Verrucuous carcinoma may arise in the skin, the oral cavity and the genitalia. In this blog only cutaneous tumors are described. Oral & genital tumors will be discussed in separate blogs.
Clinical features
•Predilection for middle-aged males but either sex may be affected at any age including exceptionally in children
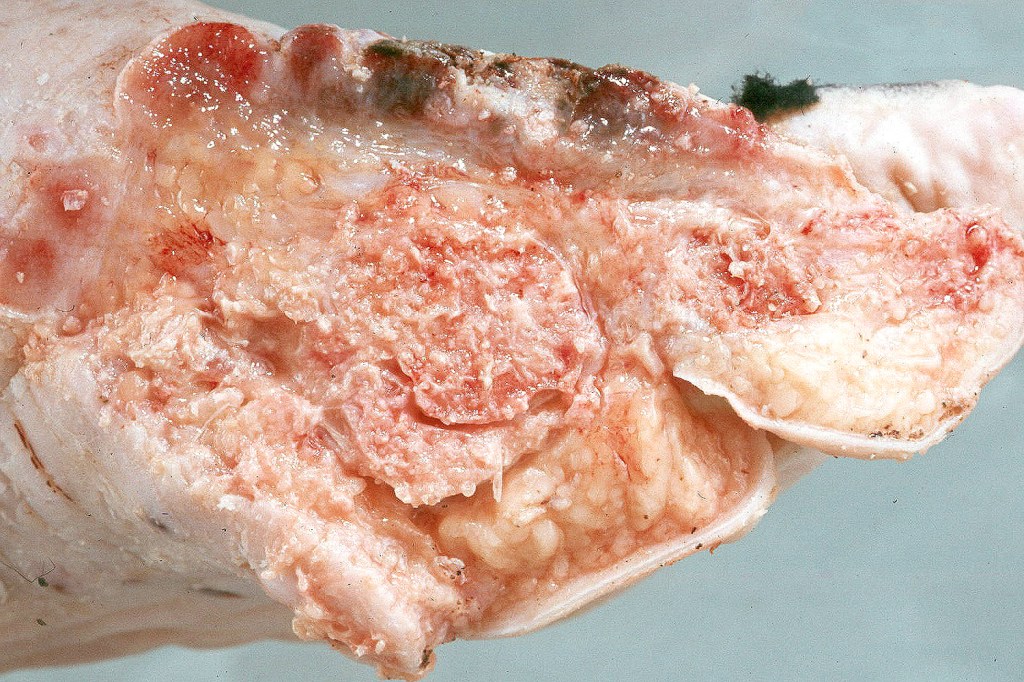
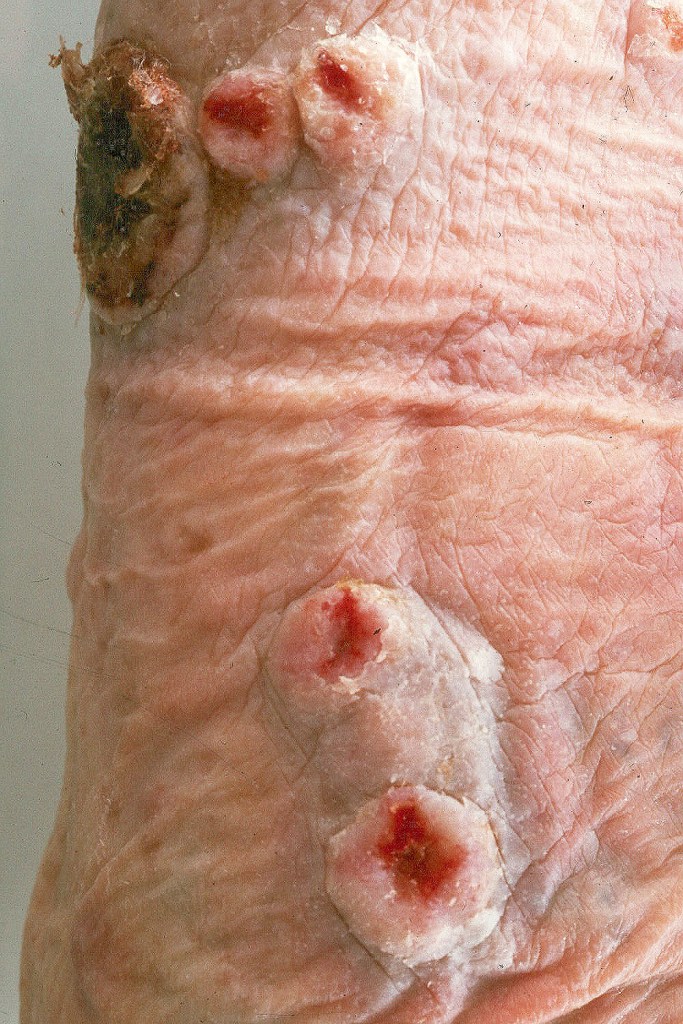
•Sole of the foot, wrists, fingers & a wide variety of other sites
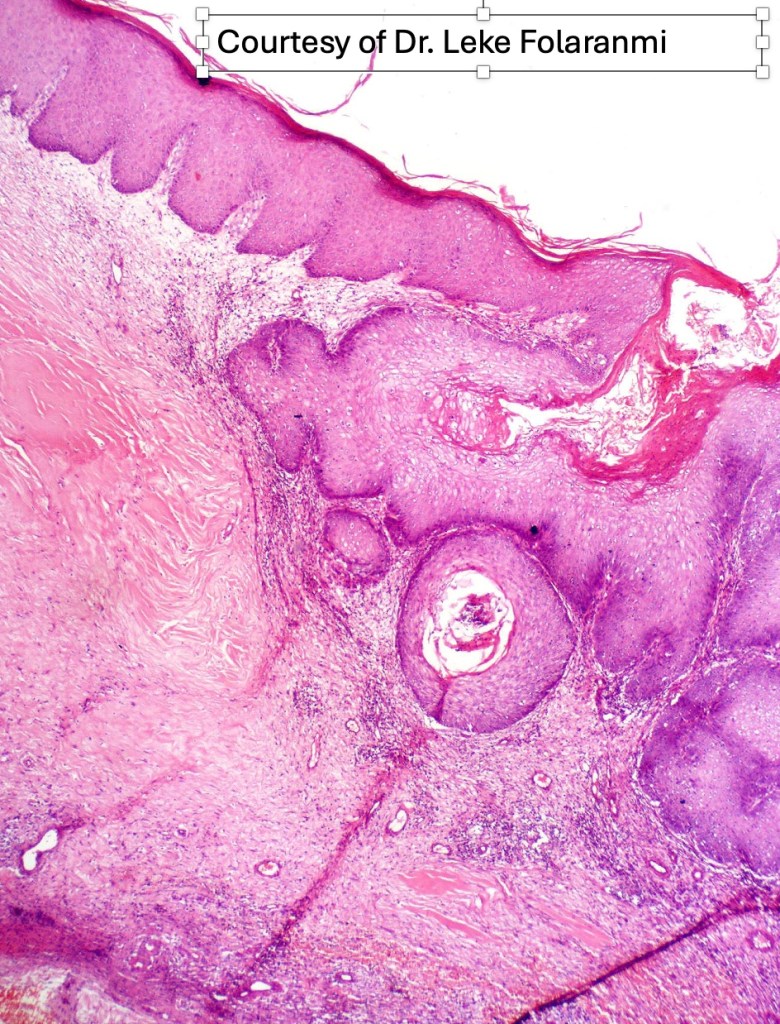
•Warty lesions with conspicuous keratin-filled sinuses (carcinoma cunniculatum due to its resemblance to a rabbit warren; Latin cunniculus- rabbit, warren)
