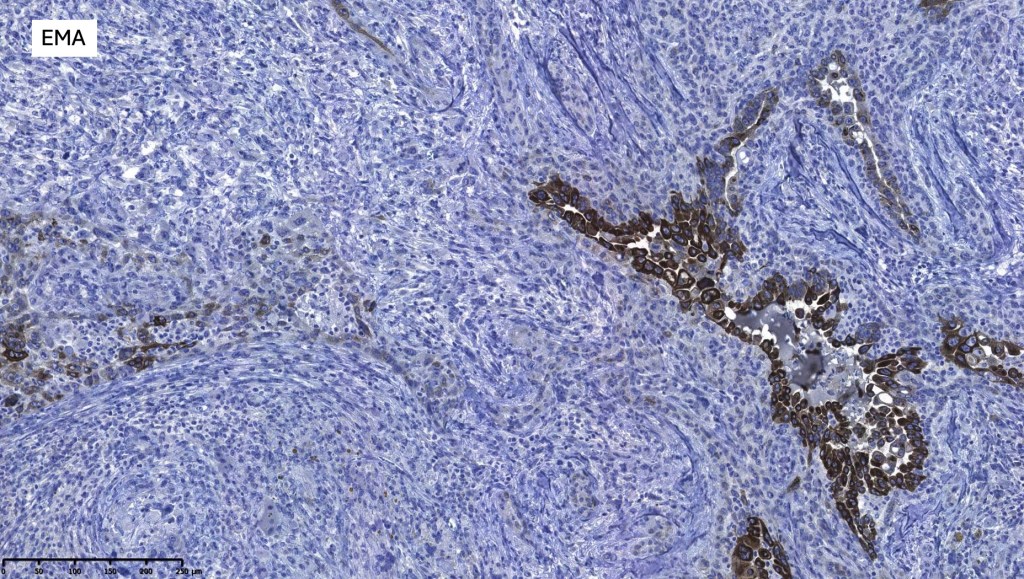
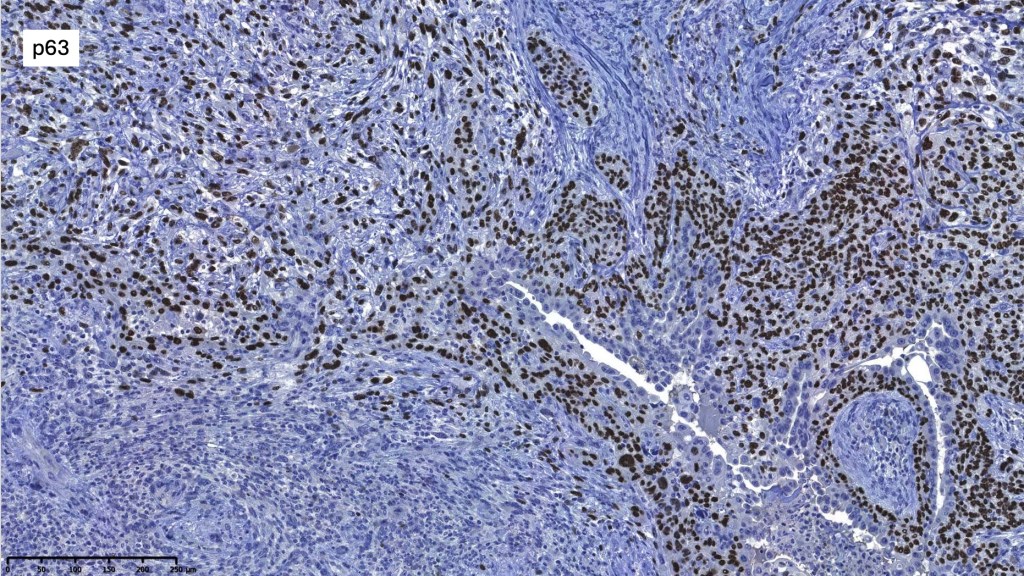
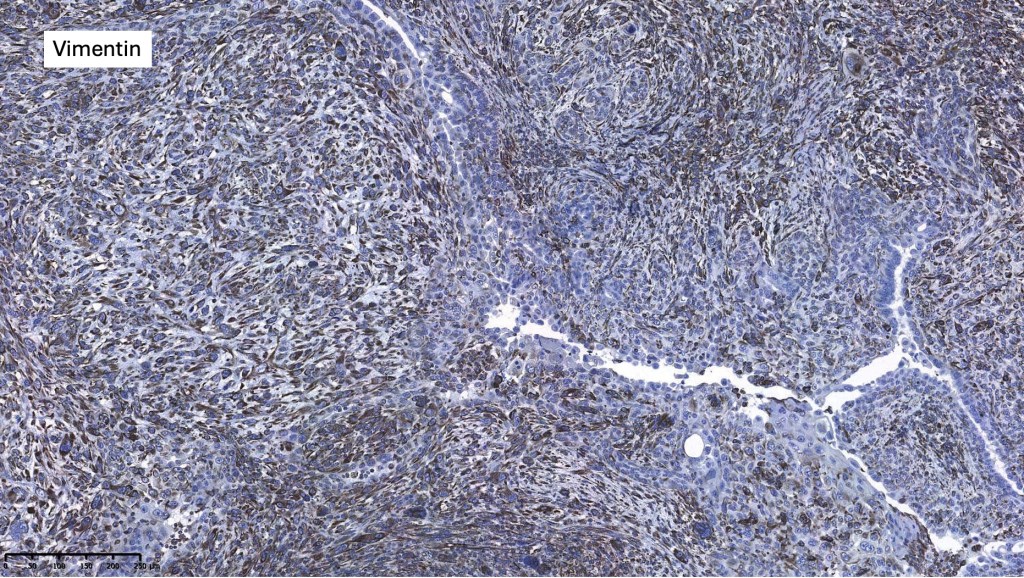