•Exceedingly high recurrence rate (due to difficulties in achieving complete excision)
•Very exceptional documentation of metastatic spread
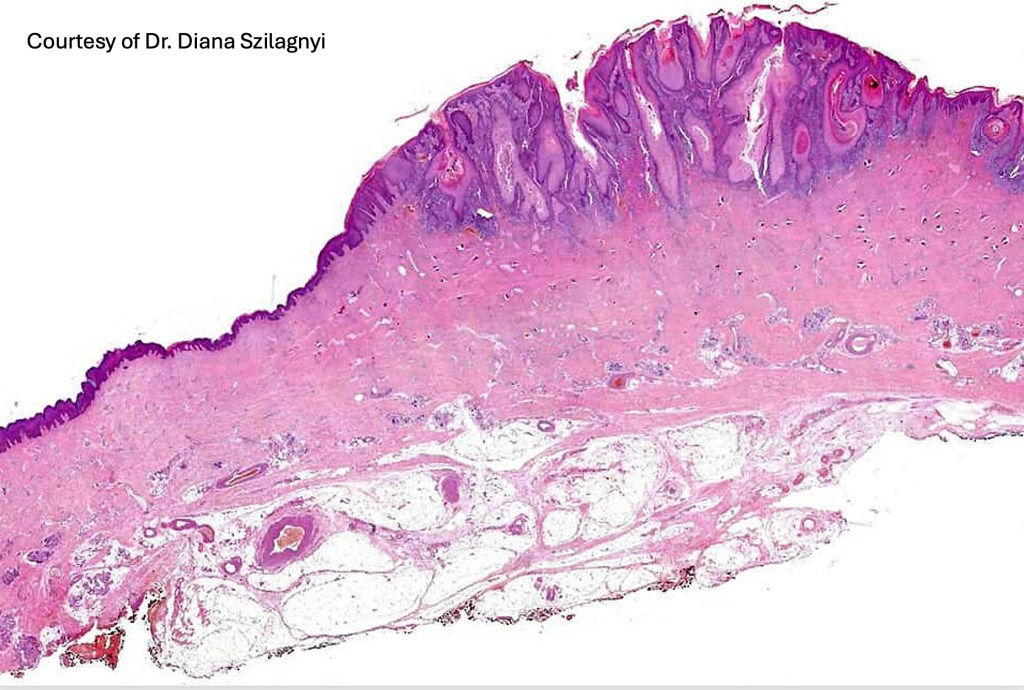
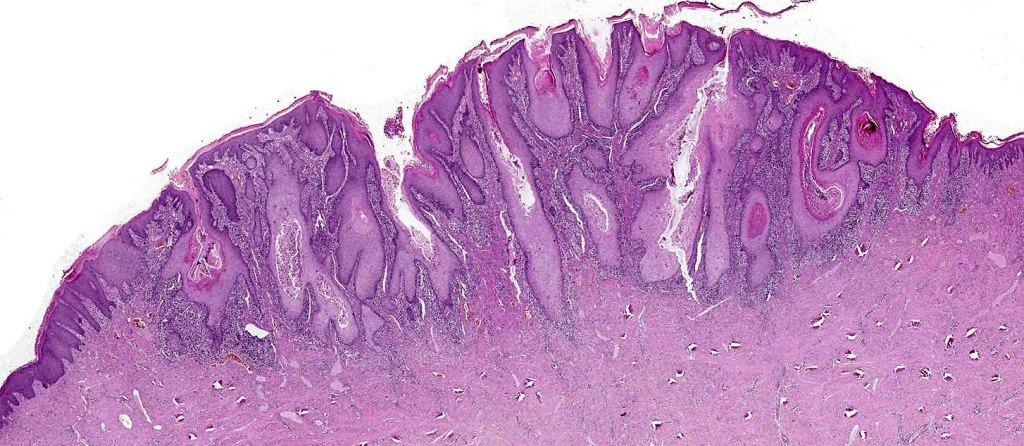
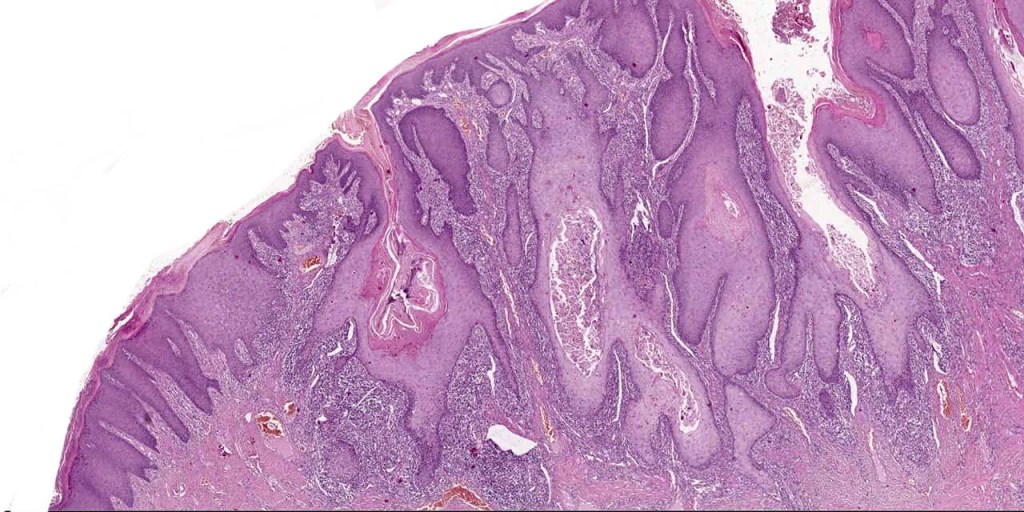
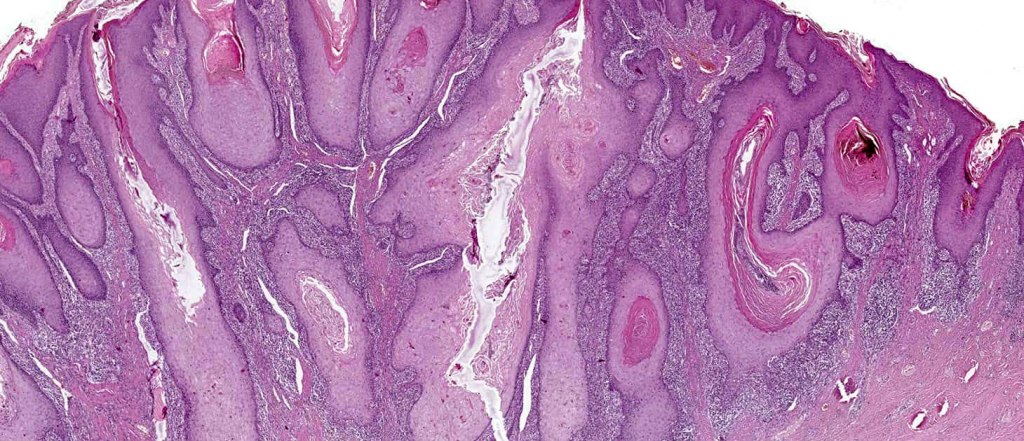
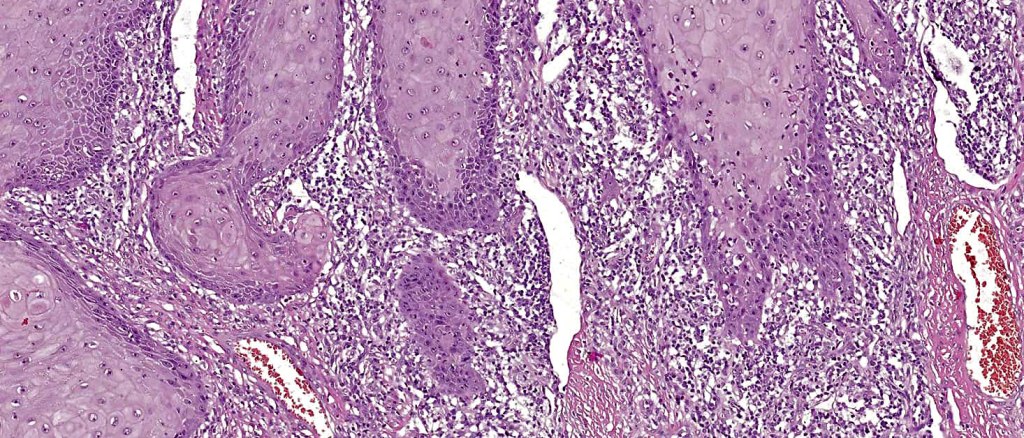
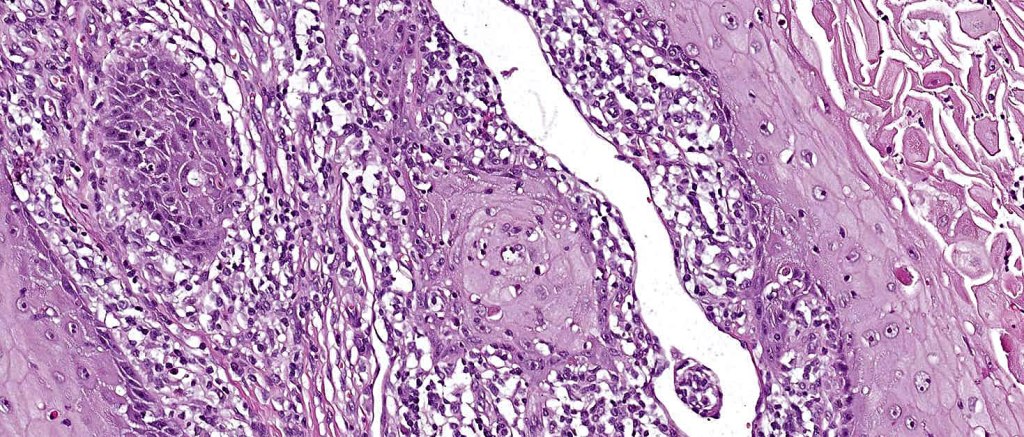
Histoloigcal features
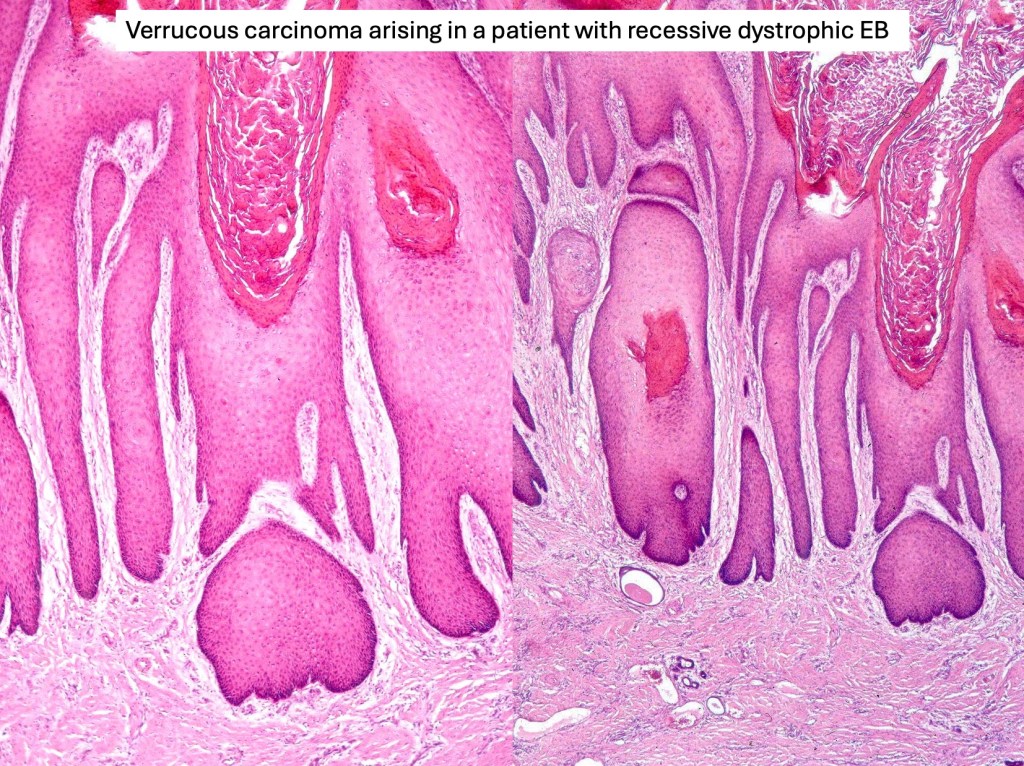
•HPV implicated in cutaneous lesion & chronic scarring
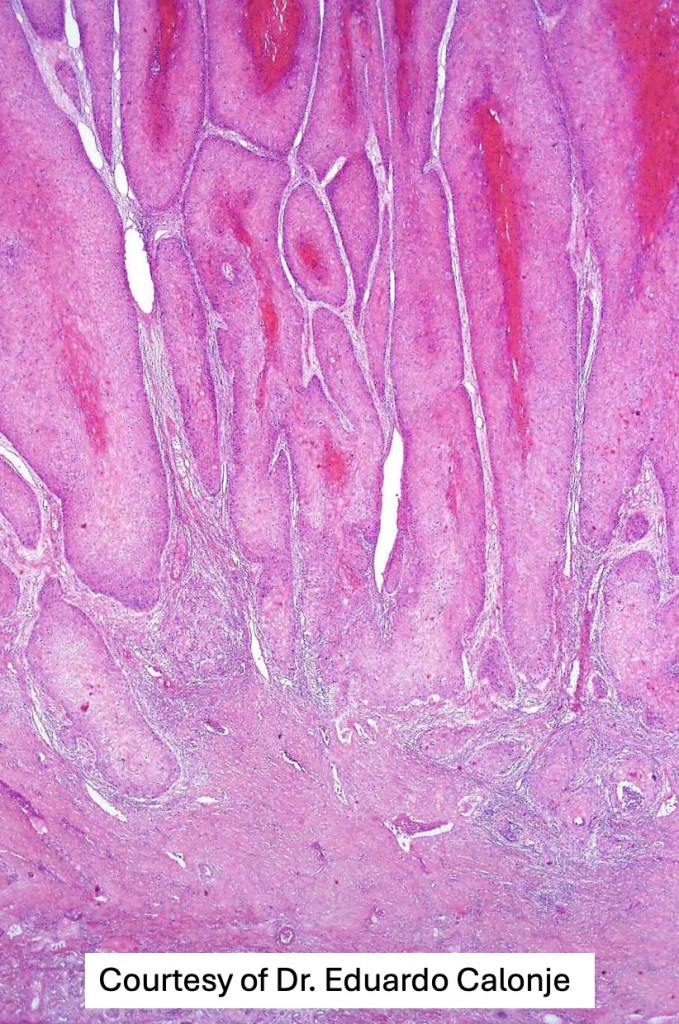
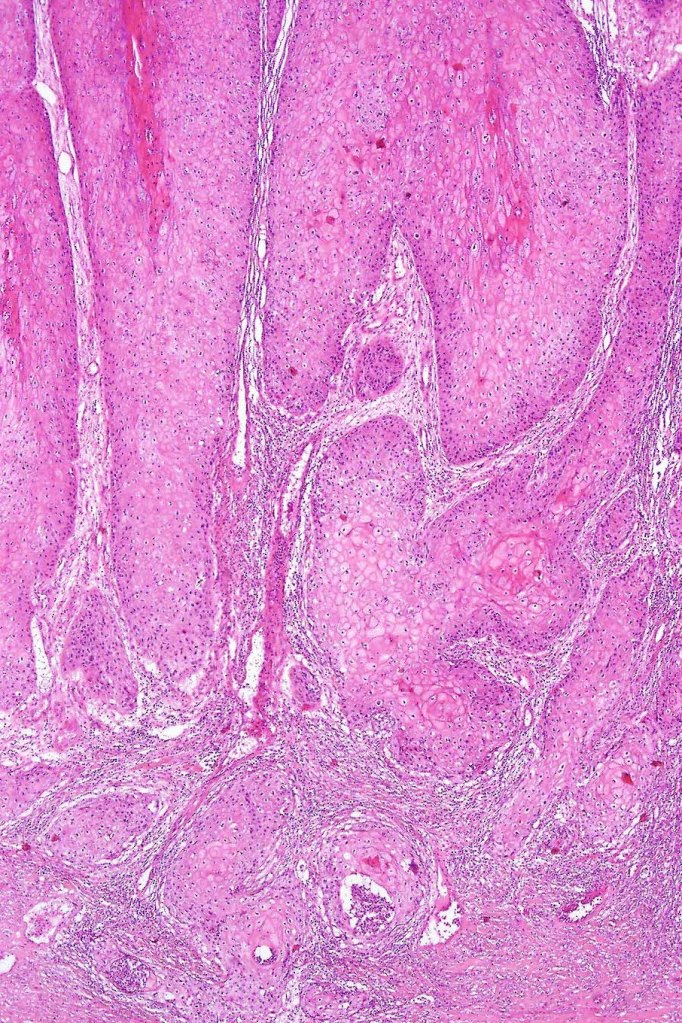
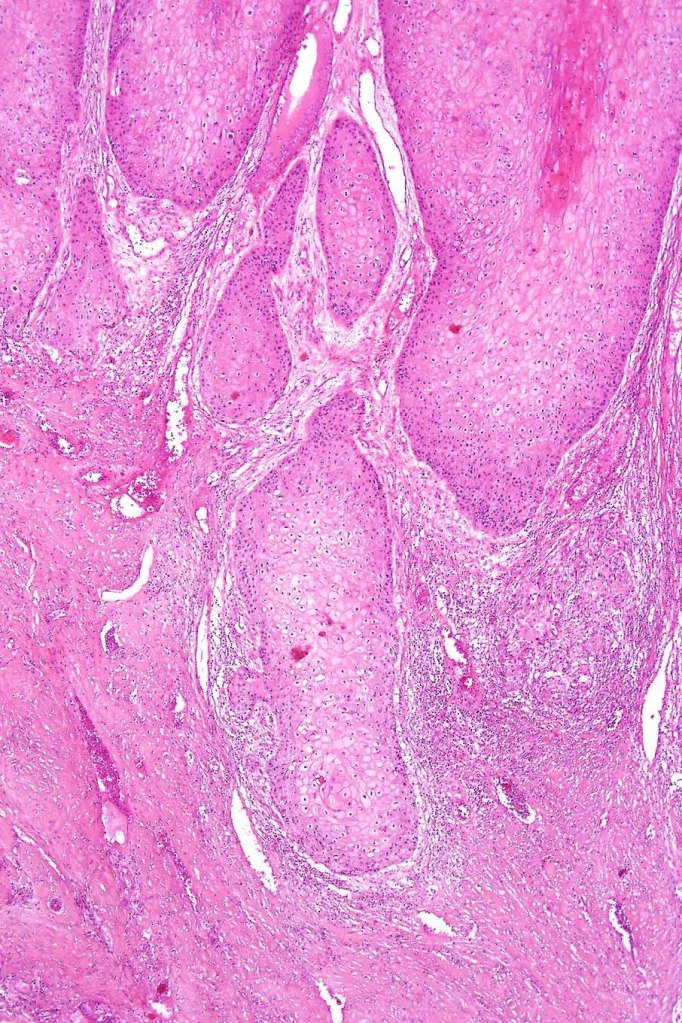