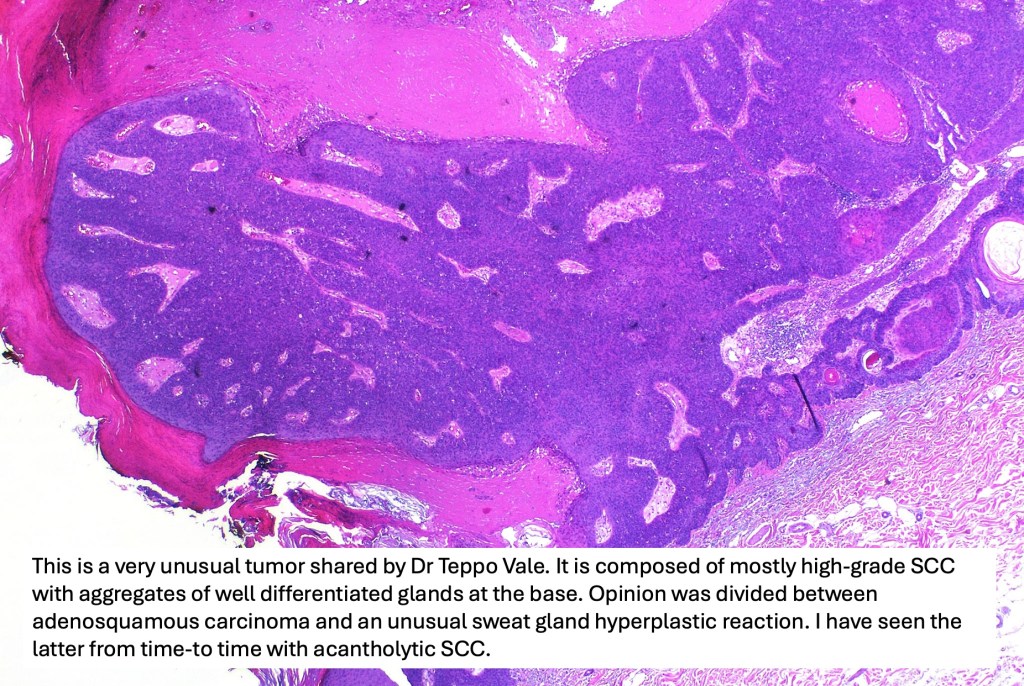
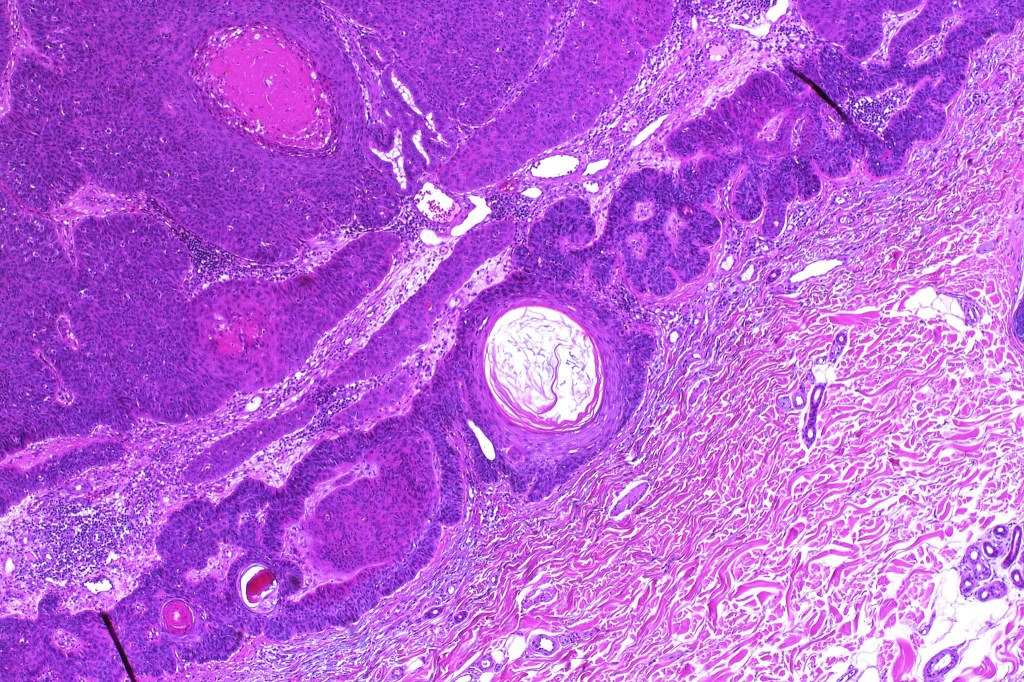


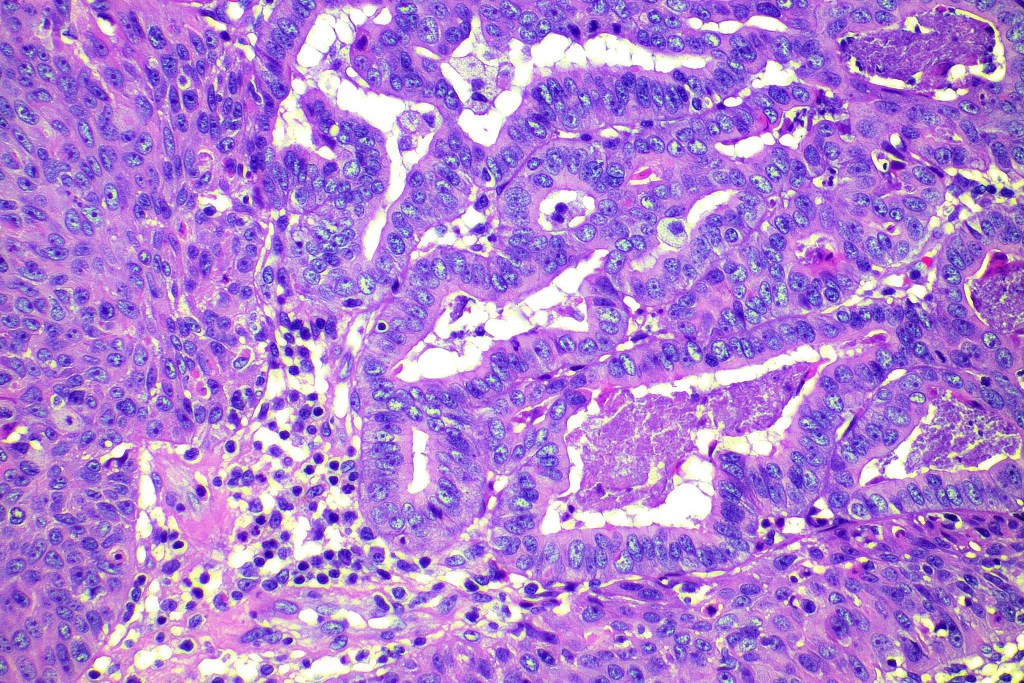

For comparison an actholytic squamous cell carcinoma- in cases of doubt, IHC and special stains for mucin will resolve the problem.





Leave a comment