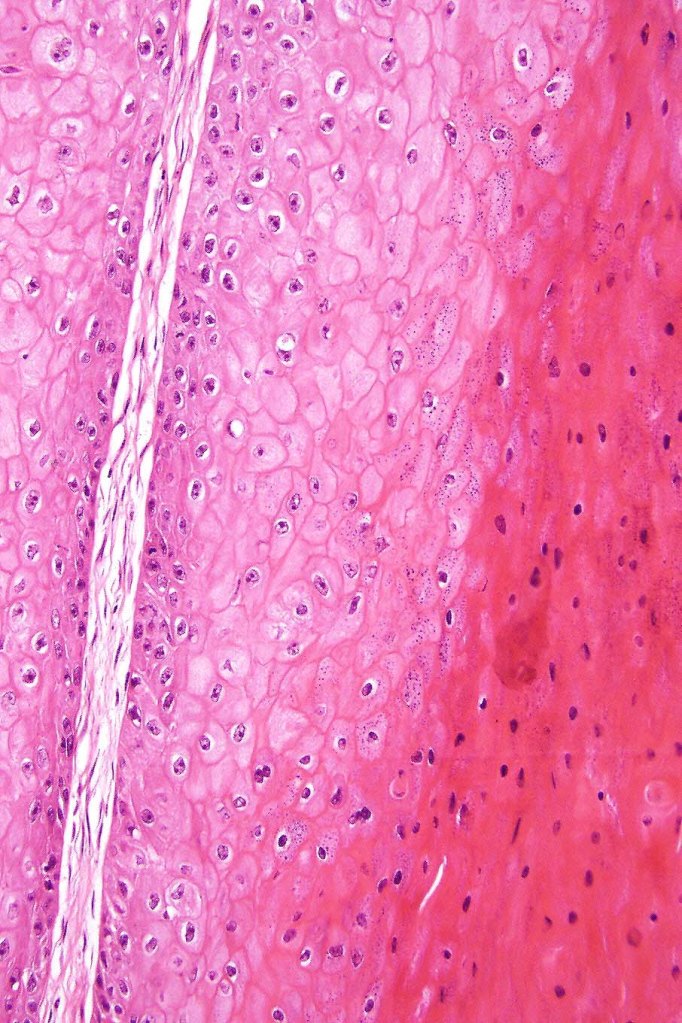
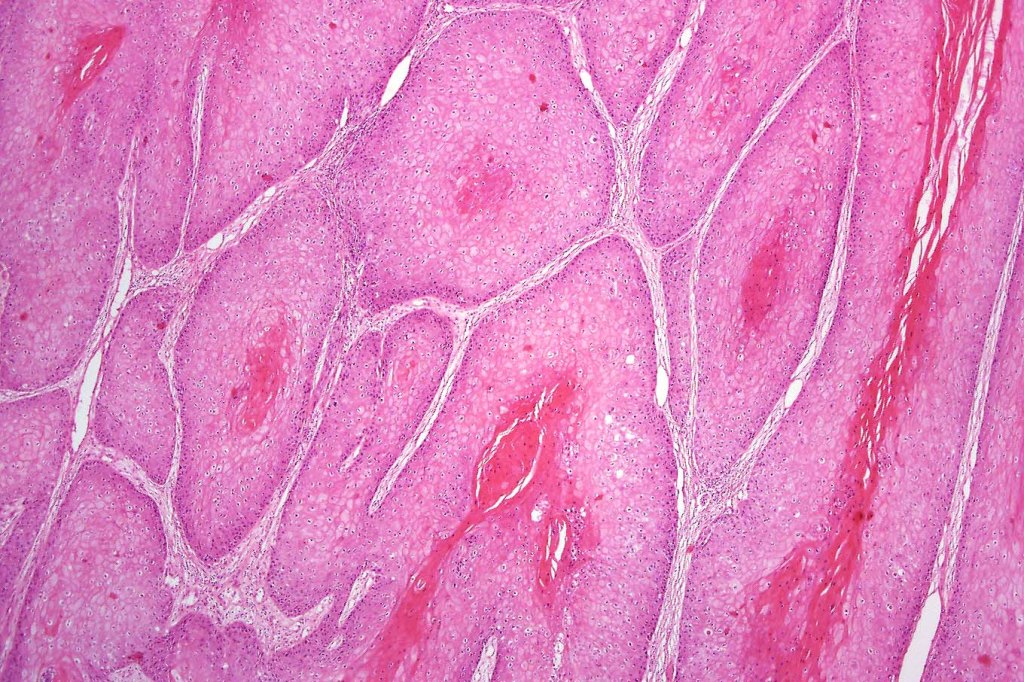
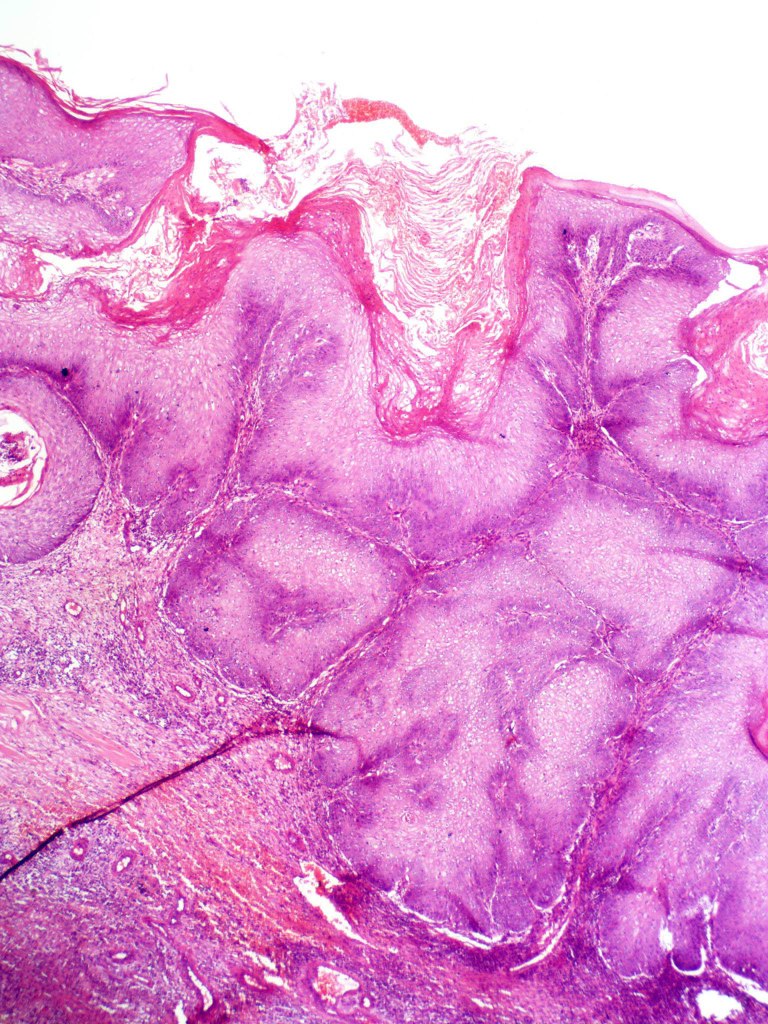
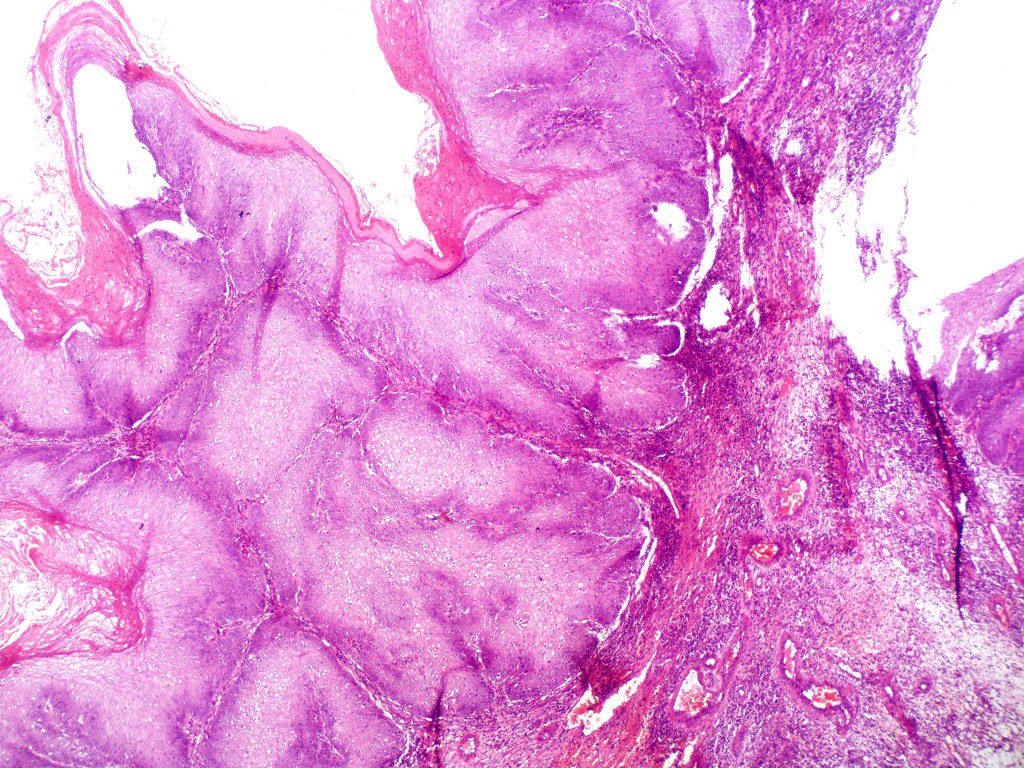
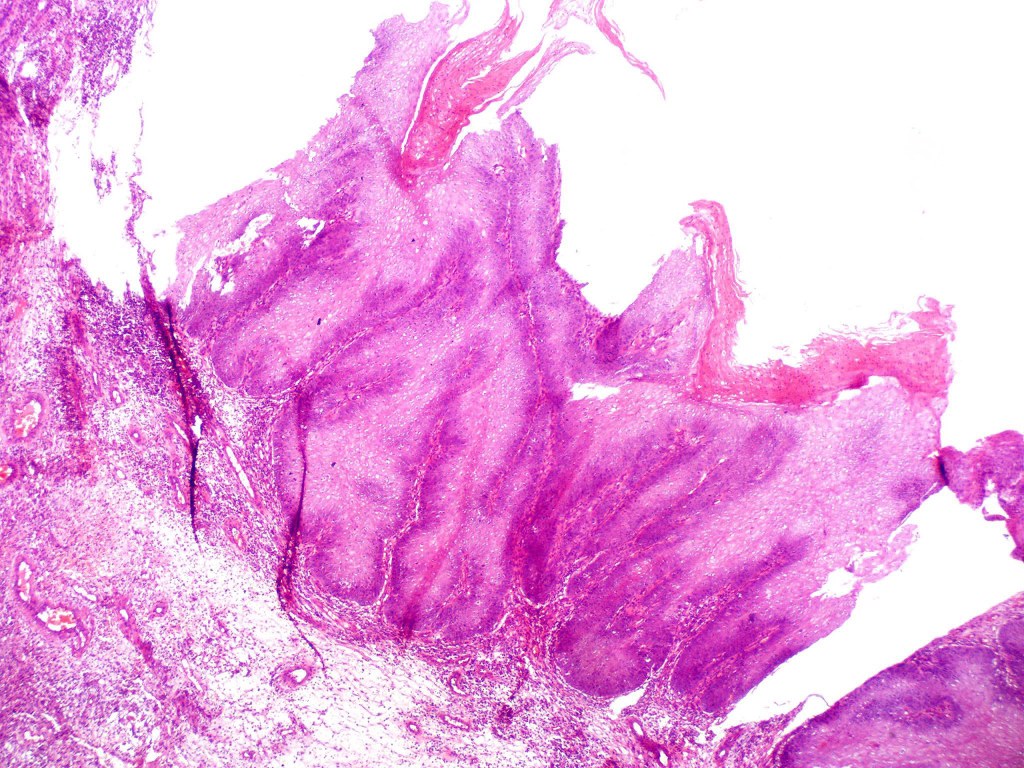
•Often massive hyperkeratosis
•Epidermal verrucous hyperplasia
•Deeply penetrating bulbous processes with a pushing rather than infiltrating lower border
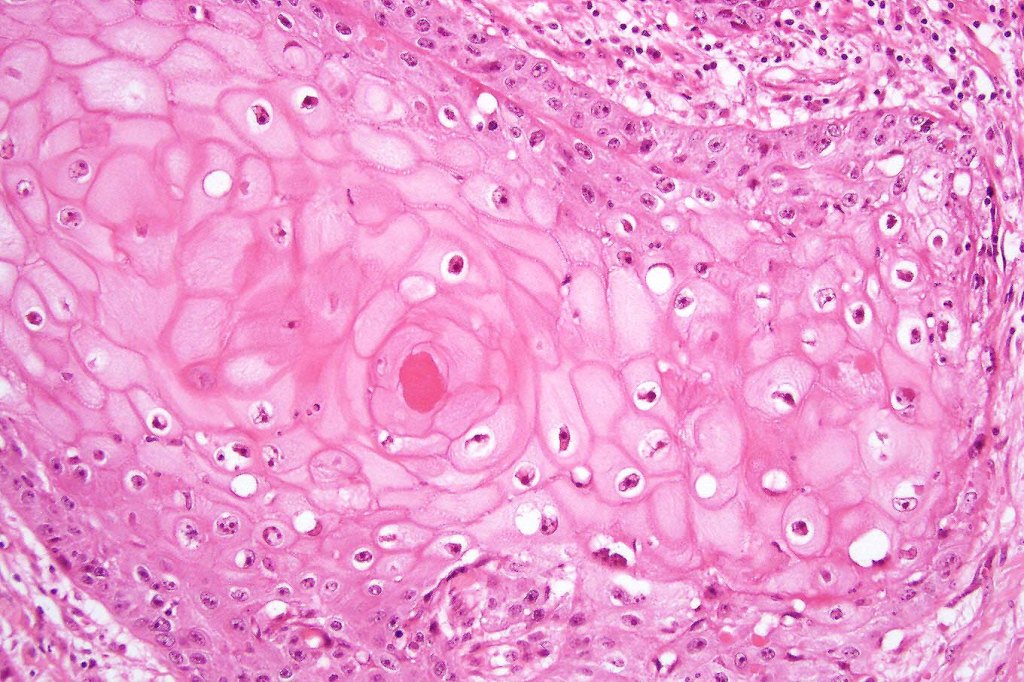
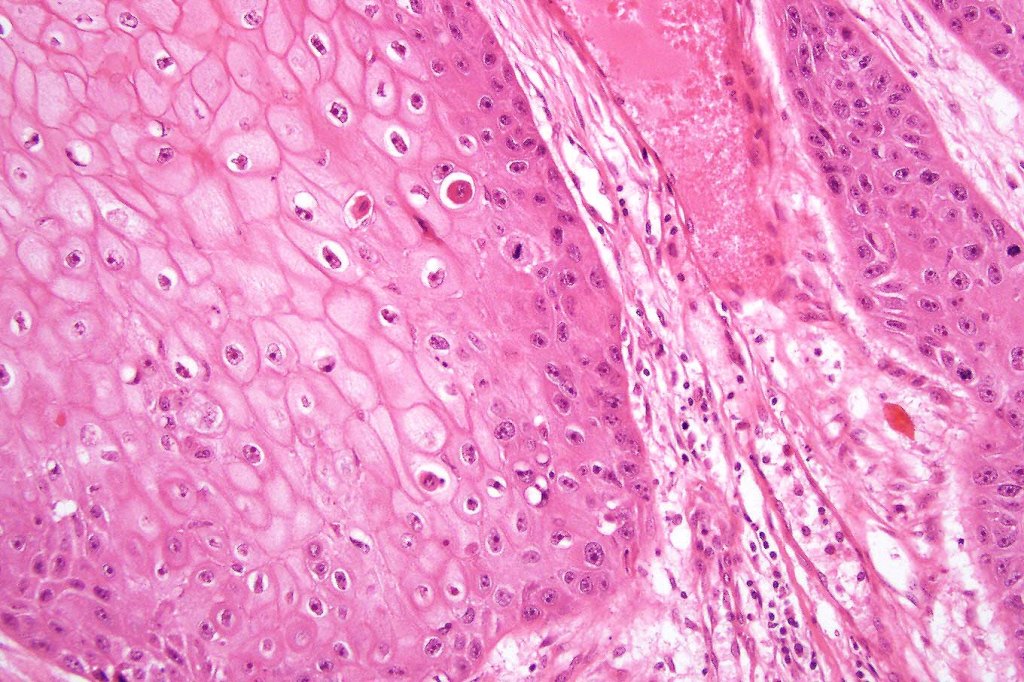
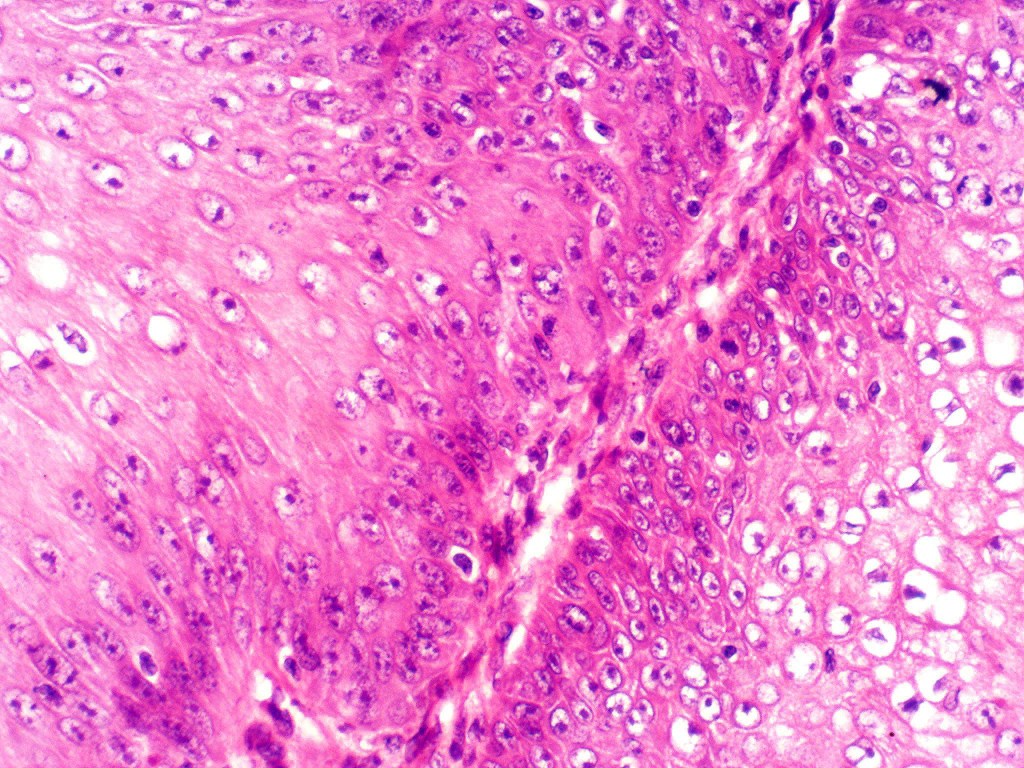
•Well differentiated epithelium characteristically having a ground glass appearance
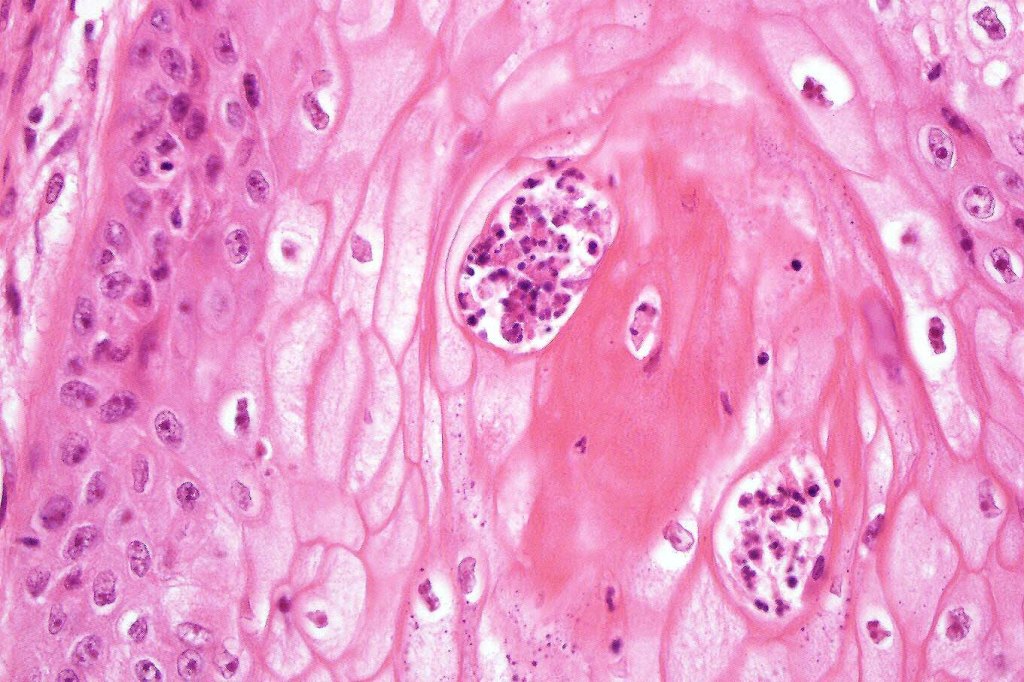
•Marked tumor necrosis
•Intraepithelial abscesses
•Basally located mitoses
•Overexpression of p53 & cyclin D1 reported
Differential diagnosis
Verrucuous carcinoma must be distinguished from a viral wart, pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and well differentiated squamous carcinoma. This can be very difficult if only superficial biopsies are available for study. Distinction from a plantar wart is sometimes very problematical since some verrucous carcinomas are associated with HPV infection. Well differentiated squamous carcinoma has an infiltrating rather than a pushing lower border. Clinicopathological correlation is essential in problematical cases.
Leave a comment